Mitosis Study Guide Review. What is the purpose of Mitosis? Division of cells to grow, or replace...
-
Upload
sharyl-miles -
Category
Documents
-
view
216 -
download
0
Transcript of Mitosis Study Guide Review. What is the purpose of Mitosis? Division of cells to grow, or replace...
What is the purpose of Mitosis?
Division of cells to grow, or replace old, diseased, dead or damaged body cells
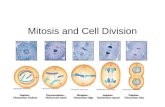
Explain each phase of the cell cycle and draw a
picture of what a cell in this phase might look like
InterphaseCell GrowsDNA is copiedVisible nucleus and nucleolusDNA is uncondensed=chromatin Chromosomes are NOT visible
ProphaseVisible condensed double-
stranded chromosomes/ sister chromatids
Centrioles begin to send out spindle fibers
Nuclear envelope disappears
MetaphaseDouble-stranded chromosomes/
Sister chromatids line up in the center of the cell
Spindle fibers connect to the centromeres of each chromosome
Chromatids are being pulled
AnaphaseSister chromatids are moving
apart= chromatids once splitChromatids are moving towards
the poles of the cellSpindle fibers pull the chromatids
to the poles
TelophaseNew nuclear membrane begins to
form around each set of chromatids
Cytoplasm begins to divideChromatids uncoil= chromatin
once uncondensedVisible cleavage furrowSpindle fibers disappear
CytokinesisCytoplasm divides2 new daughter cells identical to
the parent cellAfter cytokinesis, cell return to
interphase
MetaphaseDouble-stranded chromosomes/
Sister chromatids line up in the center of the cell
Chromatids are being pulled
AnaphaseSister chromatids are moving
apart= chromatids once splitChromatids are moving towards
the poles of the cell by means of the spindle fibers
TelophaseNew nuclear membrane begins to
form around each set of chromatids
Chromatids uncoil= chromatin once uncondensed
How do daughter cells produced in mitosis compare to the original cell?
The daughter cells are identical to the original (parent) cell.
Same function, same internal parts, SAME DNA
Explain the relationship that mitosis has with cancer.
Cancer is unregulated cell growth and division.
How do Chemotherapy drugs used in cancer treatment affect Mitosis?They stop cell division at various
stages of the cell cycle◦Prevent DNA replication
(doxorubicin)◦Cross-link with DNA to prevent
synthesis (cyclophospliamide)◦Blocks cells from making nucleotides
(methotrexate)
Why does chemotherapy tend to cause side effects like hair loss
and gastrointestinal issues?They kill off the rapidly dividing
cells of the body kill not only rapidly dividing
cancer cells but also cells of the rapidly dividing cells like those that make up hair, bone marrow, and the GI tract
Effects are NOT usually permanent
What is the difference between a scanning electron microscope and a transmission electron microscope?
Scanning Electron Microscope◦The entire organism/specimen can
be used, but it must be coated in a thin layer of gold atoms
◦The imaged obtained is a 3 dimensional surface image
What is the difference between a scanning electron microscope and a transmission electron microscope?
Transmission Electron Microscope◦Uses a thin slice of an
organism/specimen◦Used to study the internal make-up
of the specimen
How are the pictures they take different?
Scanning Electron Microscope Images show…◦3 dimensional images of surface
Transmission Electron Microscope Images show…◦Internal make-up of the specimen
(cross section)
What types of problems can occur at each stage of the Mitosis?
Prophase: nuclear membrane may not dissolve causing the cell to not be able to go through other stages
Metaphase: Chromosomes may not line up, causing an error in the remaining phases
Anaphase: Sister chromatids may not split correctly, causing an error in the number of chromosomes at each cell pole
Telophase: Chromatids may not unravel, causing the chromatin not to be enclosed in the new nuclear membrane.
What might happen to an organism if their cells lost the ability to divide via Mitosis?
Once that cell dies then that particular cell would not be able to pass on their DNA.
Furthermore, that particular organism would not be able to make new cells after the original parent cell has died
Eventually casing the death of that particular organism