Mitosis (Cell Division) MITOSIS. Vocab 1.Cell Cycle: the life cycle of a eukaryotic cell, consisting...
-
Upload
coral-hunter -
Category
Documents
-
view
236 -
download
0
Transcript of Mitosis (Cell Division) MITOSIS. Vocab 1.Cell Cycle: the life cycle of a eukaryotic cell, consisting...
Vocab1. Cell Cycle: the life cycle of a eukaryotic
cell, consisting of growth and division
2. Chromatin: uncoiled DNA
3. Chromosomes: coiled DNA and protein
Chromatin
4. Chromatids: identical chromosome copies, ½ of the X shape chromosome
5. Centromere: holds the chromatids together
ChromosomeChromatid
Centromere
Vocab cont.
6. Homologous Chromosomes: a pair of chromosomes with matching information
7. Cytokinesis: when the cytoplasm divides after mitosis
Limits to Cell Growth:
1. DNA Overload:- DNA would not be able to instruct all of the activities going on in the cell
2. Exchanging Materials:- As the cell size increases it would be more difficult for a larger cell to get oxygen and nutrients in and wastes out
Cell Division
• process by which a cell divides and produces 2 IDENTICAL daughter cells
• Why do cells divide?
1) Growth of the organism
2) Repair damaged cells
3) Reproduction
The Steps of the Cell Cycle:
• 4 phases:
1. G1: cell growth
2. S: DNA
replication
3. G2: cell growth
The Steps of the Cell Cycle:
• 4 phases:
1. G1: cell growth
2. S: DNA
replication
3. G2: cell growth
4. Mitosis: cell
division
(P, M, A, T)
Interphase
- this is the longest
phase of the cell
cycle and includes the G1, S,
and G2 phaseschromatin:(DNA)
Nucleolus
Nuclear
Membrane
Cell
Membrane
Mitosis
• Cell Division of body cells
• Shortest phase of the Cell Cycle
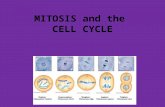
• Consists of 4 phases1. Prophase
2. Metaphase
3. Anaphase
4. Telophase
Mitosis Step 1: Prophase
- DNA coils up into
chromosomes, with 2
copies of each chromosome (sister chromatids) held together by a centromere
Mitosis Step 1: Prophase cont.
- Nucleolus and Nuclear Mem. disappear
- Spindle fibers form
Spindle Fibers
Chromosomes
Mitosis Step 2: Metaphase
- Chromosomes attach to spindle fibers by centromeres and line up across the middle
Spindle Fibers
2nd chromatid
One chromatid
Centromere
Mitosis Step 3: Anaphase
- Centromeres split apart
- Sister chromatids are pulled to opposite
ends of the cell by the spindle fibers
Spindle Fibers
Centromere
One chromatid
2nd chromatid
Mitosis Step 4: Telophase
• Chromatids reach opposite ends of the cell
• Nucleolus and Nuclear Membrane reappears
Mitosis Step 4: Telophase
- Cell membrane begins to separate
- Cytokinesis occurs:
division of cytoplasm
- animal cells: cleavage furrow
- plant cells:
cell plate
Cleavage Furrow
(Animal cell only)