Mitosis
description
Transcript of Mitosis
-
Trade your cards with another person in the class to compare your information add or change any detail if necessarystarter: summarising mitosis
-
The Cell Cycle MITOSIS (continued) identify the stages of the cell cycle and what is occurring at each stage name and explain the events occurring during each stage of mitosis be able to recognise the stages from drawings and photographs
-
The Cell CycleDNA is replicatedOrganelles grow and divide and energy stores are increasedProteins from which cell organelles are synthesised and produced
-
What is mitosis? A type of cell division (nuclear division)
occurs when body cells divide to increase their number, or an organism reproduces asexually
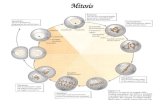
mitosis is split into 4 stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase
produces 2 daughter nuclei that have the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell and each other
**the whole process is continuous, and the four stages blend smoothly into each other
-
cellnucleusDNADNADNADNADNADNADNA1. REPLICATION2. MITOSIS3. CYTOKINESIS
-
Watch the animation of mitosis
http://www.cellsalive.com/mitosis.htm
http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter2/animation__mitosis_and_cytokinesis.html
-
a DNA in uncondensed formb DNA condensed into chromosomes
-
replicated,uncondensed DNAEND OFINTERPHASEDNA has alreadyduplicated back in theS phase. Centrosomehas doubled.pair ofcentrosomesnucleusnucleolusspindle fibers(microtubules)PROPHASEMitosis begins. Thechromosomes take shapeas the DNA condenses. The nuclear envelope begins tobreak down. The two centrosomes begin to movetoward the cellular poles,sprouting microtubules asthey go.chromosomes(each a pair of sister chromatidsjoined together)mitoticspindlemetaphaseplateMETAPHASELinkage and alignment. Somemicrotubules of the mitotic spindleform a cage around the cells formernucleus while others attach to thesister chromatids and align themat the metaphase plate. Each chromatid now faces the poleopposite that of its sister chromatid.MITOSIS AND CYTOKINESIS
-
ANAPHASESeparation. Sisterchromatids are moved to opposite poles in the cell by motor proteins that pull the chromatids along the microtubule tracks they are attached to. Each chromatid is now a full fledged chromosome.spindle fibers shorteningseparatingchromatidsTELOPHASE ANDCYTOKINESISnuclearenvelopeformingExit from mitosis.Chromosomes decondense,the mitotic spindle breaksdown, and nuclear envelopes form around the two separate complementsof chromosomes. Meanwhile, a cleavage furrow begins to form nearthe middle of the cell.cleavagefurrowCOMPLETION OFCYTOKINESISOne cell becomes two.The cell membrane pinches together completely, the membranes on either side fuses together, and the one cell becomes two. Thesetwo cells now enter the G1 phase of interphase.
-
What stages of mitosis are these? How do you know?
-
centriolechromosomechromatidchromatincentromereCentro eh??
CentrioleShort cylindrical array of microtubules. A pair of centrioles is usually found at the centre of a centrosome in animal cells.ChromosomeStructure composed of a very long DNA molecule and associated proteins that carries part (or all) of the hereditary information of an organism. ChromatidOne copy of a chromosome formed by DNA replication that is still joined at the centromere to the other copy. The two identical chromatids are called sister chromatids.ChromatinComplex of DNA and proteins (mostly histones) found in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell. The material of which chromosomes are made. CentromereRegion of a mitotic chromosome that holds sister chromatids together. It is also the site on the DNA where it is captured by microtubules from the mitotic spindle.
-
a) How does the amount of DNA in a nucleus differ between the start and the end of interphase? b) There are 46 chromosomes in a human body cell. How many DNA molecules are there in a cell nucleus at the start of prophase? c) Suggest why it is an advantage for the chromatids to contract independently during prophase? d) Suggest why it is important that the chromatids remain attached at the centromere until anaphase.2. Draw diagrams of metaphase, anaphase and telophase for the cell shown below.
Complete these questions
-
Plenary:
Card sort
*Figure: 09-04
Title:Overview of cell division.
Caption:Overview of cell division.
**Figure: 09-08
Title:DNA can be arranged in two ways.
Caption:a. Replication occurs when the chromosomes DNA comes packed in are in a relatively formless state. b. Mitosis occurs after DNA condenses into the easily discernable shapes of duplicated chromosomes. The micrograph is of color-enhanced duplicated human chromosomes.
*Figure: 09-11
Title:Cytokinesis in animals.
Caption:Cytokinesis in animal cells begins with a cleavage furrow, shown here in a dividing frog egg. (x 85)
*Figure: 09-10a
Title:Mitosis: interphase through metaphase.
Caption:Mitosis: interphase through metaphase.
*Figure: 09-10b
Title:Mitosis: anaphase through cytokinesis.
Caption:Mitosis: anaphase through cytokinesis.
anaphase*prophase*metaphase**telophase