Nervous System - Neurons Slides PDF/Lect09... · Sodium Potassium Pump To maintain this resting...
Transcript of Nervous System - Neurons Slides PDF/Lect09... · Sodium Potassium Pump To maintain this resting...

Nervous System - Neurons
Biol 105
Chapter 7

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Outline
I. Nervous system function
II. Central and peripheral nervous system
III. Nervous system cells
IV. Myelinated neurons
V. Nerve signal transmission
VI. Nerve Synapse

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Nervous Tissues
Nervous tissue functions to conduct
messages throughout the body.
When nerve cells are stimulated, an
electrical signal quickly travels through
the nerve cell to the nerve ending,
triggering events.

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Nervous System
Includes nervous tissue and sensory organs.
Nervous system functions to:
Sense the environment – it receives
information from both outside and inside
the body.
Process the information it receives.
Respond to information – send out
orders.

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
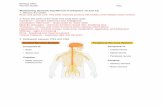
Two Parts of the Nervous System
1. Central Nervous System (CNS)
Brain and Spinal Cord.
2. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Nervous tissue outside brain and
spine.
Sense organs.

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Central Nervous System
Peripheral

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Figure 8.1 The nervous system

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Nervous System Cells
Two types of nervous tissue cells.
Neurons – The cells that are
responsible for transmitting messages.
Neuroglial Cells – Cells that support the
neurons.

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Neuroglial Cells
Microglia – Immune system cells, engulf
bacteria and cellular debris.
Astrocytes – Provide nutrients to neurons.
Oligodenrocytes and Schwann Cells –
Form myelin sheaths.

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Parts of a Neuron
Cell body – contains the nucleus, main
body of cell.
Dendrites – projections from the cell
body that carry messages to the cell
body.
Axon – one projection that carries
messages away from the cell body (can
be very long).

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Neurons Have Dendrites, a Cell Body, and an
Axon
Figure 7.2
The cell body
integrates input
from other neurons.
Dendrites receive
information from
other neurons or
from the environment.
The cell body controls
the cell’s metabolic
activities.
An axon conducts the
nerve impulse away
from the cell body.
Axon endings release
chemicals called
neurotransmitters that
affect the activity of
nearby neurons or an
effector (muscle or gland).
Receiving portion of
neuron
Sending portion of neuron
Cell
body
Axon
endings
Nucleus

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.12-12

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Neurons of the Peripheral Nervous System
Neurons in the PNS are either
carrying messages to or from the
CNS.
Afferent = Sensory neurons = Neurons
carrying messages to the CNS.
Efferent = Motor neurons = Neurons
carrying messages from the CNS.

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Interneurons in the Central Nervous System
Interneurons are located between
sensory and motor neurons within
the CNS.
Interneurons integrate and interpret
sensory signals.

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Figure 8.1 The nervous system

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Sensory Neurons
The afferent or sensory neuron cell bodies
are located in dorsal root ganglion.

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Motor Neurons
The efferent or motor neuron cell
bodies are located in the gray matter
of the spinal cord.
Their axons leave the CNS and go to
the skeletal muscles.

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
The cell bodies of these neurons are located in the dorsal
root ganglion
Moto
r
Sen
sory
50%50%1. Motor
2. Sensory

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
The cell bodies of these neurons are located in the dorsal
root ganglion
Moto
r
Sen
sory
50%50%1. Motor
2. Sensory

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Neurons of the Nervous System
Figure 7.1
Interneuron
Sensory
receptor
for pain
Muscle
(effector)
Motor
neuron
Sensory
neuronCell
body
Impulse direction

12-5

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
These neuroglial cells provide nutrients to neurons
Mic
roglia
Ast
rocy
tes
Olig
oden
rocy
tes
Sch
wan
n cel
ls
25% 25%25%25%1. Microglia
2. Astrocytes
3. Oligodenrocytes
4. Schwann cells

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
These neuroglial cells provide nutrients to neurons
Mic
roglia
Ast
rocy
tes
Olig
oden
rocy
tes
Sch
wan
n cel
ls
25% 25%25%25%1. Microglia
2. Astrocytes
3. Oligodenrocytes
4. Schwann cells

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
These are projections of the neuron cell body that carry
messages to the cell body
Axo
ns
Den
drite
s
50%50%1. Axons
2. Dendrites

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
These are projections of the neuron cell body that carry
messages to the cell body
Axo
ns
Den
drite
s
50%50%1. Axons
2. Dendrites

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Which of the following type of neuron would alert the brain
that you had touched a hot object?
effer
ent n
euro
n
affer
ent n
euro
n
50%50%1. efferent neuron
2. afferent neuron

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Which of the following type of neuron would alert the brain
that you had touched a hot object?
effer
ent n
euro
n
affer
ent n
euro
n
50%50%1. efferent neuron
2. afferent neuron

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
What type of neuron is the arrow pointing to?
Sen
sory
Moto
r
50%50%1. Sensory
2. Motor

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
What type of neuron is the arrow pointing to?
Sen
sory
Moto
r
50%50%1. Sensory
2. Motor

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Myelinated Neurons
Neurons that have axons covered with
neuroglial cells that contain the protein
myelin are called myelinated neurons.

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Functions of Myelin Sheaths
1. The main benefit of myelin sheaths is that
myelinated neurons are able to carry
messages faster than non-myelinated
neurons.
2. Myelin sheaths from Schwann cells also
help regenerate injured PNS neuron
axons.

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Two Types of Cells Myelinate neurons
Schwann cells and Oligodenrocytes are
wrapped around neuronal axons.

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Myelinated Neurons
Schwann cells are found in the PNS.
Oligodendrocytes are found in the CNS.
Nodes of Ranvier are spaces on the
axon between the glial cells.

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Myelin Sheath
Figure 7.3b

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Myelin Sheath
Figure 7.3c

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Myelinated Neurons
Figure 7.3a
(a)
Cell
body
Dendrites
Myelin sheath
Node of
Ranvier
Nucleus
Schwann cell
In saltatory conduction, the
nerve impulses jump from one
node of Ranvier to the next.

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
Caused by the destruction of the
myelin sheath that surrounds axons
found in the CNS.
Can result in paralysis and loss of
sensation, including loss of vision.

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Nerves
Nerves contain Neuron axons that
are bundled together.
These bundles contain:
Axons
Blood vessels
Connective tissue


Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Nerve
Figure 8.9d
(d) The anatomy of a nerve
Blood supply
Axons within a connective
tissue sheath
One axon
Connective tissue surrounding one nerve

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
An Ion is an atom that has gained or lost a
Neu
tron
Pro
ton
Ele
ctro
n
33% 33%33%1. Neutron
2. Proton
3. Electron

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
An Ion is an atom that has gained or lost a
Neu
tron
Pro
ton
Ele
ctro
n
33% 33%33%1. Neutron
2. Proton
3. Electron

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
How can an ion pass through a membrane
Sim
ple d
iffusi
on
Fac
ilita
ted
diffus
ion
Act
ive
transp
ort
Both
2 a
nd 3
All
of the
above
20% 20% 20%20%20%
1. Simple diffusion
2. Facilitated diffusion
3. Active transport
4. Both 2 and 3
5. All of the above

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
How can an ion pass through a membrane
Sim
ple d
iffusi
on
Fac
ilita
ted
diffus
ion
Act
ive
transp
ort
Both
2 a
nd 3
All
of the
above
20% 20% 20%20%20%
1. Simple diffusion
2. Facilitated diffusion
3. Active transport
4. Both 2 and 3
5. All of the above

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
The Nerve Impulse Is an Electrochemical
Signal
A nerve impulse, or action potential,
involves sodium ions (Na+) and potassium
ions (K+) that cross the cell membrane
through ion channels.
Each ion channel is designed to allow only
certain ions to pass through.

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Action Potential
Figure 7.4
Extracellular
fluid
Neuron plasma
membrane
Cytoplasm
Sodium-potassium pump
The sodium-potassium pump
uses cellular energy (ATP) to
pump sodium ions out of the
cell and potassium ions into
the cell
Continually open ion channels “Gated” ion channels Sodium-potassium pump
Ion channels
Ion channels can be open continuously or opened and
closed by a molecular gate
Cross section
Axon membrane

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
The difference in charge between the inside
and outside of the neuron is the membrane
potential.
Membrane Potential

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
A neuron that is not conducting a message is
said to be “Resting”.
When a neuron is resting there is more
sodium (Na+) outside the neuron cell and
more potassium (K+) inside the cell.
The inside of the cell has a negative charge
compared to the outside the cell.
Resting Membrane Potential

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Resting Membrane Potential

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
The Nerve Impulse
Figure 7.5 (1 of 4)

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Sodium Potassium Pump
To maintain this resting membrane potential
the neuron pumps Na+ out of the cell and K+
into the cell.
The transport proteins take 3 Na+ ions out for
every 2 K+ ions into the cell = Na+/K+ pump.
This is Active Transport – requiring ATP.

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
NA/K ATPase

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Action Potential
An electrochemical signal conducted along
an axon. It is a wave of depolarization
followed by repolarization.
Depolarization is caused by sodium ions
entering the axon.
Repolarization is caused by potassium
ions leaving axon.

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Steps of an Action Potential
1. The axon is depolarized when voltage gated
sodium ion channels open and Na+ comes
rushing in, causing the inside of the neuron to
become positively charged.

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Action Potential
Figure 7.5 (2 of 4)

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Steps of an Action Potential
2. The axon is repolarized when voltage gated
potassium ion channels open and allow K+ to
flow out of the axon.
This returns the membrane potential to be
negative on the inside of the neuron.
The action potential travels down the axon.

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Action Potential
Figure 7.5 (3 of 4)

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Action Potential
After the action potential, the sodium
potassium pump restores the original
conditions by pumping sodium (Na+) out of
the cell and potassium (K+) back into the
cell.

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
The Nerve Impulse
Figure 7.5 (4 of 4)

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
The Nerve Impulse
Figure 7.6

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Action Potentials
It is an all or nothing response – if it is not
a great enough stimulation the channels
won’t open. The level of the action
potential is always the same.
The direction is always one way down the
axon. The sodium channels are
inactivated for awhile after the action
potential passes = refractory period.

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
When a neuron is resting, sodium ions have a greater
concentration:
insi
de th
e neu
ron c
ell
outs
ide
the
neuro
n cel
l
conce
ntra
tion is
the
...
33% 33%33%1. inside the neuron cell
2. outside the neuron cell
3. concentration is the
same

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
When a neuron is resting, sodium ions have a greater
concentration:
insi
de th
e neu
ron c
ell
outs
ide
the
neuro
n cel
l
conce
ntra
tion is
the
...
33% 33%33%1. inside the neuron cell
2. outside the neuron cell
3. concentration is the
same

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
When a neuron is depolarizing, which ions come into the
neuron?
Cal
cium
(Ca+
+)
Sodiu
m (N
a+)
Pota
ssiu
m (K
+)
Chlo
rine
(Cl-)
25% 25%25%25%1. Calcium (Ca++)
2. Sodium (Na+)
3. Potassium (K+)
4. Chlorine (Cl-)

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
When a neuron is depolarizing, which ions come into the
neuron?
Cal
cium
(Ca+
+)
Sodiu
m (N
a+)
Pota
ssiu
m (K
+)
Chlo
rine
(Cl-)
25% 25%25%25%1. Calcium (Ca++)
2. Sodium (Na+)
3. Potassium (K+)
4. Chlorine (Cl-)

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
When a neuron is depolarizing, the inside of the neuron cell
becomes
Posi
tivel
y ch
arged
Neg
ativ
ely
char
ged
50%50%1. Positively charged
2. Negatively charged

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
When a neuron is depolarizing, the inside of the neuron cell
becomes
Posi
tivel
y ch
arged
Neg
ativ
ely
char
ged
50%50%1. Positively charged
2. Negatively charged

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Nerve Synapse
How are messages passed from one nerve to
the next or from the nerve to a muscle?
The junction between two neurons or
between a neuron and a muscle is called a
synapse.

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Components of the Synapse
1. Presynaptic neuron is the transmitting
neuron.
2. Postsynaptic neuron is the receiving neuron
or the muscle.
3. And the gap in between them = synaptic
cleft.

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Presynaptic neuron
Presynaptic neuron has synaptic
vesicles that contain
neurotransmitters.

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Synaptic Transmission
Figure 7.8 (1 of 3)
Nucleus
Impulse
Synaptic
knob
Axon
Dendrites
Cell
body
Synaptic
cleft
Synaptic
vesicle
Impulse
Membrane of
postsynaptic neuron
Step 1: The impulse reaches
the axon ending of the
presynaptic membrane.
Step 2: Synaptic
vesicles release
neurotransmitter
into the synaptic
cleft.

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Synaptic Transmission
Figure 7.8 (2 of 3)
Neurotransmitter
Receptor (of sodium ion
channel) on postsynaptic membrane
Step 3: Neurotransmitter
diffuses across synaptic cleft.
Synaptic
vesicle

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Synaptic Transmission
Figure 7.8 (3 of 3)
Step 5: Sodium ion channels open.
Step 4: Neurotransmitter molecules bind to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron.
Step 6: Sodium ions enter the postsynaptic neuron, causing depolarization and possible action potential.

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
1. The action potential gets to the end of the presynaptic axon.
2. The action potential triggers Ca2+ to enter the presynaptic axon terminal.
3. The Ca2+ triggers synaptic vesicles located at the axon terminal to merge with the neural membrane.
Transmission Across the Synaptic Cleft

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
4. The synaptic vesicles release the neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft.
5. These neurotransmitters travel across the synaptic cleft to the postsynaptic neuron (or the muscle).
6. Neurotransmitter binds to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron (or muscle).
Transmission Across the Synaptic Cleft

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Transmission Across the Synaptic Cleft
7. These receptors may be ligand gated sodium
ion channels which allow Na+ to enter the
postsynaptic neuron (or muscle) and triggers
an action potential in the postsynaptic neuron
(or muscle contraction).
8. Once the neurotransmitters are released they
need to be destroyed or contained quickly or
they will continue to stimulate the nerve.

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Neurotransmtters
Acetylcholine
Acts in both the PNS and the CNS as a
neurotransmitter.
Causes voluntary muscles to contract.
Acetylcholinesterase.
Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune
disease that attacks the acetylcholine
receptors, resulting in reduced muscle
strength.


Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Important Concepts
Read Chapter 8
What are the functions of nervous system
What are the two types of cells in nervous
tissue (neuroglial cells and neurons).
What are the three types of neuroglial cells and
their functions
What are the two main divisions of nervous
system (CNS, PNS) and where each is found

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Important Concepts
What are the parts and functions of a neuron
What are the three types of neurons (sensory,
interneuron and motor neurons) and their
functions, and where are they located
Where are the cell bodies are located for motor
and sensory nerve cells

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
What are schwann cells and oligodendrocytes and
what are their function
Where Schwann vs oligodendrocytes are found
What is the cause and effects of multiple sclerosis
What are the parts of a nerve
Important Concepts

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
How do ions pass through membranes
What is the function of the sodium potassium
pump
What are the steps of messages being conducted
through a neuron, starting with the resting stage
and ending with the next neuron or muscle being
stimulated.
Important Concepts

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
What ions enter and the leave the neuron during
the depolarization and repolarization steps of
action potential, what is the relative charge of the
inside vs the outside of the neuron during these
events, what is the order of events.
Components of the synapse
Function of neurotransmitters, how do they work,
where do they work, know the ions involved and
their functions.
Important Concepts

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
What is acetylcholine, where is it found, what effect
does it have, how is acetylcholine removed from
the synaptic cleft
What is the cause and effect of Myasthenia gravis
Important Concepts

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Definitions
Afferent neurons, efferent neurons, dendrites, axons, sensory neurons, interneuron, motor neurons, myelin, myelin sheath, myelinated neurons, schwann cells, oligodendrocytes, nodes of ranvier, nerve, ions, ion channels, ligand gated ion channels, voltage gated ion channels, action potential, repolarization, depolarization, membrane potential, resting potential, sodium potassium pump, refractory period, synapse, synaptic cleft, synaptic vesicles, neurotransmitters, acetylcholinesterase, presynaptic neuron, postsynaptic neuron, stimulate, inhibit