Muscle and Nervous Tissue Pages 97-101. Function: ◦ contract (shorten) to produce movement Three...
-
Upload
jerome-west -
Category
Documents
-
view
213 -
download
1
Transcript of Muscle and Nervous Tissue Pages 97-101. Function: ◦ contract (shorten) to produce movement Three...

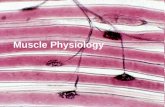
Muscle and Nervous Tissue
Pages 97-101

Function: ◦ contract (shorten) to produce movement
Three types:1.Skeletal muscle2.Cardiac muscle3.Smooth muscle
© 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.

Voluntary (consciously) control Attach to bones or skin Produce:
◦ gross body movements◦ facial expressions
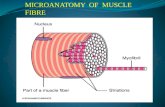
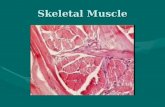
Cell Characteristics:◦ Striations (stripes)◦ Multinucleate (more than one nucleus)◦ Long, cylindrical shape
© 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.

Figure 3.20a Type of muscle tissue and their common locations in the body.
Nuclei
Part of musclefiber
Photomicrograph: Skeletal muscle (195×)(a) Diagram: Skeletal muscle

Involuntar control only in the heart Pumps blood through blood vessels Characteristics of cardiac muscle cells
◦ Striations◦ One nucleus, short, branching cells
Look somewhat like bamboo◦ Intercalated discs:
Areas between cells which contain gap junctions to connect cells together so that the impulse spreads across the heart synchronously
© 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.

Figure 3.20b Type of muscle tissue and their common locations in the body.
Intercalateddiscs
Nucleus
Photomicrograph: Cardiac muscle (475×)(b) Diagram: Cardiac muscle

Compare the two- note the differences
Skeletal Cardiac

Involuntary control
Location: where constricting and enlarging is required
◦ walls of hollow organs Peristalsis: a wavelike activity that moves digested
material through the small intestine◦ blood vessels
Characteristics:◦ No visible striations◦ Single nucleus◦ Spindle-shaped cells
© 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.

Figure 3.20c Type of muscle tissue and their common locations in the body.
Smoothmuscle cell
Nuclei
Photomicrograph: Sheet of smooth muscle (285×)(c) Diagram: Smooth muscle

Two groups of cells:◦ Neurons◦ Neuroglia (glial cells)
these insulate, protect, and support neurons
Function: receive and conduct electrochemical impulses to and from body parts◦ Irritability◦ Conductivity
© 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.

Figure 3.21 Nervous tissue.
Brain
Spinalcord
Nuclei ofsupportingcells
Cell bodyof neuron
Neuronprocesses
Nuclei ofsupportingcells
Neuronprocesses
Cell bodyof neuron
Diagram: Nervous tissue
Photomicrograph: Neurons (320×)