Nervous Tissue Li DongMei Website : m-learning.zju.edu.cn.
-
Upload
briana-hopkins -
Category
Documents
-
view
215 -
download
0
Transcript of Nervous Tissue Li DongMei Website : m-learning.zju.edu.cn.
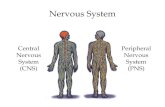
Central nervous system (CNS)Central nervous system (CNS)
Peripheral nervous system (PNS)Peripheral nervous system (PNS)
Composition of nerve tissueComposition of nerve tissue Two types of cellsTwo types of cells
---Components: ---Components: nerve cell: neuronnerve cell: neuron Glial cell: neuroglialGlial cell: neuroglial---Function: ---Function: Neurons : receive the stimulation, Neurons : receive the stimulation,
conduct the nerve impulse, conduct the nerve impulse, transmit the the impulse
Glial cell: support, protect and insulate, Glial cell: support, protect and insulate, nourish neuronsnourish neurons
1. Neuron1. Neuron
Billions Billions neurons and more glial cells fneurons and more glial cells form human nervous systemorm human nervous system..
It is the structural and functional unit It is the structural and functional unit of the nervous of the nervous tissue.tissue.
Neuron consists of cell Neuron consists of cell body(soma), dendrite and axon.body(soma), dendrite and axon.
Neuron is a cell that Neuron is a cell that receive the receive the stimulation ,conduct the nerve stimulation ,conduct the nerve impulse andimpulse and transmit the the impulse.
Nissl body(tigroid body)Location: located in cytoplasma and large dendritesLM: basophilic spot-liked or granule-liked structureEM: parallelly-arranged RER and free ribosomeFunction: synthesis of proteins, enzymes and neurotransmitters
Neurofibril:
Location: are abundant in cytoplasma and cell processes.LM: in silver impregnation methods(silver preparation), there are many thread-liked dark brown color structure to form a network.EM: neurofilament, microtubuleFunction: supporting(cytoskeleton), involving in intracellular transportation
1. Somas possess which one of the following structures?(A) Microtubules(B) Neurofilaments(C) Nissl bodies(D) Mitochondria(E) All of the above
2. Nissl bodies are composed of (A) synaptic vesicles and acetylcholine(B) Free ribosomes and rough endoplasmic reticulum(C) lipoprotein and melanin(D) neurofilaments and microtubules(E) smooth endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria
Exercises
Answers and Explanations1-E. Somas possess microtubules, neurofilaments, Nissl bodies, and mitochondria.2-B. Nissl bodies are large granular basophilic bodies composed of free ribosomes and rough endoplasmic reticulum. They are found only in neurons(in the soma cytoplasm).
② Dendrites
No Golgi complex, other contents are similar to the cell body.
Increase the receptor surface area of a neuron.
To receive stimuli from other neurons or from the external environment.
③ Axon
A Long Fiber that carries impulses away from the cell body.
Each neuron has only one axon.
The Axon Ends in a series of small swellings called axon terminals
The axon hillock contains(A) rough endoplasmic
reticulum(B) ribosomes(C) microtubules(D) Golgi complex(E) synaptic vesicles
Exercises
Answer and ExplanationC. The axon hillock contains microtubules, which are arranged in bundles.
Electrical synapsesgap junctions
Chemical synapses taking neurotransmitter as communicating medium
Classification
Synaptic transmissionSynaptic transmission
Calcium gates openCalcium gates open Synaptic vesicles release neurotransmitterSynaptic vesicles release neurotransmitter Neurotransmitter binds with postsynaptic recNeurotransmitter binds with postsynaptic rec
eptorseptors The postsynaptic membrane is excited or inhiThe postsynaptic membrane is excited or inhi
bitedbited The neurotransmitter is degraded and recycleThe neurotransmitter is degraded and recycle
d.d.
Synaptic vesicles possess which of the following characteristic?(A) Manufacture neurotransmitter(B) Enter the synaptic cleft(C) Become incorpotated into the presynaptic membrane(D) Become incorporated into the postsynaptic membrane
Exercises
Answer and ExplanationC. Synaptic vesicles release neurotransmitter into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis. In this process, the vesicle membrane is incorporated into the presynaptic membrane. Although these vesicles contain neurotransmitter, they do not manufacture it.
Schwann cellSchwann cell envelop the axon end to end to envelop the axon end to end to
form myelin-sheath in PNS and form myelin-sheath in PNS and
Satellite cellSatellite cell (capsular cell) (capsular cell) one layer of flattened or cuboidal one layer of flattened or cuboidal
cell, with round, ovoid and dark Ncell, with round, ovoid and dark N surrounding the Neuron in surrounding the Neuron in
ganglionganglion
Nerve fiber Nerve fiber
definition: definition: axon enveloped by axon enveloped by neuroglial cellsneuroglial cells
classification: classification: according to myelin-according to myelin-sheathsheath
myelinated nerve fibermyelinated nerve fiber unmyelinated nerve fiberunmyelinated nerve fiber
myelinated nerve fibermyelinated nerve fiber in CNS---structure: similar to in PNS myelin-sheath formed by flattened end
ing of oligodendrocyte’s processes one oligodendrocyte can envelop man
y axons no incisure and basement membrane