Neurohypophysis
-
Upload
laxmikanta-say -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
572 -
download
6
Transcript of Neurohypophysis

NEUROHYPOPHYSIS

ADH(Antidiuretic
Hormone)

General Characteristics
Synonim – Pressophysin, Ariginine vasopressin,
Synthesis - Supraoptic Nucleus of Hypothalamus, - magnocellular neurosecretory neurons, - Herring bodies (coarse granules),
Strored - Neurohypophysis
Physiologic Carrier - Neurophysin II

Polypeptide - MW 1000 - 9 amino acids
Half Life - 16-20 min - metabolized rapidly in Liver &
Kidney
Receptors - V1A, V1B & V2
Mode of Action - G protein coupled receptors (cAMP
mediated).

prepropressorophysin

Transport & Secretion

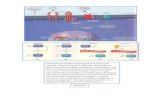
CONTROL OF SECRETION OF ADH
Osmotic stimuli Non-osmotic stimuli Osmotic inhibitor Non-osmotic inhibitor

Osmotic stimuli
Hyperosomolality
- primitive determinant - osmoreceptors -located in ant. Hypothalamus (OVLT)
- impermeable solutes - Na+, Sucrose & Mannitol, cross BBB
slowly (Na+ potent stimulators) - Hyperglycemia or Uremia less potent

Water Deficit Extracellular
Osmolarity
H2O excreted
ADH Secretion
Plasma ADH
H2O reabsorption
H2O permeablity in Distal tubules,Collecting duct

Non osmotic stimuli
Hypovolemia Pain, emotion, stress Nausea, vomiting Pulmonary disease- pneumonia, TB CNS disease- stroke, meningitis,
subdural hematoma Geriatric hyponatremic patient Cirrhosis of Liver & Nephrosis

INHIBITOR OSMOTIC INHIBITOR - increase water intake or hyposmolality
NON-OSMOTIC INHIBITOR - arterial B.P or blood volume,
- drugs – anticholinergics, atropine, ethanol, phenytoin, lithium & caffeine,
- Inhalation of CO2


Regulation of ADH Secretion
Increased ADH - Plasma
Osmolarity - Blood Volume - Blood Pressure - Nausea - HypoxiaDrugs - Morphine - Nicotine - Cyclophosphamide
Decreased ADH - Plasma
Osmolarity - Blood Volume - Blood Pressure
Drugs - Alcohol - Clonidine - Haloperidol

PHYSIOLOGICAL ACTION OF ADH
1.Antidiuretic2.Vasoconstricton3.Glycogenolysis4.Act as Neurotransmitter5.ACTH secretion

Applied
SIADH ( Syndrome of Inappropriate ADH secretion)
DI (Diabetes Insipidus)

SIADH (Syndrome of InappropriateADH secretion)
Cause - inappropriate secretion - ectopic source – Carcinoma
Characteristic Features - water retention - hypernatriurea, - hyponatremia
T/t - Demiclocycline

DI (Diabetes Insipidus)
Cause
- Central or Neurogenic DI - complete or partial failure of ADH
secretion
- Nephrogenic - complete or partial failure of response of CT
Features – polyurea, polydypsia
If thirst mechanism is absent - severe dehydration
T/t - Desmopressin

OXYTOCIN

General Characteristics
Synthesis - Paraventricular Nuclei - magnocellular neurosecretory system
Strored - Neurohypophysis
Physiologic Carrier - Neurophysin I
Polypeptide – 9 amino acids

prepro-oxyphysin

Control of secretion of oxytocin
Stimulators Inhibitors
Milk ejection reflex
Genital tract stimulation
Cholinergic neuron stimulation
Activation of sympathetic neuron
Emotional stress
Psychic factor Ethanol,
Enkephalin

Milk ejection reflexor
Milk Let-Down Reflex

Physiological action of oxytocin
1. In Mammary gland – Milk Ejection
2. In Pregnant uterus – Induction of Labour
3. In Non pregnant uterus - facilitates passage of sperms
from female genital tract to Uterine tube
4. In Blood vessel -High doses – relaxatation of
blood vessels, leads to fall in BP
5. In Male - facilitates the transport of sperms

THANK YOU