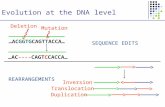
Mutation A mutation is a change in the normal base pair sequence Commonly used to define DNA...
-
date post
19-Dec-2015 -
Category
Documents
-
view
222 -
download
0
Transcript of Mutation A mutation is a change in the normal base pair sequence Commonly used to define DNA...
MutationA mutation is a change in the normal base pair sequence
Commonly used to define DNA sequence Commonly used to define DNA sequence changes that alter protein functionchanges that alter protein function
מוטציה – השתנות ברצף הנורמאלי של זיווגי הבסיסים
Mutation• DNA replication is extremely accurate, BUT…
– Errors in polymerization occur – מוטציות במהלך הרפליקציה – Environmental factors, such as chemicals and ultraviolet
radiation, can alter DNA – מוטציות כתוצאה מגורמים סביבתיים • Irreversible changes to the cellular DNA can be lethal• שינויים לא הפיכים יכולים להיות קטלנים• Non-lethal changes can cause a heritable alteration
of the genetic information, called a mutation• Genetic changes are more noticeable in germ line
cells than in somatic cells• Systems exist for the repair of damaged DNA
A human DNA repair defect:
Xeroderma pigmentosum
Multiple skin cancers due to unrepaired UV damage to DNA
• DNA replication must accurately replicate 6 x 109 base pairs every time a human cell divides –
• בכל חלוקת תא יש להכפיל שישה טרליון נוקלאוטדים
• In man we see one new mutation per gene per 100,000 cells per cell cycle. (spontaneous mutation frequency) –
• באדם מוטציה אחת בכל מאה אלף חלוקות .תא
Spontaneous mutagenesis and errors in DNA replication
i.e. 1 error per 1010 bp incorporated
DNA polymerases have two main methods for ensuring accuracy:
(a) Base selection
(b) Proofreading
Only AT and GC base pairs fit properly in the active site of the polymerase
If a wrong base is inserted, then it is removed and replaced with the correct one before the next one is added
Induced mutagenesis
Can be caused by environmental agents that damage DNA:
• UV light• X-rays and -rays• Chemical carcinogens e.g. cigarette
smoke
DNA damage can lead to mutations unless it is removed by DNA repair enzymes
Unrepaired damage can have serious consequences
Somatic vs. germ line mutations
• Somatic ((גוף mutations can lead to cancer
• Germ (נבט/ראשוני) line mutations can lead to birth defects (מום מולד)
• Most mutations cause neither– Some fall in non-coding DNA– Others are silent
רוב המוטציות אינן גורמות למחלות מכיוון שאינן פוגעות בנוקלאוטיד המעורב בתהליך התבטאות הגנים
(אינטר-גני או אינטרונים)
האם נזקי קרינת נחשבים למוטציות ספונטניות?
. לא, מכיוון שניתן לא להיחשף לשמש.1•
. כן, אין אפשרות להימנע מחשיפה לשמש, 2•ולכל קרינה אחרת שמקורה לא מהשמש.
נכונות.2 +1. תשובה 3•
. אין מספיק אינפורמציה על מנת לענות 4•תשובה נכונה.
Natural causes of mutationsמוטציות שנגרמות ע"י גורם טבעי
• Base tautomerization – שינויים טאוטומרים
• UV damage – נזקי קרינה
• Spontaneous deamination - דאמינציות
הבסיסים עוברים בצורה נדירה השתנות טאוטומרים ספונטנית רברסבילית - שינוים
שינוי טאוטומרי בזמן הרפליקציה יוביל לזיווג בסיסים לא תקין
UV Radiation and Pyrimidine Dimers
• UV radiation (200-300 nm) induces the formation of dimers between adjacent thymine residues
• Cytosine-cytosine and thymine-cytosine dimers occur less frequently
• These pyrimidine dimers disrupt the structure of the double helix, blocking replication until the lesion is repaired
ל שחודרים DNAכימיקליםאבל לנוקלאוטידים דומים נראים
נכונים לא בסיסים לזיווגי גורמים
מחסירים או שמוסיפים כימיקליםגורמים לבסיסים הקשורות קבוצות
נכונים לא בסיסים לזיווגי
נקודתיות מוטציות התוצאההרפליקציה DNAב במהלך
Mutations and Cancer
• Mutations that affect nonessential DNA or that have negligible effects on a gene’s function are called silent mutations
• Many mutations are detrimental, and a correlation exists between the accumulation of mutations and cancer
• New chemicals, such as pharmaceuticals, must be tested for carcinogenic potential
• Standard animal tests for carcinogenesis are lengthy and expensive
• The simple Ames test measures the potential of a given chemical to promote mutations in a specialized bacterial strain
The Ames Test for Mutagenesis
• S. typhimurium having a defect in histidine biosynthesis are plated on a histidine-free medium
• Chemical to be tested is placed on a disk of filter paper in the center of the culture plate
• Revertant bacterial colonies are caused by mutagens
• 80% to 90% of compounds found to be carcinogenic in animal tests are mutagens in the Ames test
Intercalating Agents
• Intercalating agents slip in between stacked base pairs
• Distance between base pairs is doubled by an intercalating agent
• Insertions or deletions of one or more nucleotides can occur during the replication of such distorted DNA
Chemical Mutagens
• Classes of damage produced by chemical mutagens – Point mutations: one base pair is replaced by
another
– Insertions or deletions: one or more nucleotide pairs are inserted in or deleted from DNA
• Important types of chemical mutagens
–Alkylating agents אלקילציות –Deaminating agents דיאמינציות –Intercalating agents
אינטרקלציות
Deamination of Cytosineדאמינציה -
• Nitrous acid can be formed from nitrite and nitrate salts• Nitrous acid oxidatively deaminates aromatic amines• Cytosine is converted to uracil upon treatment with nitrous
acid, causing a GC to AT transition• Cytosine sometimes spontanteously deaminates to uracil,
indicating why DNA contains thymine rather than uracil
קבוצת אמין
About 3% of the cytosine residues are methylated (intentionally).
באחת מתאי הבת תהיה
מוטציה נקודתית
"התיקון" ע"י BER
About 50% of the time the G is “corrected” to A resulting in a mutation
Alkylating Agents
• Alkylating agents such as dimethyl sulfate are electrophiles
• Such agents react most often with the nucleophilic N7 position of the guanine base
• Alkylation at N7 can generate an apurinic site in DNA
• Point mutations occur when guanine is replaced by another base
• DNA methylation can be useful
SO O
O OH3C CH3
S-O O
H3CO O
NH
N
N
O
NH2N
O
O
PO
O
O
O-
NH
N
N
O
NH2N
O
O
PO
O
O
O-
CH3
NH
N
N
O
NH2N
CH3H2O
O
O
PO
O
O
O-
OH
:
+
+ H+
Apurinic DNA
dimethyl sulfate
אלקילציות
BERהתיקון ע"י
Chemical mutagensסיכום – כימיקלים שגורמים למוטציות
• Chemicals that accelerate the deamidation reaction –מאיצים דיאמינציה
• Base analogues – אנלוגים לבסיסים • Alkylating agents – מבצעים אלקילציה
• Intercalation agents - אינטרקלטורים
Overview of DNA repair pathways
•A. Base excision repair
•B. Nucleotide excision repair.•C. Mismatch repair
•D. Double-strand break repair by • homologous recombination.
•E. Double-strand break by end joining
DNAמוטציות שמתרחשות במהלך הרפליקציה יתוקנו (אם אפשר) ע"י פולימראז
MRכאלה שלא תוקנו במהלך הרפליקציה יתוקנו מיד בסיומה ע"י
NER או BERמוטציות שאינן במסגרת הרפליקציה יתוקנו בכל זמן ע"י
Three general types of DNA repair pathways:1) Direct Repair2) Base excision Repair3) Nucleotide excision repair
Direct repair
Mismatch repair
פועל פעם אחת במהלך הרפליקציה.
חייב להבחין בין גדיל חדש לישן (ע"י המתילים).
לאחר השלמת התהליך הגדיל החדש עובר מתילציה.
-100משפר דיוק רפליקציה פי 1000.
Occurs just after replicationImproves accuracy 102 - 103 foldMust distinguish the parent from the daughter strand
מה ההבדל בין תיקון דנא במנגנון לבין מנגנון mismatch repair (MR)ה- ?nucleotide excision repair (NER)ה-
. שניהם פועלים בכל מהלך מחזור התא1•
NER בעוד שה-G1 פועל בשלב ה-MR. ה-2• במחזור התא.Mבשלב ה-
NER בעוד שה-M פועל בשלב ה-MR. ה-3• במחזור התא.G1בשלב ה-
NER בעוד שה-G0 פועל בשלב ה-MR. ה-4• במחזור התא.G1בשלב ה-
What happens when mismatch repair fails in humans?
• Missing enzymes homologous to MutS and MutL
• Patients usually die by age 30• Disease: hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal
cancer (HPCC) (מעי גס)• 1 in 200 people affected
Homologous End-Joiningrecovers information from thehomologous chromosome
Information lost
Information restored
A
Crossing over
Overview of DNA repair pathways
•A. Base excision repair
•B. Nucleotide excision repair.•C. Mismatch repair
•D. Double-strand break repair by • homologous recombination.
•E. Double-strand break by end joining