Nervous System
description
Transcript of Nervous System

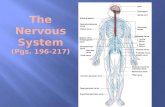
Nervous System

-Central Nervous System
-Peripheral Nervous System
Brain
Spinal Cord
Cranial Nerves
Spinal Nerves
Peripheral Ganglia
Division of the nervous system

-Central Nervous System
-Peripheral Nervous System
Brain
Spinal Cord
Cranial Nerves
Spinal Nerves
Peripheral Ganglia
Division of the nervous system

Central Nervous System (CNS)
7 Main Parts of the CNS
• Spinal Cord• Medulla oblongata• Pons• Cerebellum• Midbrain• Diencephalon• Cerebrum

Directions in the nervous system - Axes
Orientation Axes in the brain
Rostral-Caudal (front-back) anterior-posterior
Dorsal-Ventral (up – down)
Lateral-Medial (sideways – mid)

Directions in the nervous system - Planes

Maturation of the CNS
Brain weight at birth: 400 gAt 2 years ~ 1000 gAdult ~1500 g
Maturation is mostly based on differentiation of nerve-cell connectivty

Nerve cells (neurons)

Sketch of a neuronNucleus
DendritesDendrites
Myelin
Axons
• Dendrites -- Input• Cell body (soma) -- Integration• Axon -- Output

Structure of neurons - Dendrites
At dendrites, the neurons recieve input via axons of other neurons at synapses
dendritic spine

Structure of neurons - Soma
In the soma of the cells, the cell nucleus is located (containing the DNA, i.e. genetic code); the synthesis of the proteins (within ribosomes and endoplasmatic reticulum) as well as energy production (mitochondria) are performed.

Structure of neurons - Axon
The axon transmits the information electrically from the soma to the synapses –it is surrounded by myelin that insulate the axon, provided by oligodendrocytes (glial cells)

Sketch of a neuronNucleus
DendritesDendrites
Myelin
Axons
• Dendrites -- Input• Cell body (soma) – Integration; protein production, genes, energy production• Axon -- Output

Electrical properties of neurons
The cell membrane isolates the intracellular from extracellular space
extracellular
intracellular


Electrical properties of neurons
The membrane potential
In the resting state, the intracellular space contains more negative ions than the extracellular space
extracellular
intracellular
difference of -70 mV

Ion channels connect the intra- and extracellular space
Opening of ion channels lead to a flux of ions through the membrane and to a change of the membrane potential

Different types of ion channels

The action potentialThe action potential is generated by ion flux through voltage gated channels
All or nothing principle!!

Propagation of the action potential

Synapse – Communication between neurons

Synapse – Communication between neurons

Presynaptic vesicles with neurotransmitter
Released transmitter
Transmitter binds to receptor
Na+Transmitter-
Resorption from synaptic cleft
Synapse – Communication between neurons

• Animasi

Excitatory and Inhibitory Synapses
Depending on the neurotransmitter and the receptor, the postsynaptic potential can be excitatory or inhibitory
Excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) Inhibitory postsynaptic potential (EPSP)

Important Neurotransmitters
•Dopamine
•Epinephrine
•Norepinephrine
•Acetylcholine
•Serotonine
•Glycine
•GABA
•Glutamate

Two forms of integration of information

EPSC at dendrite can lead to action potential

Effect of inhibition on excitation

Glial cells
astrocytes oligodendrocytes

Astrocytes
Astrocytes connect the extraneuronal space with the blood vessels

Oligodendrocytes
Oligodendrocytes sheat the axons of the neurons to increase conductance of action potential

Summary neuronal communication
• intracellular electrical transmission of information (action
potential)
• neurons communicate via biochemical transmission
(neurotransmitters and receptors)
• integration of information in neurons by means of spatial and
temporal summation