minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis
-
Upload
sagar-tomar -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
188 -
download
2
Transcript of minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis

OUTCOME OF DISTAL END TIBIA FRACTURES MANAGED
BY MINIMALLY INVASIVE PLATE OSTEOSYNTHESIS
TECHNIQUE
Dr sagar tomarLlrm medical college meerut up
INTRODUCTION
Earlier the treatment of distal tibia was done using intramedullary osteosynthesis but it does not provide a stable rigid fixation
open reduction and internal fixation was attempted with classical plates but it requires a quite larger incision causing larger periosteal damage
This Traditional ORIF results in extensive
soft tissue dissection and periosteal injury and are associated with high rates of infection delayed union and non‐union
Because of these drawbacks research and development leads to the invention of new plates called ldquoBIOLOGICAL PLATErdquo and new surgical procedures one of which is ldquoMINIMALLY INVASIVE PLATE OSTEOSYNTHESISrdquo
MIPO technique
In this technique only the normal bone cortexes both proximal and distal to the fracture site are exposed for positioning the plate and inserting the screws while the fracture site is not explored so that osteogenic tissues surrounding the fracture are well protected and their blood supply is also well preserved
biomechanics
Mipo relies on relative stability rather than absolute rigid fixation because of which micromotion is produced at the fracture site and a larger and rapid callus formation occurs leading to rapid bone healing
Relative stability does not require accurate apposition of fragments as the gap are filled up by bridging callus
Indication of mipo in distal tibial
intraarticular or periarticular fractures which
are considered unsuitable for intramedullary nailing
They include
Communited fractures
low-grade open fractures of the distal tibia
displaced pilon fractures with sufficient medial soft-tissue coverage to allow articular reconstruction and percutaneous plating
unstable distal metaphyseal and diaphyseal fractures
Contra-indication
MIPO is contraindicated in situations where the medial soft tissue is compromised such as in severe open fractures or badly contused skin
If the bone is osteoporotic or comminution is so excessive that surgery cannot restore or stabilize the joint then other methods of treatment must be sought such as external fixator
In severely shattered pilon fractures when only choice is external fixator
Advantage of mipo
minimizes risk of soft tissue damage
preserve vascular supply to bone and soft tissue
decrease periosteum damage
have better and faster callus formation
have better healing and union rate
decrease complication of infection and re-fracture
decrease the use of supplementary bone grafting
IMPLANT CHOICE
Choice of implant could be
bullMetaphysealplate (broad or narrow)
bullPrecountoureddistal tibia locking plate
bullClowerleaf LCP
procedure
POSITIONING OF PATIENT
INCISION
anteromedial approach a 2ndash3 cm incision is made starting at the level of the tibial plafond and extending proximally along the medial surface of the distal tibia ORposteromedial incision along the
posterior border of medialmalleolus about 4ndash5 cm in length and slightly curved can beused
PRELIMINARY REDUCTION
REDUCTION COULD BE BY MANUAL TRACTION OR BY USE OF DISTRACTOR AND REDUCTION FORCEPS PERCUTANEOUSLY
PLATE INSERTION
PLATE COULD BE INSERTED WITH HELP OF INSERTION DEVICE OR WITH HELP OF LOCKING SLEEVE UNDER SUBMUSCULAR PLANE
PRELIMINARY PLATE STABILIZATION
BY USE OF K-WIRE FOR TEMPORARY FIXATION OF PLATE
PLATE FIXATION
A MINIMUM OF 6 CORTICES ON BOTH SIDE OF FRACTURE ARE USED AND INTERFRAGMENATRY COMPRESSION SCREW WHERE NEEDED
REVIEW OF WORK
THE VARIOUS STUDY DONE TO CHECK THE EFFECTIVENESS OF MIPO TECHNIQUE FOR DISTAL END TIBIA FRACTURES ARE AS FOLLOWS
REVIEW OF WORK
STUDY NO OF FRACTURE
FIXATION OUTCOME COMPLICATION
Ronga M et al2010
19 MIPO Union 18 (223 wks range 12-24)
Nonunion1 No malunion ( ge7deg deformity or ge1 cm LLD) Deep infection3
Ahmad MA et al 2010
18 MIPO Union 15 (212 wks)
Delayed union 3 Superficial wound infarction 1 Chronic wound infection 1 Implant failure 1
Ronga M Longo UG Maffulli N Minimally invasive locked plating of distal tibia fractures is safe and effective Clin Orthop Relat Res 2010
Ahmad MA Sivaraman A Zia A Rai A Patel AD Percutaneouslocking plates for fractures of the distal tibia Our experience and a review of the literature J Trauma 2010
HasenbohehlerE et al (2007)
32 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 29 ( 277 wks range 24ndash60)
Nonunion 2 No malunion (ge 5deg deformity or ge 1 cm LLD) Plate bending (18deg) 1 Pseudoarthrosis 2
Hazarika S et al (2006)
20 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 18 ( 285 wks range 9ndash68)
Nonunion 2 Delayed wound break down 2 Wound infection 1 Implant failure 1 Secondary procedure 2
Hasenboehler E RikliD Babst R Locking compression plate with minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in diaphyseal and distal tibial fracture a retrospective study of 32 patients Injury 2007
Hazarika S Chakravarthy J Cooper J Minimally invasive locking plate osteosynthesis for fractures of the distal tibia-results in 20 patients Injury 2006
Bahari S et al (2007)
42 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 42 (224 wks)
No malunionSuperficial wound infection 2 Deep infection 1 Implant failure 1
Collinge C et al(2010)
38 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 38 (21 wks range 9ndash48)
Malunion ( ge 5degdeformity) 1 Secondary procedure 3
Mushtaq A et al (2009)
21 (open fracture 4)
MIPO Union 21( 55 months range 3ndash13)
Delayed union 1 Non union 1 Wound infection 2 Secondary procedure 2
Bahari S LenehanB Khan H Mcelwain JP Minimally invasive percutaneous plate fixation of distal tibia fractures Acta Orthop Belg2007
Collinge C Protzman R Outcomes of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis for metaphyseal distal tibia fractures J OrthopTrauma 2010
Mushtaq A Shahid R AsifM Maqsood M Distal tibialfracture fixation with locking compression plate (LCP) using the minimally invasive percutaneousosteosynthesis (MIPO) technique Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg 2009
Lau TW et al (2008)
48 (open fracture 9)
MIPO Union 47 ( 187 wks range 12-44 wks)
Delayed union 5 Wound infection 8 Secondary procedure1
Gupta RK et al(2010)
80 (open fracture19)
MIPO Union 77 (19 wks range 16-32)
Delayed union 7 Non union 3 Malunion (ge 5degdeformity or ge 1 cm LLD) 2 Wound infection1 Wound breakdown 2 Secondary procedure 2
Lau TW Leung F Chan CF Chow SP Wound complication of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in distal tibia fractures Inter Orthop 2008
Gupta RK RohillaRK Sangwan K Singh V Walia S Locking plate fixation in distal metaphysealtibial fractures series of 79 patients Inter Orthop 2010
Shreshta et al(2011)
20 MIPO Union 20 (185 wks range 14-28)
Delayed union 1 No malunion (ge 5deg deformity or ge 1 cm LLD) Superficial wound infection 2 Deep infection 1 Secondary procedure 1
Oog Jin et al 10 MIPO Union10(21 wksrange17-28)
no non-union no angular deformity gt 5deg shortening gt 10 mm no infection
Shrestha D Acharya BM Shrestha PM Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis with locking compression plate for distal diametaphyseal tibia fracture Kathmandu Univ Med J 2011
hong et al
Fractures of the Distal Tibia Treated with PolyaxialLocking Plating
Hong Gao MD Chang-Qing Zhang MD PhD Cong-FengLuo MD PhD Zu-Bin Zhou MD and Bing-Fang Zeng
MDClin Orthop Relat Res 2009 March 467(3) 831ndash837 Total pts 32 The average healing time was 13 weeks (range 10ndash18 weeks)
for fractures using the MIPO technique and 156 weeks (range 10ndash20 weeks p = 00045) for fractures using the ORIF technique
The fracture healing time was shorter in the MIPO technique group than in the ORIF technique group which might be related to minimizing soft tissue trauma to the injured zone and preserving better blood supply around the fracture area
ADVANTAGE OF MIPPO OVER
ORIF
mipo orif
Smaller incision
Fracture site is undisturbed
Better callus formation
Blood supply to fracture fragments maintained
Larger incision
Fracture site explored
Callus formation is delayed
Blood supply is hampered
mipo orif
Low infection rate due to smaller incision and decrease soft tisuedamage
decreased need for bone grafting
High infection rate due to poor soft tissue handling over large incised wound
Bone grafting is required sometimes
conclusion
Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis(MIPO) of the distal tibia offers several theoretical advantages compared to classic open reduction and internal fixation A mechanically stable fracture-bridging osteosynthesis can be obtained without significant dissection and surgical trauma to the bone and surrounding soft tissues
MIPO has a high union rate and less complication rate
Thank you

INTRODUCTION
Earlier the treatment of distal tibia was done using intramedullary osteosynthesis but it does not provide a stable rigid fixation
open reduction and internal fixation was attempted with classical plates but it requires a quite larger incision causing larger periosteal damage
This Traditional ORIF results in extensive
soft tissue dissection and periosteal injury and are associated with high rates of infection delayed union and non‐union
Because of these drawbacks research and development leads to the invention of new plates called ldquoBIOLOGICAL PLATErdquo and new surgical procedures one of which is ldquoMINIMALLY INVASIVE PLATE OSTEOSYNTHESISrdquo
MIPO technique
In this technique only the normal bone cortexes both proximal and distal to the fracture site are exposed for positioning the plate and inserting the screws while the fracture site is not explored so that osteogenic tissues surrounding the fracture are well protected and their blood supply is also well preserved
biomechanics
Mipo relies on relative stability rather than absolute rigid fixation because of which micromotion is produced at the fracture site and a larger and rapid callus formation occurs leading to rapid bone healing
Relative stability does not require accurate apposition of fragments as the gap are filled up by bridging callus
Indication of mipo in distal tibial
intraarticular or periarticular fractures which
are considered unsuitable for intramedullary nailing
They include
Communited fractures
low-grade open fractures of the distal tibia
displaced pilon fractures with sufficient medial soft-tissue coverage to allow articular reconstruction and percutaneous plating
unstable distal metaphyseal and diaphyseal fractures
Contra-indication
MIPO is contraindicated in situations where the medial soft tissue is compromised such as in severe open fractures or badly contused skin
If the bone is osteoporotic or comminution is so excessive that surgery cannot restore or stabilize the joint then other methods of treatment must be sought such as external fixator
In severely shattered pilon fractures when only choice is external fixator
Advantage of mipo
minimizes risk of soft tissue damage
preserve vascular supply to bone and soft tissue
decrease periosteum damage
have better and faster callus formation
have better healing and union rate
decrease complication of infection and re-fracture
decrease the use of supplementary bone grafting
IMPLANT CHOICE
Choice of implant could be
bullMetaphysealplate (broad or narrow)
bullPrecountoureddistal tibia locking plate
bullClowerleaf LCP
procedure
POSITIONING OF PATIENT
INCISION
anteromedial approach a 2ndash3 cm incision is made starting at the level of the tibial plafond and extending proximally along the medial surface of the distal tibia ORposteromedial incision along the
posterior border of medialmalleolus about 4ndash5 cm in length and slightly curved can beused
PRELIMINARY REDUCTION
REDUCTION COULD BE BY MANUAL TRACTION OR BY USE OF DISTRACTOR AND REDUCTION FORCEPS PERCUTANEOUSLY
PLATE INSERTION
PLATE COULD BE INSERTED WITH HELP OF INSERTION DEVICE OR WITH HELP OF LOCKING SLEEVE UNDER SUBMUSCULAR PLANE
PRELIMINARY PLATE STABILIZATION
BY USE OF K-WIRE FOR TEMPORARY FIXATION OF PLATE
PLATE FIXATION
A MINIMUM OF 6 CORTICES ON BOTH SIDE OF FRACTURE ARE USED AND INTERFRAGMENATRY COMPRESSION SCREW WHERE NEEDED
REVIEW OF WORK
THE VARIOUS STUDY DONE TO CHECK THE EFFECTIVENESS OF MIPO TECHNIQUE FOR DISTAL END TIBIA FRACTURES ARE AS FOLLOWS
REVIEW OF WORK
STUDY NO OF FRACTURE
FIXATION OUTCOME COMPLICATION
Ronga M et al2010
19 MIPO Union 18 (223 wks range 12-24)
Nonunion1 No malunion ( ge7deg deformity or ge1 cm LLD) Deep infection3
Ahmad MA et al 2010
18 MIPO Union 15 (212 wks)
Delayed union 3 Superficial wound infarction 1 Chronic wound infection 1 Implant failure 1
Ronga M Longo UG Maffulli N Minimally invasive locked plating of distal tibia fractures is safe and effective Clin Orthop Relat Res 2010
Ahmad MA Sivaraman A Zia A Rai A Patel AD Percutaneouslocking plates for fractures of the distal tibia Our experience and a review of the literature J Trauma 2010
HasenbohehlerE et al (2007)
32 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 29 ( 277 wks range 24ndash60)
Nonunion 2 No malunion (ge 5deg deformity or ge 1 cm LLD) Plate bending (18deg) 1 Pseudoarthrosis 2
Hazarika S et al (2006)
20 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 18 ( 285 wks range 9ndash68)
Nonunion 2 Delayed wound break down 2 Wound infection 1 Implant failure 1 Secondary procedure 2
Hasenboehler E RikliD Babst R Locking compression plate with minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in diaphyseal and distal tibial fracture a retrospective study of 32 patients Injury 2007
Hazarika S Chakravarthy J Cooper J Minimally invasive locking plate osteosynthesis for fractures of the distal tibia-results in 20 patients Injury 2006
Bahari S et al (2007)
42 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 42 (224 wks)
No malunionSuperficial wound infection 2 Deep infection 1 Implant failure 1
Collinge C et al(2010)
38 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 38 (21 wks range 9ndash48)
Malunion ( ge 5degdeformity) 1 Secondary procedure 3
Mushtaq A et al (2009)
21 (open fracture 4)
MIPO Union 21( 55 months range 3ndash13)
Delayed union 1 Non union 1 Wound infection 2 Secondary procedure 2
Bahari S LenehanB Khan H Mcelwain JP Minimally invasive percutaneous plate fixation of distal tibia fractures Acta Orthop Belg2007
Collinge C Protzman R Outcomes of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis for metaphyseal distal tibia fractures J OrthopTrauma 2010
Mushtaq A Shahid R AsifM Maqsood M Distal tibialfracture fixation with locking compression plate (LCP) using the minimally invasive percutaneousosteosynthesis (MIPO) technique Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg 2009
Lau TW et al (2008)
48 (open fracture 9)
MIPO Union 47 ( 187 wks range 12-44 wks)
Delayed union 5 Wound infection 8 Secondary procedure1
Gupta RK et al(2010)
80 (open fracture19)
MIPO Union 77 (19 wks range 16-32)
Delayed union 7 Non union 3 Malunion (ge 5degdeformity or ge 1 cm LLD) 2 Wound infection1 Wound breakdown 2 Secondary procedure 2
Lau TW Leung F Chan CF Chow SP Wound complication of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in distal tibia fractures Inter Orthop 2008
Gupta RK RohillaRK Sangwan K Singh V Walia S Locking plate fixation in distal metaphysealtibial fractures series of 79 patients Inter Orthop 2010
Shreshta et al(2011)
20 MIPO Union 20 (185 wks range 14-28)
Delayed union 1 No malunion (ge 5deg deformity or ge 1 cm LLD) Superficial wound infection 2 Deep infection 1 Secondary procedure 1
Oog Jin et al 10 MIPO Union10(21 wksrange17-28)
no non-union no angular deformity gt 5deg shortening gt 10 mm no infection
Shrestha D Acharya BM Shrestha PM Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis with locking compression plate for distal diametaphyseal tibia fracture Kathmandu Univ Med J 2011
hong et al
Fractures of the Distal Tibia Treated with PolyaxialLocking Plating
Hong Gao MD Chang-Qing Zhang MD PhD Cong-FengLuo MD PhD Zu-Bin Zhou MD and Bing-Fang Zeng
MDClin Orthop Relat Res 2009 March 467(3) 831ndash837 Total pts 32 The average healing time was 13 weeks (range 10ndash18 weeks)
for fractures using the MIPO technique and 156 weeks (range 10ndash20 weeks p = 00045) for fractures using the ORIF technique
The fracture healing time was shorter in the MIPO technique group than in the ORIF technique group which might be related to minimizing soft tissue trauma to the injured zone and preserving better blood supply around the fracture area
ADVANTAGE OF MIPPO OVER
ORIF
mipo orif
Smaller incision
Fracture site is undisturbed
Better callus formation
Blood supply to fracture fragments maintained
Larger incision
Fracture site explored
Callus formation is delayed
Blood supply is hampered
mipo orif
Low infection rate due to smaller incision and decrease soft tisuedamage
decreased need for bone grafting
High infection rate due to poor soft tissue handling over large incised wound
Bone grafting is required sometimes
conclusion
Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis(MIPO) of the distal tibia offers several theoretical advantages compared to classic open reduction and internal fixation A mechanically stable fracture-bridging osteosynthesis can be obtained without significant dissection and surgical trauma to the bone and surrounding soft tissues
MIPO has a high union rate and less complication rate
Thank you

Because of these drawbacks research and development leads to the invention of new plates called ldquoBIOLOGICAL PLATErdquo and new surgical procedures one of which is ldquoMINIMALLY INVASIVE PLATE OSTEOSYNTHESISrdquo
MIPO technique
In this technique only the normal bone cortexes both proximal and distal to the fracture site are exposed for positioning the plate and inserting the screws while the fracture site is not explored so that osteogenic tissues surrounding the fracture are well protected and their blood supply is also well preserved
biomechanics
Mipo relies on relative stability rather than absolute rigid fixation because of which micromotion is produced at the fracture site and a larger and rapid callus formation occurs leading to rapid bone healing
Relative stability does not require accurate apposition of fragments as the gap are filled up by bridging callus
Indication of mipo in distal tibial
intraarticular or periarticular fractures which
are considered unsuitable for intramedullary nailing
They include
Communited fractures
low-grade open fractures of the distal tibia
displaced pilon fractures with sufficient medial soft-tissue coverage to allow articular reconstruction and percutaneous plating
unstable distal metaphyseal and diaphyseal fractures
Contra-indication
MIPO is contraindicated in situations where the medial soft tissue is compromised such as in severe open fractures or badly contused skin
If the bone is osteoporotic or comminution is so excessive that surgery cannot restore or stabilize the joint then other methods of treatment must be sought such as external fixator
In severely shattered pilon fractures when only choice is external fixator
Advantage of mipo
minimizes risk of soft tissue damage
preserve vascular supply to bone and soft tissue
decrease periosteum damage
have better and faster callus formation
have better healing and union rate
decrease complication of infection and re-fracture
decrease the use of supplementary bone grafting
IMPLANT CHOICE
Choice of implant could be
bullMetaphysealplate (broad or narrow)
bullPrecountoureddistal tibia locking plate
bullClowerleaf LCP
procedure
POSITIONING OF PATIENT
INCISION
anteromedial approach a 2ndash3 cm incision is made starting at the level of the tibial plafond and extending proximally along the medial surface of the distal tibia ORposteromedial incision along the
posterior border of medialmalleolus about 4ndash5 cm in length and slightly curved can beused
PRELIMINARY REDUCTION
REDUCTION COULD BE BY MANUAL TRACTION OR BY USE OF DISTRACTOR AND REDUCTION FORCEPS PERCUTANEOUSLY
PLATE INSERTION
PLATE COULD BE INSERTED WITH HELP OF INSERTION DEVICE OR WITH HELP OF LOCKING SLEEVE UNDER SUBMUSCULAR PLANE
PRELIMINARY PLATE STABILIZATION
BY USE OF K-WIRE FOR TEMPORARY FIXATION OF PLATE
PLATE FIXATION
A MINIMUM OF 6 CORTICES ON BOTH SIDE OF FRACTURE ARE USED AND INTERFRAGMENATRY COMPRESSION SCREW WHERE NEEDED
REVIEW OF WORK
THE VARIOUS STUDY DONE TO CHECK THE EFFECTIVENESS OF MIPO TECHNIQUE FOR DISTAL END TIBIA FRACTURES ARE AS FOLLOWS
REVIEW OF WORK
STUDY NO OF FRACTURE
FIXATION OUTCOME COMPLICATION
Ronga M et al2010
19 MIPO Union 18 (223 wks range 12-24)
Nonunion1 No malunion ( ge7deg deformity or ge1 cm LLD) Deep infection3
Ahmad MA et al 2010
18 MIPO Union 15 (212 wks)
Delayed union 3 Superficial wound infarction 1 Chronic wound infection 1 Implant failure 1
Ronga M Longo UG Maffulli N Minimally invasive locked plating of distal tibia fractures is safe and effective Clin Orthop Relat Res 2010
Ahmad MA Sivaraman A Zia A Rai A Patel AD Percutaneouslocking plates for fractures of the distal tibia Our experience and a review of the literature J Trauma 2010
HasenbohehlerE et al (2007)
32 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 29 ( 277 wks range 24ndash60)
Nonunion 2 No malunion (ge 5deg deformity or ge 1 cm LLD) Plate bending (18deg) 1 Pseudoarthrosis 2
Hazarika S et al (2006)
20 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 18 ( 285 wks range 9ndash68)
Nonunion 2 Delayed wound break down 2 Wound infection 1 Implant failure 1 Secondary procedure 2
Hasenboehler E RikliD Babst R Locking compression plate with minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in diaphyseal and distal tibial fracture a retrospective study of 32 patients Injury 2007
Hazarika S Chakravarthy J Cooper J Minimally invasive locking plate osteosynthesis for fractures of the distal tibia-results in 20 patients Injury 2006
Bahari S et al (2007)
42 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 42 (224 wks)
No malunionSuperficial wound infection 2 Deep infection 1 Implant failure 1
Collinge C et al(2010)
38 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 38 (21 wks range 9ndash48)
Malunion ( ge 5degdeformity) 1 Secondary procedure 3
Mushtaq A et al (2009)
21 (open fracture 4)
MIPO Union 21( 55 months range 3ndash13)
Delayed union 1 Non union 1 Wound infection 2 Secondary procedure 2
Bahari S LenehanB Khan H Mcelwain JP Minimally invasive percutaneous plate fixation of distal tibia fractures Acta Orthop Belg2007
Collinge C Protzman R Outcomes of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis for metaphyseal distal tibia fractures J OrthopTrauma 2010
Mushtaq A Shahid R AsifM Maqsood M Distal tibialfracture fixation with locking compression plate (LCP) using the minimally invasive percutaneousosteosynthesis (MIPO) technique Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg 2009
Lau TW et al (2008)
48 (open fracture 9)
MIPO Union 47 ( 187 wks range 12-44 wks)
Delayed union 5 Wound infection 8 Secondary procedure1
Gupta RK et al(2010)
80 (open fracture19)
MIPO Union 77 (19 wks range 16-32)
Delayed union 7 Non union 3 Malunion (ge 5degdeformity or ge 1 cm LLD) 2 Wound infection1 Wound breakdown 2 Secondary procedure 2
Lau TW Leung F Chan CF Chow SP Wound complication of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in distal tibia fractures Inter Orthop 2008
Gupta RK RohillaRK Sangwan K Singh V Walia S Locking plate fixation in distal metaphysealtibial fractures series of 79 patients Inter Orthop 2010
Shreshta et al(2011)
20 MIPO Union 20 (185 wks range 14-28)
Delayed union 1 No malunion (ge 5deg deformity or ge 1 cm LLD) Superficial wound infection 2 Deep infection 1 Secondary procedure 1
Oog Jin et al 10 MIPO Union10(21 wksrange17-28)
no non-union no angular deformity gt 5deg shortening gt 10 mm no infection
Shrestha D Acharya BM Shrestha PM Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis with locking compression plate for distal diametaphyseal tibia fracture Kathmandu Univ Med J 2011
hong et al
Fractures of the Distal Tibia Treated with PolyaxialLocking Plating
Hong Gao MD Chang-Qing Zhang MD PhD Cong-FengLuo MD PhD Zu-Bin Zhou MD and Bing-Fang Zeng
MDClin Orthop Relat Res 2009 March 467(3) 831ndash837 Total pts 32 The average healing time was 13 weeks (range 10ndash18 weeks)
for fractures using the MIPO technique and 156 weeks (range 10ndash20 weeks p = 00045) for fractures using the ORIF technique
The fracture healing time was shorter in the MIPO technique group than in the ORIF technique group which might be related to minimizing soft tissue trauma to the injured zone and preserving better blood supply around the fracture area
ADVANTAGE OF MIPPO OVER
ORIF
mipo orif
Smaller incision
Fracture site is undisturbed
Better callus formation
Blood supply to fracture fragments maintained
Larger incision
Fracture site explored
Callus formation is delayed
Blood supply is hampered
mipo orif
Low infection rate due to smaller incision and decrease soft tisuedamage
decreased need for bone grafting
High infection rate due to poor soft tissue handling over large incised wound
Bone grafting is required sometimes
conclusion
Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis(MIPO) of the distal tibia offers several theoretical advantages compared to classic open reduction and internal fixation A mechanically stable fracture-bridging osteosynthesis can be obtained without significant dissection and surgical trauma to the bone and surrounding soft tissues
MIPO has a high union rate and less complication rate
Thank you

MIPO technique
In this technique only the normal bone cortexes both proximal and distal to the fracture site are exposed for positioning the plate and inserting the screws while the fracture site is not explored so that osteogenic tissues surrounding the fracture are well protected and their blood supply is also well preserved
biomechanics
Mipo relies on relative stability rather than absolute rigid fixation because of which micromotion is produced at the fracture site and a larger and rapid callus formation occurs leading to rapid bone healing
Relative stability does not require accurate apposition of fragments as the gap are filled up by bridging callus
Indication of mipo in distal tibial
intraarticular or periarticular fractures which
are considered unsuitable for intramedullary nailing
They include
Communited fractures
low-grade open fractures of the distal tibia
displaced pilon fractures with sufficient medial soft-tissue coverage to allow articular reconstruction and percutaneous plating
unstable distal metaphyseal and diaphyseal fractures
Contra-indication
MIPO is contraindicated in situations where the medial soft tissue is compromised such as in severe open fractures or badly contused skin
If the bone is osteoporotic or comminution is so excessive that surgery cannot restore or stabilize the joint then other methods of treatment must be sought such as external fixator
In severely shattered pilon fractures when only choice is external fixator
Advantage of mipo
minimizes risk of soft tissue damage
preserve vascular supply to bone and soft tissue
decrease periosteum damage
have better and faster callus formation
have better healing and union rate
decrease complication of infection and re-fracture
decrease the use of supplementary bone grafting
IMPLANT CHOICE
Choice of implant could be
bullMetaphysealplate (broad or narrow)
bullPrecountoureddistal tibia locking plate
bullClowerleaf LCP
procedure
POSITIONING OF PATIENT
INCISION
anteromedial approach a 2ndash3 cm incision is made starting at the level of the tibial plafond and extending proximally along the medial surface of the distal tibia ORposteromedial incision along the
posterior border of medialmalleolus about 4ndash5 cm in length and slightly curved can beused
PRELIMINARY REDUCTION
REDUCTION COULD BE BY MANUAL TRACTION OR BY USE OF DISTRACTOR AND REDUCTION FORCEPS PERCUTANEOUSLY
PLATE INSERTION
PLATE COULD BE INSERTED WITH HELP OF INSERTION DEVICE OR WITH HELP OF LOCKING SLEEVE UNDER SUBMUSCULAR PLANE
PRELIMINARY PLATE STABILIZATION
BY USE OF K-WIRE FOR TEMPORARY FIXATION OF PLATE
PLATE FIXATION
A MINIMUM OF 6 CORTICES ON BOTH SIDE OF FRACTURE ARE USED AND INTERFRAGMENATRY COMPRESSION SCREW WHERE NEEDED
REVIEW OF WORK
THE VARIOUS STUDY DONE TO CHECK THE EFFECTIVENESS OF MIPO TECHNIQUE FOR DISTAL END TIBIA FRACTURES ARE AS FOLLOWS
REVIEW OF WORK
STUDY NO OF FRACTURE
FIXATION OUTCOME COMPLICATION
Ronga M et al2010
19 MIPO Union 18 (223 wks range 12-24)
Nonunion1 No malunion ( ge7deg deformity or ge1 cm LLD) Deep infection3
Ahmad MA et al 2010
18 MIPO Union 15 (212 wks)
Delayed union 3 Superficial wound infarction 1 Chronic wound infection 1 Implant failure 1
Ronga M Longo UG Maffulli N Minimally invasive locked plating of distal tibia fractures is safe and effective Clin Orthop Relat Res 2010
Ahmad MA Sivaraman A Zia A Rai A Patel AD Percutaneouslocking plates for fractures of the distal tibia Our experience and a review of the literature J Trauma 2010
HasenbohehlerE et al (2007)
32 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 29 ( 277 wks range 24ndash60)
Nonunion 2 No malunion (ge 5deg deformity or ge 1 cm LLD) Plate bending (18deg) 1 Pseudoarthrosis 2
Hazarika S et al (2006)
20 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 18 ( 285 wks range 9ndash68)
Nonunion 2 Delayed wound break down 2 Wound infection 1 Implant failure 1 Secondary procedure 2
Hasenboehler E RikliD Babst R Locking compression plate with minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in diaphyseal and distal tibial fracture a retrospective study of 32 patients Injury 2007
Hazarika S Chakravarthy J Cooper J Minimally invasive locking plate osteosynthesis for fractures of the distal tibia-results in 20 patients Injury 2006
Bahari S et al (2007)
42 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 42 (224 wks)
No malunionSuperficial wound infection 2 Deep infection 1 Implant failure 1
Collinge C et al(2010)
38 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 38 (21 wks range 9ndash48)
Malunion ( ge 5degdeformity) 1 Secondary procedure 3
Mushtaq A et al (2009)
21 (open fracture 4)
MIPO Union 21( 55 months range 3ndash13)
Delayed union 1 Non union 1 Wound infection 2 Secondary procedure 2
Bahari S LenehanB Khan H Mcelwain JP Minimally invasive percutaneous plate fixation of distal tibia fractures Acta Orthop Belg2007
Collinge C Protzman R Outcomes of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis for metaphyseal distal tibia fractures J OrthopTrauma 2010
Mushtaq A Shahid R AsifM Maqsood M Distal tibialfracture fixation with locking compression plate (LCP) using the minimally invasive percutaneousosteosynthesis (MIPO) technique Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg 2009
Lau TW et al (2008)
48 (open fracture 9)
MIPO Union 47 ( 187 wks range 12-44 wks)
Delayed union 5 Wound infection 8 Secondary procedure1
Gupta RK et al(2010)
80 (open fracture19)
MIPO Union 77 (19 wks range 16-32)
Delayed union 7 Non union 3 Malunion (ge 5degdeformity or ge 1 cm LLD) 2 Wound infection1 Wound breakdown 2 Secondary procedure 2
Lau TW Leung F Chan CF Chow SP Wound complication of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in distal tibia fractures Inter Orthop 2008
Gupta RK RohillaRK Sangwan K Singh V Walia S Locking plate fixation in distal metaphysealtibial fractures series of 79 patients Inter Orthop 2010
Shreshta et al(2011)
20 MIPO Union 20 (185 wks range 14-28)
Delayed union 1 No malunion (ge 5deg deformity or ge 1 cm LLD) Superficial wound infection 2 Deep infection 1 Secondary procedure 1
Oog Jin et al 10 MIPO Union10(21 wksrange17-28)
no non-union no angular deformity gt 5deg shortening gt 10 mm no infection
Shrestha D Acharya BM Shrestha PM Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis with locking compression plate for distal diametaphyseal tibia fracture Kathmandu Univ Med J 2011
hong et al
Fractures of the Distal Tibia Treated with PolyaxialLocking Plating
Hong Gao MD Chang-Qing Zhang MD PhD Cong-FengLuo MD PhD Zu-Bin Zhou MD and Bing-Fang Zeng
MDClin Orthop Relat Res 2009 March 467(3) 831ndash837 Total pts 32 The average healing time was 13 weeks (range 10ndash18 weeks)
for fractures using the MIPO technique and 156 weeks (range 10ndash20 weeks p = 00045) for fractures using the ORIF technique
The fracture healing time was shorter in the MIPO technique group than in the ORIF technique group which might be related to minimizing soft tissue trauma to the injured zone and preserving better blood supply around the fracture area
ADVANTAGE OF MIPPO OVER
ORIF
mipo orif
Smaller incision
Fracture site is undisturbed
Better callus formation
Blood supply to fracture fragments maintained
Larger incision
Fracture site explored
Callus formation is delayed
Blood supply is hampered
mipo orif
Low infection rate due to smaller incision and decrease soft tisuedamage
decreased need for bone grafting
High infection rate due to poor soft tissue handling over large incised wound
Bone grafting is required sometimes
conclusion
Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis(MIPO) of the distal tibia offers several theoretical advantages compared to classic open reduction and internal fixation A mechanically stable fracture-bridging osteosynthesis can be obtained without significant dissection and surgical trauma to the bone and surrounding soft tissues
MIPO has a high union rate and less complication rate
Thank you

biomechanics
Mipo relies on relative stability rather than absolute rigid fixation because of which micromotion is produced at the fracture site and a larger and rapid callus formation occurs leading to rapid bone healing
Relative stability does not require accurate apposition of fragments as the gap are filled up by bridging callus
Indication of mipo in distal tibial
intraarticular or periarticular fractures which
are considered unsuitable for intramedullary nailing
They include
Communited fractures
low-grade open fractures of the distal tibia
displaced pilon fractures with sufficient medial soft-tissue coverage to allow articular reconstruction and percutaneous plating
unstable distal metaphyseal and diaphyseal fractures
Contra-indication
MIPO is contraindicated in situations where the medial soft tissue is compromised such as in severe open fractures or badly contused skin
If the bone is osteoporotic or comminution is so excessive that surgery cannot restore or stabilize the joint then other methods of treatment must be sought such as external fixator
In severely shattered pilon fractures when only choice is external fixator
Advantage of mipo
minimizes risk of soft tissue damage
preserve vascular supply to bone and soft tissue
decrease periosteum damage
have better and faster callus formation
have better healing and union rate
decrease complication of infection and re-fracture
decrease the use of supplementary bone grafting
IMPLANT CHOICE
Choice of implant could be
bullMetaphysealplate (broad or narrow)
bullPrecountoureddistal tibia locking plate
bullClowerleaf LCP
procedure
POSITIONING OF PATIENT
INCISION
anteromedial approach a 2ndash3 cm incision is made starting at the level of the tibial plafond and extending proximally along the medial surface of the distal tibia ORposteromedial incision along the
posterior border of medialmalleolus about 4ndash5 cm in length and slightly curved can beused
PRELIMINARY REDUCTION
REDUCTION COULD BE BY MANUAL TRACTION OR BY USE OF DISTRACTOR AND REDUCTION FORCEPS PERCUTANEOUSLY
PLATE INSERTION
PLATE COULD BE INSERTED WITH HELP OF INSERTION DEVICE OR WITH HELP OF LOCKING SLEEVE UNDER SUBMUSCULAR PLANE
PRELIMINARY PLATE STABILIZATION
BY USE OF K-WIRE FOR TEMPORARY FIXATION OF PLATE
PLATE FIXATION
A MINIMUM OF 6 CORTICES ON BOTH SIDE OF FRACTURE ARE USED AND INTERFRAGMENATRY COMPRESSION SCREW WHERE NEEDED
REVIEW OF WORK
THE VARIOUS STUDY DONE TO CHECK THE EFFECTIVENESS OF MIPO TECHNIQUE FOR DISTAL END TIBIA FRACTURES ARE AS FOLLOWS
REVIEW OF WORK
STUDY NO OF FRACTURE
FIXATION OUTCOME COMPLICATION
Ronga M et al2010
19 MIPO Union 18 (223 wks range 12-24)
Nonunion1 No malunion ( ge7deg deformity or ge1 cm LLD) Deep infection3
Ahmad MA et al 2010
18 MIPO Union 15 (212 wks)
Delayed union 3 Superficial wound infarction 1 Chronic wound infection 1 Implant failure 1
Ronga M Longo UG Maffulli N Minimally invasive locked plating of distal tibia fractures is safe and effective Clin Orthop Relat Res 2010
Ahmad MA Sivaraman A Zia A Rai A Patel AD Percutaneouslocking plates for fractures of the distal tibia Our experience and a review of the literature J Trauma 2010
HasenbohehlerE et al (2007)
32 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 29 ( 277 wks range 24ndash60)
Nonunion 2 No malunion (ge 5deg deformity or ge 1 cm LLD) Plate bending (18deg) 1 Pseudoarthrosis 2
Hazarika S et al (2006)
20 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 18 ( 285 wks range 9ndash68)
Nonunion 2 Delayed wound break down 2 Wound infection 1 Implant failure 1 Secondary procedure 2
Hasenboehler E RikliD Babst R Locking compression plate with minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in diaphyseal and distal tibial fracture a retrospective study of 32 patients Injury 2007
Hazarika S Chakravarthy J Cooper J Minimally invasive locking plate osteosynthesis for fractures of the distal tibia-results in 20 patients Injury 2006
Bahari S et al (2007)
42 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 42 (224 wks)
No malunionSuperficial wound infection 2 Deep infection 1 Implant failure 1
Collinge C et al(2010)
38 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 38 (21 wks range 9ndash48)
Malunion ( ge 5degdeformity) 1 Secondary procedure 3
Mushtaq A et al (2009)
21 (open fracture 4)
MIPO Union 21( 55 months range 3ndash13)
Delayed union 1 Non union 1 Wound infection 2 Secondary procedure 2
Bahari S LenehanB Khan H Mcelwain JP Minimally invasive percutaneous plate fixation of distal tibia fractures Acta Orthop Belg2007
Collinge C Protzman R Outcomes of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis for metaphyseal distal tibia fractures J OrthopTrauma 2010
Mushtaq A Shahid R AsifM Maqsood M Distal tibialfracture fixation with locking compression plate (LCP) using the minimally invasive percutaneousosteosynthesis (MIPO) technique Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg 2009
Lau TW et al (2008)
48 (open fracture 9)
MIPO Union 47 ( 187 wks range 12-44 wks)
Delayed union 5 Wound infection 8 Secondary procedure1
Gupta RK et al(2010)
80 (open fracture19)
MIPO Union 77 (19 wks range 16-32)
Delayed union 7 Non union 3 Malunion (ge 5degdeformity or ge 1 cm LLD) 2 Wound infection1 Wound breakdown 2 Secondary procedure 2
Lau TW Leung F Chan CF Chow SP Wound complication of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in distal tibia fractures Inter Orthop 2008
Gupta RK RohillaRK Sangwan K Singh V Walia S Locking plate fixation in distal metaphysealtibial fractures series of 79 patients Inter Orthop 2010
Shreshta et al(2011)
20 MIPO Union 20 (185 wks range 14-28)
Delayed union 1 No malunion (ge 5deg deformity or ge 1 cm LLD) Superficial wound infection 2 Deep infection 1 Secondary procedure 1
Oog Jin et al 10 MIPO Union10(21 wksrange17-28)
no non-union no angular deformity gt 5deg shortening gt 10 mm no infection
Shrestha D Acharya BM Shrestha PM Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis with locking compression plate for distal diametaphyseal tibia fracture Kathmandu Univ Med J 2011
hong et al
Fractures of the Distal Tibia Treated with PolyaxialLocking Plating
Hong Gao MD Chang-Qing Zhang MD PhD Cong-FengLuo MD PhD Zu-Bin Zhou MD and Bing-Fang Zeng
MDClin Orthop Relat Res 2009 March 467(3) 831ndash837 Total pts 32 The average healing time was 13 weeks (range 10ndash18 weeks)
for fractures using the MIPO technique and 156 weeks (range 10ndash20 weeks p = 00045) for fractures using the ORIF technique
The fracture healing time was shorter in the MIPO technique group than in the ORIF technique group which might be related to minimizing soft tissue trauma to the injured zone and preserving better blood supply around the fracture area
ADVANTAGE OF MIPPO OVER
ORIF
mipo orif
Smaller incision
Fracture site is undisturbed
Better callus formation
Blood supply to fracture fragments maintained
Larger incision
Fracture site explored
Callus formation is delayed
Blood supply is hampered
mipo orif
Low infection rate due to smaller incision and decrease soft tisuedamage
decreased need for bone grafting
High infection rate due to poor soft tissue handling over large incised wound
Bone grafting is required sometimes
conclusion
Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis(MIPO) of the distal tibia offers several theoretical advantages compared to classic open reduction and internal fixation A mechanically stable fracture-bridging osteosynthesis can be obtained without significant dissection and surgical trauma to the bone and surrounding soft tissues
MIPO has a high union rate and less complication rate
Thank you

Indication of mipo in distal tibial
intraarticular or periarticular fractures which
are considered unsuitable for intramedullary nailing
They include
Communited fractures
low-grade open fractures of the distal tibia
displaced pilon fractures with sufficient medial soft-tissue coverage to allow articular reconstruction and percutaneous plating
unstable distal metaphyseal and diaphyseal fractures
Contra-indication
MIPO is contraindicated in situations where the medial soft tissue is compromised such as in severe open fractures or badly contused skin
If the bone is osteoporotic or comminution is so excessive that surgery cannot restore or stabilize the joint then other methods of treatment must be sought such as external fixator
In severely shattered pilon fractures when only choice is external fixator
Advantage of mipo
minimizes risk of soft tissue damage
preserve vascular supply to bone and soft tissue
decrease periosteum damage
have better and faster callus formation
have better healing and union rate
decrease complication of infection and re-fracture
decrease the use of supplementary bone grafting
IMPLANT CHOICE
Choice of implant could be
bullMetaphysealplate (broad or narrow)
bullPrecountoureddistal tibia locking plate
bullClowerleaf LCP
procedure
POSITIONING OF PATIENT
INCISION
anteromedial approach a 2ndash3 cm incision is made starting at the level of the tibial plafond and extending proximally along the medial surface of the distal tibia ORposteromedial incision along the
posterior border of medialmalleolus about 4ndash5 cm in length and slightly curved can beused
PRELIMINARY REDUCTION
REDUCTION COULD BE BY MANUAL TRACTION OR BY USE OF DISTRACTOR AND REDUCTION FORCEPS PERCUTANEOUSLY
PLATE INSERTION
PLATE COULD BE INSERTED WITH HELP OF INSERTION DEVICE OR WITH HELP OF LOCKING SLEEVE UNDER SUBMUSCULAR PLANE
PRELIMINARY PLATE STABILIZATION
BY USE OF K-WIRE FOR TEMPORARY FIXATION OF PLATE
PLATE FIXATION
A MINIMUM OF 6 CORTICES ON BOTH SIDE OF FRACTURE ARE USED AND INTERFRAGMENATRY COMPRESSION SCREW WHERE NEEDED
REVIEW OF WORK
THE VARIOUS STUDY DONE TO CHECK THE EFFECTIVENESS OF MIPO TECHNIQUE FOR DISTAL END TIBIA FRACTURES ARE AS FOLLOWS
REVIEW OF WORK
STUDY NO OF FRACTURE
FIXATION OUTCOME COMPLICATION
Ronga M et al2010
19 MIPO Union 18 (223 wks range 12-24)
Nonunion1 No malunion ( ge7deg deformity or ge1 cm LLD) Deep infection3
Ahmad MA et al 2010
18 MIPO Union 15 (212 wks)
Delayed union 3 Superficial wound infarction 1 Chronic wound infection 1 Implant failure 1
Ronga M Longo UG Maffulli N Minimally invasive locked plating of distal tibia fractures is safe and effective Clin Orthop Relat Res 2010
Ahmad MA Sivaraman A Zia A Rai A Patel AD Percutaneouslocking plates for fractures of the distal tibia Our experience and a review of the literature J Trauma 2010
HasenbohehlerE et al (2007)
32 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 29 ( 277 wks range 24ndash60)
Nonunion 2 No malunion (ge 5deg deformity or ge 1 cm LLD) Plate bending (18deg) 1 Pseudoarthrosis 2
Hazarika S et al (2006)
20 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 18 ( 285 wks range 9ndash68)
Nonunion 2 Delayed wound break down 2 Wound infection 1 Implant failure 1 Secondary procedure 2
Hasenboehler E RikliD Babst R Locking compression plate with minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in diaphyseal and distal tibial fracture a retrospective study of 32 patients Injury 2007
Hazarika S Chakravarthy J Cooper J Minimally invasive locking plate osteosynthesis for fractures of the distal tibia-results in 20 patients Injury 2006
Bahari S et al (2007)
42 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 42 (224 wks)
No malunionSuperficial wound infection 2 Deep infection 1 Implant failure 1
Collinge C et al(2010)
38 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 38 (21 wks range 9ndash48)
Malunion ( ge 5degdeformity) 1 Secondary procedure 3
Mushtaq A et al (2009)
21 (open fracture 4)
MIPO Union 21( 55 months range 3ndash13)
Delayed union 1 Non union 1 Wound infection 2 Secondary procedure 2
Bahari S LenehanB Khan H Mcelwain JP Minimally invasive percutaneous plate fixation of distal tibia fractures Acta Orthop Belg2007
Collinge C Protzman R Outcomes of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis for metaphyseal distal tibia fractures J OrthopTrauma 2010
Mushtaq A Shahid R AsifM Maqsood M Distal tibialfracture fixation with locking compression plate (LCP) using the minimally invasive percutaneousosteosynthesis (MIPO) technique Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg 2009
Lau TW et al (2008)
48 (open fracture 9)
MIPO Union 47 ( 187 wks range 12-44 wks)
Delayed union 5 Wound infection 8 Secondary procedure1
Gupta RK et al(2010)
80 (open fracture19)
MIPO Union 77 (19 wks range 16-32)
Delayed union 7 Non union 3 Malunion (ge 5degdeformity or ge 1 cm LLD) 2 Wound infection1 Wound breakdown 2 Secondary procedure 2
Lau TW Leung F Chan CF Chow SP Wound complication of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in distal tibia fractures Inter Orthop 2008
Gupta RK RohillaRK Sangwan K Singh V Walia S Locking plate fixation in distal metaphysealtibial fractures series of 79 patients Inter Orthop 2010
Shreshta et al(2011)
20 MIPO Union 20 (185 wks range 14-28)
Delayed union 1 No malunion (ge 5deg deformity or ge 1 cm LLD) Superficial wound infection 2 Deep infection 1 Secondary procedure 1
Oog Jin et al 10 MIPO Union10(21 wksrange17-28)
no non-union no angular deformity gt 5deg shortening gt 10 mm no infection
Shrestha D Acharya BM Shrestha PM Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis with locking compression plate for distal diametaphyseal tibia fracture Kathmandu Univ Med J 2011
hong et al
Fractures of the Distal Tibia Treated with PolyaxialLocking Plating
Hong Gao MD Chang-Qing Zhang MD PhD Cong-FengLuo MD PhD Zu-Bin Zhou MD and Bing-Fang Zeng
MDClin Orthop Relat Res 2009 March 467(3) 831ndash837 Total pts 32 The average healing time was 13 weeks (range 10ndash18 weeks)
for fractures using the MIPO technique and 156 weeks (range 10ndash20 weeks p = 00045) for fractures using the ORIF technique
The fracture healing time was shorter in the MIPO technique group than in the ORIF technique group which might be related to minimizing soft tissue trauma to the injured zone and preserving better blood supply around the fracture area
ADVANTAGE OF MIPPO OVER
ORIF
mipo orif
Smaller incision
Fracture site is undisturbed
Better callus formation
Blood supply to fracture fragments maintained
Larger incision
Fracture site explored
Callus formation is delayed
Blood supply is hampered
mipo orif
Low infection rate due to smaller incision and decrease soft tisuedamage
decreased need for bone grafting
High infection rate due to poor soft tissue handling over large incised wound
Bone grafting is required sometimes
conclusion
Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis(MIPO) of the distal tibia offers several theoretical advantages compared to classic open reduction and internal fixation A mechanically stable fracture-bridging osteosynthesis can be obtained without significant dissection and surgical trauma to the bone and surrounding soft tissues
MIPO has a high union rate and less complication rate
Thank you

Contra-indication
MIPO is contraindicated in situations where the medial soft tissue is compromised such as in severe open fractures or badly contused skin
If the bone is osteoporotic or comminution is so excessive that surgery cannot restore or stabilize the joint then other methods of treatment must be sought such as external fixator
In severely shattered pilon fractures when only choice is external fixator
Advantage of mipo
minimizes risk of soft tissue damage
preserve vascular supply to bone and soft tissue
decrease periosteum damage
have better and faster callus formation
have better healing and union rate
decrease complication of infection and re-fracture
decrease the use of supplementary bone grafting
IMPLANT CHOICE
Choice of implant could be
bullMetaphysealplate (broad or narrow)
bullPrecountoureddistal tibia locking plate
bullClowerleaf LCP
procedure
POSITIONING OF PATIENT
INCISION
anteromedial approach a 2ndash3 cm incision is made starting at the level of the tibial plafond and extending proximally along the medial surface of the distal tibia ORposteromedial incision along the
posterior border of medialmalleolus about 4ndash5 cm in length and slightly curved can beused
PRELIMINARY REDUCTION
REDUCTION COULD BE BY MANUAL TRACTION OR BY USE OF DISTRACTOR AND REDUCTION FORCEPS PERCUTANEOUSLY
PLATE INSERTION
PLATE COULD BE INSERTED WITH HELP OF INSERTION DEVICE OR WITH HELP OF LOCKING SLEEVE UNDER SUBMUSCULAR PLANE
PRELIMINARY PLATE STABILIZATION
BY USE OF K-WIRE FOR TEMPORARY FIXATION OF PLATE
PLATE FIXATION
A MINIMUM OF 6 CORTICES ON BOTH SIDE OF FRACTURE ARE USED AND INTERFRAGMENATRY COMPRESSION SCREW WHERE NEEDED
REVIEW OF WORK
THE VARIOUS STUDY DONE TO CHECK THE EFFECTIVENESS OF MIPO TECHNIQUE FOR DISTAL END TIBIA FRACTURES ARE AS FOLLOWS
REVIEW OF WORK
STUDY NO OF FRACTURE
FIXATION OUTCOME COMPLICATION
Ronga M et al2010
19 MIPO Union 18 (223 wks range 12-24)
Nonunion1 No malunion ( ge7deg deformity or ge1 cm LLD) Deep infection3
Ahmad MA et al 2010
18 MIPO Union 15 (212 wks)
Delayed union 3 Superficial wound infarction 1 Chronic wound infection 1 Implant failure 1
Ronga M Longo UG Maffulli N Minimally invasive locked plating of distal tibia fractures is safe and effective Clin Orthop Relat Res 2010
Ahmad MA Sivaraman A Zia A Rai A Patel AD Percutaneouslocking plates for fractures of the distal tibia Our experience and a review of the literature J Trauma 2010
HasenbohehlerE et al (2007)
32 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 29 ( 277 wks range 24ndash60)
Nonunion 2 No malunion (ge 5deg deformity or ge 1 cm LLD) Plate bending (18deg) 1 Pseudoarthrosis 2
Hazarika S et al (2006)
20 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 18 ( 285 wks range 9ndash68)
Nonunion 2 Delayed wound break down 2 Wound infection 1 Implant failure 1 Secondary procedure 2
Hasenboehler E RikliD Babst R Locking compression plate with minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in diaphyseal and distal tibial fracture a retrospective study of 32 patients Injury 2007
Hazarika S Chakravarthy J Cooper J Minimally invasive locking plate osteosynthesis for fractures of the distal tibia-results in 20 patients Injury 2006
Bahari S et al (2007)
42 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 42 (224 wks)
No malunionSuperficial wound infection 2 Deep infection 1 Implant failure 1
Collinge C et al(2010)
38 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 38 (21 wks range 9ndash48)
Malunion ( ge 5degdeformity) 1 Secondary procedure 3
Mushtaq A et al (2009)
21 (open fracture 4)
MIPO Union 21( 55 months range 3ndash13)
Delayed union 1 Non union 1 Wound infection 2 Secondary procedure 2
Bahari S LenehanB Khan H Mcelwain JP Minimally invasive percutaneous plate fixation of distal tibia fractures Acta Orthop Belg2007
Collinge C Protzman R Outcomes of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis for metaphyseal distal tibia fractures J OrthopTrauma 2010
Mushtaq A Shahid R AsifM Maqsood M Distal tibialfracture fixation with locking compression plate (LCP) using the minimally invasive percutaneousosteosynthesis (MIPO) technique Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg 2009
Lau TW et al (2008)
48 (open fracture 9)
MIPO Union 47 ( 187 wks range 12-44 wks)
Delayed union 5 Wound infection 8 Secondary procedure1
Gupta RK et al(2010)
80 (open fracture19)
MIPO Union 77 (19 wks range 16-32)
Delayed union 7 Non union 3 Malunion (ge 5degdeformity or ge 1 cm LLD) 2 Wound infection1 Wound breakdown 2 Secondary procedure 2
Lau TW Leung F Chan CF Chow SP Wound complication of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in distal tibia fractures Inter Orthop 2008
Gupta RK RohillaRK Sangwan K Singh V Walia S Locking plate fixation in distal metaphysealtibial fractures series of 79 patients Inter Orthop 2010
Shreshta et al(2011)
20 MIPO Union 20 (185 wks range 14-28)
Delayed union 1 No malunion (ge 5deg deformity or ge 1 cm LLD) Superficial wound infection 2 Deep infection 1 Secondary procedure 1
Oog Jin et al 10 MIPO Union10(21 wksrange17-28)
no non-union no angular deformity gt 5deg shortening gt 10 mm no infection
Shrestha D Acharya BM Shrestha PM Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis with locking compression plate for distal diametaphyseal tibia fracture Kathmandu Univ Med J 2011
hong et al
Fractures of the Distal Tibia Treated with PolyaxialLocking Plating
Hong Gao MD Chang-Qing Zhang MD PhD Cong-FengLuo MD PhD Zu-Bin Zhou MD and Bing-Fang Zeng
MDClin Orthop Relat Res 2009 March 467(3) 831ndash837 Total pts 32 The average healing time was 13 weeks (range 10ndash18 weeks)
for fractures using the MIPO technique and 156 weeks (range 10ndash20 weeks p = 00045) for fractures using the ORIF technique
The fracture healing time was shorter in the MIPO technique group than in the ORIF technique group which might be related to minimizing soft tissue trauma to the injured zone and preserving better blood supply around the fracture area
ADVANTAGE OF MIPPO OVER
ORIF
mipo orif
Smaller incision
Fracture site is undisturbed
Better callus formation
Blood supply to fracture fragments maintained
Larger incision
Fracture site explored
Callus formation is delayed
Blood supply is hampered
mipo orif
Low infection rate due to smaller incision and decrease soft tisuedamage
decreased need for bone grafting
High infection rate due to poor soft tissue handling over large incised wound
Bone grafting is required sometimes
conclusion
Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis(MIPO) of the distal tibia offers several theoretical advantages compared to classic open reduction and internal fixation A mechanically stable fracture-bridging osteosynthesis can be obtained without significant dissection and surgical trauma to the bone and surrounding soft tissues
MIPO has a high union rate and less complication rate
Thank you

Advantage of mipo
minimizes risk of soft tissue damage
preserve vascular supply to bone and soft tissue
decrease periosteum damage
have better and faster callus formation
have better healing and union rate
decrease complication of infection and re-fracture
decrease the use of supplementary bone grafting
IMPLANT CHOICE
Choice of implant could be
bullMetaphysealplate (broad or narrow)
bullPrecountoureddistal tibia locking plate
bullClowerleaf LCP
procedure
POSITIONING OF PATIENT
INCISION
anteromedial approach a 2ndash3 cm incision is made starting at the level of the tibial plafond and extending proximally along the medial surface of the distal tibia ORposteromedial incision along the
posterior border of medialmalleolus about 4ndash5 cm in length and slightly curved can beused
PRELIMINARY REDUCTION
REDUCTION COULD BE BY MANUAL TRACTION OR BY USE OF DISTRACTOR AND REDUCTION FORCEPS PERCUTANEOUSLY
PLATE INSERTION
PLATE COULD BE INSERTED WITH HELP OF INSERTION DEVICE OR WITH HELP OF LOCKING SLEEVE UNDER SUBMUSCULAR PLANE
PRELIMINARY PLATE STABILIZATION
BY USE OF K-WIRE FOR TEMPORARY FIXATION OF PLATE
PLATE FIXATION
A MINIMUM OF 6 CORTICES ON BOTH SIDE OF FRACTURE ARE USED AND INTERFRAGMENATRY COMPRESSION SCREW WHERE NEEDED
REVIEW OF WORK
THE VARIOUS STUDY DONE TO CHECK THE EFFECTIVENESS OF MIPO TECHNIQUE FOR DISTAL END TIBIA FRACTURES ARE AS FOLLOWS
REVIEW OF WORK
STUDY NO OF FRACTURE
FIXATION OUTCOME COMPLICATION
Ronga M et al2010
19 MIPO Union 18 (223 wks range 12-24)
Nonunion1 No malunion ( ge7deg deformity or ge1 cm LLD) Deep infection3
Ahmad MA et al 2010
18 MIPO Union 15 (212 wks)
Delayed union 3 Superficial wound infarction 1 Chronic wound infection 1 Implant failure 1
Ronga M Longo UG Maffulli N Minimally invasive locked plating of distal tibia fractures is safe and effective Clin Orthop Relat Res 2010
Ahmad MA Sivaraman A Zia A Rai A Patel AD Percutaneouslocking plates for fractures of the distal tibia Our experience and a review of the literature J Trauma 2010
HasenbohehlerE et al (2007)
32 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 29 ( 277 wks range 24ndash60)
Nonunion 2 No malunion (ge 5deg deformity or ge 1 cm LLD) Plate bending (18deg) 1 Pseudoarthrosis 2
Hazarika S et al (2006)
20 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 18 ( 285 wks range 9ndash68)
Nonunion 2 Delayed wound break down 2 Wound infection 1 Implant failure 1 Secondary procedure 2
Hasenboehler E RikliD Babst R Locking compression plate with minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in diaphyseal and distal tibial fracture a retrospective study of 32 patients Injury 2007
Hazarika S Chakravarthy J Cooper J Minimally invasive locking plate osteosynthesis for fractures of the distal tibia-results in 20 patients Injury 2006
Bahari S et al (2007)
42 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 42 (224 wks)
No malunionSuperficial wound infection 2 Deep infection 1 Implant failure 1
Collinge C et al(2010)
38 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 38 (21 wks range 9ndash48)
Malunion ( ge 5degdeformity) 1 Secondary procedure 3
Mushtaq A et al (2009)
21 (open fracture 4)
MIPO Union 21( 55 months range 3ndash13)
Delayed union 1 Non union 1 Wound infection 2 Secondary procedure 2
Bahari S LenehanB Khan H Mcelwain JP Minimally invasive percutaneous plate fixation of distal tibia fractures Acta Orthop Belg2007
Collinge C Protzman R Outcomes of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis for metaphyseal distal tibia fractures J OrthopTrauma 2010
Mushtaq A Shahid R AsifM Maqsood M Distal tibialfracture fixation with locking compression plate (LCP) using the minimally invasive percutaneousosteosynthesis (MIPO) technique Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg 2009
Lau TW et al (2008)
48 (open fracture 9)
MIPO Union 47 ( 187 wks range 12-44 wks)
Delayed union 5 Wound infection 8 Secondary procedure1
Gupta RK et al(2010)
80 (open fracture19)
MIPO Union 77 (19 wks range 16-32)
Delayed union 7 Non union 3 Malunion (ge 5degdeformity or ge 1 cm LLD) 2 Wound infection1 Wound breakdown 2 Secondary procedure 2
Lau TW Leung F Chan CF Chow SP Wound complication of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in distal tibia fractures Inter Orthop 2008
Gupta RK RohillaRK Sangwan K Singh V Walia S Locking plate fixation in distal metaphysealtibial fractures series of 79 patients Inter Orthop 2010
Shreshta et al(2011)
20 MIPO Union 20 (185 wks range 14-28)
Delayed union 1 No malunion (ge 5deg deformity or ge 1 cm LLD) Superficial wound infection 2 Deep infection 1 Secondary procedure 1
Oog Jin et al 10 MIPO Union10(21 wksrange17-28)
no non-union no angular deformity gt 5deg shortening gt 10 mm no infection
Shrestha D Acharya BM Shrestha PM Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis with locking compression plate for distal diametaphyseal tibia fracture Kathmandu Univ Med J 2011
hong et al
Fractures of the Distal Tibia Treated with PolyaxialLocking Plating
Hong Gao MD Chang-Qing Zhang MD PhD Cong-FengLuo MD PhD Zu-Bin Zhou MD and Bing-Fang Zeng
MDClin Orthop Relat Res 2009 March 467(3) 831ndash837 Total pts 32 The average healing time was 13 weeks (range 10ndash18 weeks)
for fractures using the MIPO technique and 156 weeks (range 10ndash20 weeks p = 00045) for fractures using the ORIF technique
The fracture healing time was shorter in the MIPO technique group than in the ORIF technique group which might be related to minimizing soft tissue trauma to the injured zone and preserving better blood supply around the fracture area
ADVANTAGE OF MIPPO OVER
ORIF
mipo orif
Smaller incision
Fracture site is undisturbed
Better callus formation
Blood supply to fracture fragments maintained
Larger incision
Fracture site explored
Callus formation is delayed
Blood supply is hampered
mipo orif
Low infection rate due to smaller incision and decrease soft tisuedamage
decreased need for bone grafting
High infection rate due to poor soft tissue handling over large incised wound
Bone grafting is required sometimes
conclusion
Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis(MIPO) of the distal tibia offers several theoretical advantages compared to classic open reduction and internal fixation A mechanically stable fracture-bridging osteosynthesis can be obtained without significant dissection and surgical trauma to the bone and surrounding soft tissues
MIPO has a high union rate and less complication rate
Thank you

IMPLANT CHOICE
Choice of implant could be
bullMetaphysealplate (broad or narrow)
bullPrecountoureddistal tibia locking plate
bullClowerleaf LCP
procedure
POSITIONING OF PATIENT
INCISION
anteromedial approach a 2ndash3 cm incision is made starting at the level of the tibial plafond and extending proximally along the medial surface of the distal tibia ORposteromedial incision along the
posterior border of medialmalleolus about 4ndash5 cm in length and slightly curved can beused
PRELIMINARY REDUCTION
REDUCTION COULD BE BY MANUAL TRACTION OR BY USE OF DISTRACTOR AND REDUCTION FORCEPS PERCUTANEOUSLY
PLATE INSERTION
PLATE COULD BE INSERTED WITH HELP OF INSERTION DEVICE OR WITH HELP OF LOCKING SLEEVE UNDER SUBMUSCULAR PLANE
PRELIMINARY PLATE STABILIZATION
BY USE OF K-WIRE FOR TEMPORARY FIXATION OF PLATE
PLATE FIXATION
A MINIMUM OF 6 CORTICES ON BOTH SIDE OF FRACTURE ARE USED AND INTERFRAGMENATRY COMPRESSION SCREW WHERE NEEDED
REVIEW OF WORK
THE VARIOUS STUDY DONE TO CHECK THE EFFECTIVENESS OF MIPO TECHNIQUE FOR DISTAL END TIBIA FRACTURES ARE AS FOLLOWS
REVIEW OF WORK
STUDY NO OF FRACTURE
FIXATION OUTCOME COMPLICATION
Ronga M et al2010
19 MIPO Union 18 (223 wks range 12-24)
Nonunion1 No malunion ( ge7deg deformity or ge1 cm LLD) Deep infection3
Ahmad MA et al 2010
18 MIPO Union 15 (212 wks)
Delayed union 3 Superficial wound infarction 1 Chronic wound infection 1 Implant failure 1
Ronga M Longo UG Maffulli N Minimally invasive locked plating of distal tibia fractures is safe and effective Clin Orthop Relat Res 2010
Ahmad MA Sivaraman A Zia A Rai A Patel AD Percutaneouslocking plates for fractures of the distal tibia Our experience and a review of the literature J Trauma 2010
HasenbohehlerE et al (2007)
32 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 29 ( 277 wks range 24ndash60)
Nonunion 2 No malunion (ge 5deg deformity or ge 1 cm LLD) Plate bending (18deg) 1 Pseudoarthrosis 2
Hazarika S et al (2006)
20 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 18 ( 285 wks range 9ndash68)
Nonunion 2 Delayed wound break down 2 Wound infection 1 Implant failure 1 Secondary procedure 2
Hasenboehler E RikliD Babst R Locking compression plate with minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in diaphyseal and distal tibial fracture a retrospective study of 32 patients Injury 2007
Hazarika S Chakravarthy J Cooper J Minimally invasive locking plate osteosynthesis for fractures of the distal tibia-results in 20 patients Injury 2006
Bahari S et al (2007)
42 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 42 (224 wks)
No malunionSuperficial wound infection 2 Deep infection 1 Implant failure 1
Collinge C et al(2010)
38 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 38 (21 wks range 9ndash48)
Malunion ( ge 5degdeformity) 1 Secondary procedure 3
Mushtaq A et al (2009)
21 (open fracture 4)
MIPO Union 21( 55 months range 3ndash13)
Delayed union 1 Non union 1 Wound infection 2 Secondary procedure 2
Bahari S LenehanB Khan H Mcelwain JP Minimally invasive percutaneous plate fixation of distal tibia fractures Acta Orthop Belg2007
Collinge C Protzman R Outcomes of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis for metaphyseal distal tibia fractures J OrthopTrauma 2010
Mushtaq A Shahid R AsifM Maqsood M Distal tibialfracture fixation with locking compression plate (LCP) using the minimally invasive percutaneousosteosynthesis (MIPO) technique Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg 2009
Lau TW et al (2008)
48 (open fracture 9)
MIPO Union 47 ( 187 wks range 12-44 wks)
Delayed union 5 Wound infection 8 Secondary procedure1
Gupta RK et al(2010)
80 (open fracture19)
MIPO Union 77 (19 wks range 16-32)
Delayed union 7 Non union 3 Malunion (ge 5degdeformity or ge 1 cm LLD) 2 Wound infection1 Wound breakdown 2 Secondary procedure 2
Lau TW Leung F Chan CF Chow SP Wound complication of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in distal tibia fractures Inter Orthop 2008
Gupta RK RohillaRK Sangwan K Singh V Walia S Locking plate fixation in distal metaphysealtibial fractures series of 79 patients Inter Orthop 2010
Shreshta et al(2011)
20 MIPO Union 20 (185 wks range 14-28)
Delayed union 1 No malunion (ge 5deg deformity or ge 1 cm LLD) Superficial wound infection 2 Deep infection 1 Secondary procedure 1
Oog Jin et al 10 MIPO Union10(21 wksrange17-28)
no non-union no angular deformity gt 5deg shortening gt 10 mm no infection
Shrestha D Acharya BM Shrestha PM Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis with locking compression plate for distal diametaphyseal tibia fracture Kathmandu Univ Med J 2011
hong et al
Fractures of the Distal Tibia Treated with PolyaxialLocking Plating
Hong Gao MD Chang-Qing Zhang MD PhD Cong-FengLuo MD PhD Zu-Bin Zhou MD and Bing-Fang Zeng
MDClin Orthop Relat Res 2009 March 467(3) 831ndash837 Total pts 32 The average healing time was 13 weeks (range 10ndash18 weeks)
for fractures using the MIPO technique and 156 weeks (range 10ndash20 weeks p = 00045) for fractures using the ORIF technique
The fracture healing time was shorter in the MIPO technique group than in the ORIF technique group which might be related to minimizing soft tissue trauma to the injured zone and preserving better blood supply around the fracture area
ADVANTAGE OF MIPPO OVER
ORIF
mipo orif
Smaller incision
Fracture site is undisturbed
Better callus formation
Blood supply to fracture fragments maintained
Larger incision
Fracture site explored
Callus formation is delayed
Blood supply is hampered
mipo orif
Low infection rate due to smaller incision and decrease soft tisuedamage
decreased need for bone grafting
High infection rate due to poor soft tissue handling over large incised wound
Bone grafting is required sometimes
conclusion
Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis(MIPO) of the distal tibia offers several theoretical advantages compared to classic open reduction and internal fixation A mechanically stable fracture-bridging osteosynthesis can be obtained without significant dissection and surgical trauma to the bone and surrounding soft tissues
MIPO has a high union rate and less complication rate
Thank you

procedure
POSITIONING OF PATIENT
INCISION
anteromedial approach a 2ndash3 cm incision is made starting at the level of the tibial plafond and extending proximally along the medial surface of the distal tibia ORposteromedial incision along the
posterior border of medialmalleolus about 4ndash5 cm in length and slightly curved can beused
PRELIMINARY REDUCTION
REDUCTION COULD BE BY MANUAL TRACTION OR BY USE OF DISTRACTOR AND REDUCTION FORCEPS PERCUTANEOUSLY
PLATE INSERTION
PLATE COULD BE INSERTED WITH HELP OF INSERTION DEVICE OR WITH HELP OF LOCKING SLEEVE UNDER SUBMUSCULAR PLANE
PRELIMINARY PLATE STABILIZATION
BY USE OF K-WIRE FOR TEMPORARY FIXATION OF PLATE
PLATE FIXATION
A MINIMUM OF 6 CORTICES ON BOTH SIDE OF FRACTURE ARE USED AND INTERFRAGMENATRY COMPRESSION SCREW WHERE NEEDED
REVIEW OF WORK
THE VARIOUS STUDY DONE TO CHECK THE EFFECTIVENESS OF MIPO TECHNIQUE FOR DISTAL END TIBIA FRACTURES ARE AS FOLLOWS
REVIEW OF WORK
STUDY NO OF FRACTURE
FIXATION OUTCOME COMPLICATION
Ronga M et al2010
19 MIPO Union 18 (223 wks range 12-24)
Nonunion1 No malunion ( ge7deg deformity or ge1 cm LLD) Deep infection3
Ahmad MA et al 2010
18 MIPO Union 15 (212 wks)
Delayed union 3 Superficial wound infarction 1 Chronic wound infection 1 Implant failure 1
Ronga M Longo UG Maffulli N Minimally invasive locked plating of distal tibia fractures is safe and effective Clin Orthop Relat Res 2010
Ahmad MA Sivaraman A Zia A Rai A Patel AD Percutaneouslocking plates for fractures of the distal tibia Our experience and a review of the literature J Trauma 2010
HasenbohehlerE et al (2007)
32 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 29 ( 277 wks range 24ndash60)
Nonunion 2 No malunion (ge 5deg deformity or ge 1 cm LLD) Plate bending (18deg) 1 Pseudoarthrosis 2
Hazarika S et al (2006)
20 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 18 ( 285 wks range 9ndash68)
Nonunion 2 Delayed wound break down 2 Wound infection 1 Implant failure 1 Secondary procedure 2
Hasenboehler E RikliD Babst R Locking compression plate with minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in diaphyseal and distal tibial fracture a retrospective study of 32 patients Injury 2007
Hazarika S Chakravarthy J Cooper J Minimally invasive locking plate osteosynthesis for fractures of the distal tibia-results in 20 patients Injury 2006
Bahari S et al (2007)
42 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 42 (224 wks)
No malunionSuperficial wound infection 2 Deep infection 1 Implant failure 1
Collinge C et al(2010)
38 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 38 (21 wks range 9ndash48)
Malunion ( ge 5degdeformity) 1 Secondary procedure 3
Mushtaq A et al (2009)
21 (open fracture 4)
MIPO Union 21( 55 months range 3ndash13)
Delayed union 1 Non union 1 Wound infection 2 Secondary procedure 2
Bahari S LenehanB Khan H Mcelwain JP Minimally invasive percutaneous plate fixation of distal tibia fractures Acta Orthop Belg2007
Collinge C Protzman R Outcomes of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis for metaphyseal distal tibia fractures J OrthopTrauma 2010
Mushtaq A Shahid R AsifM Maqsood M Distal tibialfracture fixation with locking compression plate (LCP) using the minimally invasive percutaneousosteosynthesis (MIPO) technique Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg 2009
Lau TW et al (2008)
48 (open fracture 9)
MIPO Union 47 ( 187 wks range 12-44 wks)
Delayed union 5 Wound infection 8 Secondary procedure1
Gupta RK et al(2010)
80 (open fracture19)
MIPO Union 77 (19 wks range 16-32)
Delayed union 7 Non union 3 Malunion (ge 5degdeformity or ge 1 cm LLD) 2 Wound infection1 Wound breakdown 2 Secondary procedure 2
Lau TW Leung F Chan CF Chow SP Wound complication of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in distal tibia fractures Inter Orthop 2008
Gupta RK RohillaRK Sangwan K Singh V Walia S Locking plate fixation in distal metaphysealtibial fractures series of 79 patients Inter Orthop 2010
Shreshta et al(2011)
20 MIPO Union 20 (185 wks range 14-28)
Delayed union 1 No malunion (ge 5deg deformity or ge 1 cm LLD) Superficial wound infection 2 Deep infection 1 Secondary procedure 1
Oog Jin et al 10 MIPO Union10(21 wksrange17-28)
no non-union no angular deformity gt 5deg shortening gt 10 mm no infection
Shrestha D Acharya BM Shrestha PM Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis with locking compression plate for distal diametaphyseal tibia fracture Kathmandu Univ Med J 2011
hong et al
Fractures of the Distal Tibia Treated with PolyaxialLocking Plating
Hong Gao MD Chang-Qing Zhang MD PhD Cong-FengLuo MD PhD Zu-Bin Zhou MD and Bing-Fang Zeng
MDClin Orthop Relat Res 2009 March 467(3) 831ndash837 Total pts 32 The average healing time was 13 weeks (range 10ndash18 weeks)
for fractures using the MIPO technique and 156 weeks (range 10ndash20 weeks p = 00045) for fractures using the ORIF technique
The fracture healing time was shorter in the MIPO technique group than in the ORIF technique group which might be related to minimizing soft tissue trauma to the injured zone and preserving better blood supply around the fracture area
ADVANTAGE OF MIPPO OVER
ORIF
mipo orif
Smaller incision
Fracture site is undisturbed
Better callus formation
Blood supply to fracture fragments maintained
Larger incision
Fracture site explored
Callus formation is delayed
Blood supply is hampered
mipo orif
Low infection rate due to smaller incision and decrease soft tisuedamage
decreased need for bone grafting
High infection rate due to poor soft tissue handling over large incised wound
Bone grafting is required sometimes
conclusion
Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis(MIPO) of the distal tibia offers several theoretical advantages compared to classic open reduction and internal fixation A mechanically stable fracture-bridging osteosynthesis can be obtained without significant dissection and surgical trauma to the bone and surrounding soft tissues
MIPO has a high union rate and less complication rate
Thank you

INCISION
anteromedial approach a 2ndash3 cm incision is made starting at the level of the tibial plafond and extending proximally along the medial surface of the distal tibia ORposteromedial incision along the
posterior border of medialmalleolus about 4ndash5 cm in length and slightly curved can beused
PRELIMINARY REDUCTION
REDUCTION COULD BE BY MANUAL TRACTION OR BY USE OF DISTRACTOR AND REDUCTION FORCEPS PERCUTANEOUSLY
PLATE INSERTION
PLATE COULD BE INSERTED WITH HELP OF INSERTION DEVICE OR WITH HELP OF LOCKING SLEEVE UNDER SUBMUSCULAR PLANE
PRELIMINARY PLATE STABILIZATION
BY USE OF K-WIRE FOR TEMPORARY FIXATION OF PLATE
PLATE FIXATION
A MINIMUM OF 6 CORTICES ON BOTH SIDE OF FRACTURE ARE USED AND INTERFRAGMENATRY COMPRESSION SCREW WHERE NEEDED
REVIEW OF WORK
THE VARIOUS STUDY DONE TO CHECK THE EFFECTIVENESS OF MIPO TECHNIQUE FOR DISTAL END TIBIA FRACTURES ARE AS FOLLOWS
REVIEW OF WORK
STUDY NO OF FRACTURE
FIXATION OUTCOME COMPLICATION
Ronga M et al2010
19 MIPO Union 18 (223 wks range 12-24)
Nonunion1 No malunion ( ge7deg deformity or ge1 cm LLD) Deep infection3
Ahmad MA et al 2010
18 MIPO Union 15 (212 wks)
Delayed union 3 Superficial wound infarction 1 Chronic wound infection 1 Implant failure 1
Ronga M Longo UG Maffulli N Minimally invasive locked plating of distal tibia fractures is safe and effective Clin Orthop Relat Res 2010
Ahmad MA Sivaraman A Zia A Rai A Patel AD Percutaneouslocking plates for fractures of the distal tibia Our experience and a review of the literature J Trauma 2010
HasenbohehlerE et al (2007)
32 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 29 ( 277 wks range 24ndash60)
Nonunion 2 No malunion (ge 5deg deformity or ge 1 cm LLD) Plate bending (18deg) 1 Pseudoarthrosis 2
Hazarika S et al (2006)
20 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 18 ( 285 wks range 9ndash68)
Nonunion 2 Delayed wound break down 2 Wound infection 1 Implant failure 1 Secondary procedure 2
Hasenboehler E RikliD Babst R Locking compression plate with minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in diaphyseal and distal tibial fracture a retrospective study of 32 patients Injury 2007
Hazarika S Chakravarthy J Cooper J Minimally invasive locking plate osteosynthesis for fractures of the distal tibia-results in 20 patients Injury 2006
Bahari S et al (2007)
42 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 42 (224 wks)
No malunionSuperficial wound infection 2 Deep infection 1 Implant failure 1
Collinge C et al(2010)
38 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 38 (21 wks range 9ndash48)
Malunion ( ge 5degdeformity) 1 Secondary procedure 3
Mushtaq A et al (2009)
21 (open fracture 4)
MIPO Union 21( 55 months range 3ndash13)
Delayed union 1 Non union 1 Wound infection 2 Secondary procedure 2
Bahari S LenehanB Khan H Mcelwain JP Minimally invasive percutaneous plate fixation of distal tibia fractures Acta Orthop Belg2007
Collinge C Protzman R Outcomes of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis for metaphyseal distal tibia fractures J OrthopTrauma 2010
Mushtaq A Shahid R AsifM Maqsood M Distal tibialfracture fixation with locking compression plate (LCP) using the minimally invasive percutaneousosteosynthesis (MIPO) technique Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg 2009
Lau TW et al (2008)
48 (open fracture 9)
MIPO Union 47 ( 187 wks range 12-44 wks)
Delayed union 5 Wound infection 8 Secondary procedure1
Gupta RK et al(2010)
80 (open fracture19)
MIPO Union 77 (19 wks range 16-32)
Delayed union 7 Non union 3 Malunion (ge 5degdeformity or ge 1 cm LLD) 2 Wound infection1 Wound breakdown 2 Secondary procedure 2
Lau TW Leung F Chan CF Chow SP Wound complication of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in distal tibia fractures Inter Orthop 2008
Gupta RK RohillaRK Sangwan K Singh V Walia S Locking plate fixation in distal metaphysealtibial fractures series of 79 patients Inter Orthop 2010
Shreshta et al(2011)
20 MIPO Union 20 (185 wks range 14-28)
Delayed union 1 No malunion (ge 5deg deformity or ge 1 cm LLD) Superficial wound infection 2 Deep infection 1 Secondary procedure 1
Oog Jin et al 10 MIPO Union10(21 wksrange17-28)
no non-union no angular deformity gt 5deg shortening gt 10 mm no infection
Shrestha D Acharya BM Shrestha PM Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis with locking compression plate for distal diametaphyseal tibia fracture Kathmandu Univ Med J 2011
hong et al
Fractures of the Distal Tibia Treated with PolyaxialLocking Plating
Hong Gao MD Chang-Qing Zhang MD PhD Cong-FengLuo MD PhD Zu-Bin Zhou MD and Bing-Fang Zeng
MDClin Orthop Relat Res 2009 March 467(3) 831ndash837 Total pts 32 The average healing time was 13 weeks (range 10ndash18 weeks)
for fractures using the MIPO technique and 156 weeks (range 10ndash20 weeks p = 00045) for fractures using the ORIF technique
The fracture healing time was shorter in the MIPO technique group than in the ORIF technique group which might be related to minimizing soft tissue trauma to the injured zone and preserving better blood supply around the fracture area
ADVANTAGE OF MIPPO OVER
ORIF
mipo orif
Smaller incision
Fracture site is undisturbed
Better callus formation
Blood supply to fracture fragments maintained
Larger incision
Fracture site explored
Callus formation is delayed
Blood supply is hampered
mipo orif
Low infection rate due to smaller incision and decrease soft tisuedamage
decreased need for bone grafting
High infection rate due to poor soft tissue handling over large incised wound
Bone grafting is required sometimes
conclusion
Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis(MIPO) of the distal tibia offers several theoretical advantages compared to classic open reduction and internal fixation A mechanically stable fracture-bridging osteosynthesis can be obtained without significant dissection and surgical trauma to the bone and surrounding soft tissues
MIPO has a high union rate and less complication rate
Thank you

PRELIMINARY REDUCTION
REDUCTION COULD BE BY MANUAL TRACTION OR BY USE OF DISTRACTOR AND REDUCTION FORCEPS PERCUTANEOUSLY
PLATE INSERTION
PLATE COULD BE INSERTED WITH HELP OF INSERTION DEVICE OR WITH HELP OF LOCKING SLEEVE UNDER SUBMUSCULAR PLANE
PRELIMINARY PLATE STABILIZATION
BY USE OF K-WIRE FOR TEMPORARY FIXATION OF PLATE
PLATE FIXATION
A MINIMUM OF 6 CORTICES ON BOTH SIDE OF FRACTURE ARE USED AND INTERFRAGMENATRY COMPRESSION SCREW WHERE NEEDED
REVIEW OF WORK
THE VARIOUS STUDY DONE TO CHECK THE EFFECTIVENESS OF MIPO TECHNIQUE FOR DISTAL END TIBIA FRACTURES ARE AS FOLLOWS
REVIEW OF WORK
STUDY NO OF FRACTURE
FIXATION OUTCOME COMPLICATION
Ronga M et al2010
19 MIPO Union 18 (223 wks range 12-24)
Nonunion1 No malunion ( ge7deg deformity or ge1 cm LLD) Deep infection3
Ahmad MA et al 2010
18 MIPO Union 15 (212 wks)
Delayed union 3 Superficial wound infarction 1 Chronic wound infection 1 Implant failure 1
Ronga M Longo UG Maffulli N Minimally invasive locked plating of distal tibia fractures is safe and effective Clin Orthop Relat Res 2010
Ahmad MA Sivaraman A Zia A Rai A Patel AD Percutaneouslocking plates for fractures of the distal tibia Our experience and a review of the literature J Trauma 2010
HasenbohehlerE et al (2007)
32 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 29 ( 277 wks range 24ndash60)
Nonunion 2 No malunion (ge 5deg deformity or ge 1 cm LLD) Plate bending (18deg) 1 Pseudoarthrosis 2
Hazarika S et al (2006)
20 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 18 ( 285 wks range 9ndash68)
Nonunion 2 Delayed wound break down 2 Wound infection 1 Implant failure 1 Secondary procedure 2
Hasenboehler E RikliD Babst R Locking compression plate with minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in diaphyseal and distal tibial fracture a retrospective study of 32 patients Injury 2007
Hazarika S Chakravarthy J Cooper J Minimally invasive locking plate osteosynthesis for fractures of the distal tibia-results in 20 patients Injury 2006
Bahari S et al (2007)
42 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 42 (224 wks)
No malunionSuperficial wound infection 2 Deep infection 1 Implant failure 1
Collinge C et al(2010)
38 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 38 (21 wks range 9ndash48)
Malunion ( ge 5degdeformity) 1 Secondary procedure 3
Mushtaq A et al (2009)
21 (open fracture 4)
MIPO Union 21( 55 months range 3ndash13)
Delayed union 1 Non union 1 Wound infection 2 Secondary procedure 2
Bahari S LenehanB Khan H Mcelwain JP Minimally invasive percutaneous plate fixation of distal tibia fractures Acta Orthop Belg2007
Collinge C Protzman R Outcomes of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis for metaphyseal distal tibia fractures J OrthopTrauma 2010
Mushtaq A Shahid R AsifM Maqsood M Distal tibialfracture fixation with locking compression plate (LCP) using the minimally invasive percutaneousosteosynthesis (MIPO) technique Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg 2009
Lau TW et al (2008)
48 (open fracture 9)
MIPO Union 47 ( 187 wks range 12-44 wks)
Delayed union 5 Wound infection 8 Secondary procedure1
Gupta RK et al(2010)
80 (open fracture19)
MIPO Union 77 (19 wks range 16-32)
Delayed union 7 Non union 3 Malunion (ge 5degdeformity or ge 1 cm LLD) 2 Wound infection1 Wound breakdown 2 Secondary procedure 2
Lau TW Leung F Chan CF Chow SP Wound complication of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in distal tibia fractures Inter Orthop 2008
Gupta RK RohillaRK Sangwan K Singh V Walia S Locking plate fixation in distal metaphysealtibial fractures series of 79 patients Inter Orthop 2010
Shreshta et al(2011)
20 MIPO Union 20 (185 wks range 14-28)
Delayed union 1 No malunion (ge 5deg deformity or ge 1 cm LLD) Superficial wound infection 2 Deep infection 1 Secondary procedure 1
Oog Jin et al 10 MIPO Union10(21 wksrange17-28)
no non-union no angular deformity gt 5deg shortening gt 10 mm no infection
Shrestha D Acharya BM Shrestha PM Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis with locking compression plate for distal diametaphyseal tibia fracture Kathmandu Univ Med J 2011
hong et al
Fractures of the Distal Tibia Treated with PolyaxialLocking Plating
Hong Gao MD Chang-Qing Zhang MD PhD Cong-FengLuo MD PhD Zu-Bin Zhou MD and Bing-Fang Zeng
MDClin Orthop Relat Res 2009 March 467(3) 831ndash837 Total pts 32 The average healing time was 13 weeks (range 10ndash18 weeks)
for fractures using the MIPO technique and 156 weeks (range 10ndash20 weeks p = 00045) for fractures using the ORIF technique
The fracture healing time was shorter in the MIPO technique group than in the ORIF technique group which might be related to minimizing soft tissue trauma to the injured zone and preserving better blood supply around the fracture area
ADVANTAGE OF MIPPO OVER
ORIF
mipo orif
Smaller incision
Fracture site is undisturbed
Better callus formation
Blood supply to fracture fragments maintained
Larger incision
Fracture site explored
Callus formation is delayed
Blood supply is hampered
mipo orif
Low infection rate due to smaller incision and decrease soft tisuedamage
decreased need for bone grafting
High infection rate due to poor soft tissue handling over large incised wound
Bone grafting is required sometimes
conclusion
Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis(MIPO) of the distal tibia offers several theoretical advantages compared to classic open reduction and internal fixation A mechanically stable fracture-bridging osteosynthesis can be obtained without significant dissection and surgical trauma to the bone and surrounding soft tissues
MIPO has a high union rate and less complication rate
Thank you

PRELIMINARY PLATE STABILIZATION
BY USE OF K-WIRE FOR TEMPORARY FIXATION OF PLATE
PLATE FIXATION
A MINIMUM OF 6 CORTICES ON BOTH SIDE OF FRACTURE ARE USED AND INTERFRAGMENATRY COMPRESSION SCREW WHERE NEEDED
REVIEW OF WORK
THE VARIOUS STUDY DONE TO CHECK THE EFFECTIVENESS OF MIPO TECHNIQUE FOR DISTAL END TIBIA FRACTURES ARE AS FOLLOWS
REVIEW OF WORK
STUDY NO OF FRACTURE
FIXATION OUTCOME COMPLICATION
Ronga M et al2010
19 MIPO Union 18 (223 wks range 12-24)
Nonunion1 No malunion ( ge7deg deformity or ge1 cm LLD) Deep infection3
Ahmad MA et al 2010
18 MIPO Union 15 (212 wks)
Delayed union 3 Superficial wound infarction 1 Chronic wound infection 1 Implant failure 1
Ronga M Longo UG Maffulli N Minimally invasive locked plating of distal tibia fractures is safe and effective Clin Orthop Relat Res 2010
Ahmad MA Sivaraman A Zia A Rai A Patel AD Percutaneouslocking plates for fractures of the distal tibia Our experience and a review of the literature J Trauma 2010
HasenbohehlerE et al (2007)
32 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 29 ( 277 wks range 24ndash60)
Nonunion 2 No malunion (ge 5deg deformity or ge 1 cm LLD) Plate bending (18deg) 1 Pseudoarthrosis 2
Hazarika S et al (2006)
20 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 18 ( 285 wks range 9ndash68)
Nonunion 2 Delayed wound break down 2 Wound infection 1 Implant failure 1 Secondary procedure 2
Hasenboehler E RikliD Babst R Locking compression plate with minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in diaphyseal and distal tibial fracture a retrospective study of 32 patients Injury 2007
Hazarika S Chakravarthy J Cooper J Minimally invasive locking plate osteosynthesis for fractures of the distal tibia-results in 20 patients Injury 2006
Bahari S et al (2007)
42 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 42 (224 wks)
No malunionSuperficial wound infection 2 Deep infection 1 Implant failure 1
Collinge C et al(2010)
38 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 38 (21 wks range 9ndash48)
Malunion ( ge 5degdeformity) 1 Secondary procedure 3
Mushtaq A et al (2009)
21 (open fracture 4)
MIPO Union 21( 55 months range 3ndash13)
Delayed union 1 Non union 1 Wound infection 2 Secondary procedure 2
Bahari S LenehanB Khan H Mcelwain JP Minimally invasive percutaneous plate fixation of distal tibia fractures Acta Orthop Belg2007
Collinge C Protzman R Outcomes of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis for metaphyseal distal tibia fractures J OrthopTrauma 2010
Mushtaq A Shahid R AsifM Maqsood M Distal tibialfracture fixation with locking compression plate (LCP) using the minimally invasive percutaneousosteosynthesis (MIPO) technique Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg 2009
Lau TW et al (2008)
48 (open fracture 9)
MIPO Union 47 ( 187 wks range 12-44 wks)
Delayed union 5 Wound infection 8 Secondary procedure1
Gupta RK et al(2010)
80 (open fracture19)
MIPO Union 77 (19 wks range 16-32)
Delayed union 7 Non union 3 Malunion (ge 5degdeformity or ge 1 cm LLD) 2 Wound infection1 Wound breakdown 2 Secondary procedure 2
Lau TW Leung F Chan CF Chow SP Wound complication of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in distal tibia fractures Inter Orthop 2008
Gupta RK RohillaRK Sangwan K Singh V Walia S Locking plate fixation in distal metaphysealtibial fractures series of 79 patients Inter Orthop 2010
Shreshta et al(2011)
20 MIPO Union 20 (185 wks range 14-28)
Delayed union 1 No malunion (ge 5deg deformity or ge 1 cm LLD) Superficial wound infection 2 Deep infection 1 Secondary procedure 1
Oog Jin et al 10 MIPO Union10(21 wksrange17-28)
no non-union no angular deformity gt 5deg shortening gt 10 mm no infection
Shrestha D Acharya BM Shrestha PM Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis with locking compression plate for distal diametaphyseal tibia fracture Kathmandu Univ Med J 2011
hong et al
Fractures of the Distal Tibia Treated with PolyaxialLocking Plating
Hong Gao MD Chang-Qing Zhang MD PhD Cong-FengLuo MD PhD Zu-Bin Zhou MD and Bing-Fang Zeng
MDClin Orthop Relat Res 2009 March 467(3) 831ndash837 Total pts 32 The average healing time was 13 weeks (range 10ndash18 weeks)
for fractures using the MIPO technique and 156 weeks (range 10ndash20 weeks p = 00045) for fractures using the ORIF technique
The fracture healing time was shorter in the MIPO technique group than in the ORIF technique group which might be related to minimizing soft tissue trauma to the injured zone and preserving better blood supply around the fracture area
ADVANTAGE OF MIPPO OVER
ORIF
mipo orif
Smaller incision
Fracture site is undisturbed
Better callus formation
Blood supply to fracture fragments maintained
Larger incision
Fracture site explored
Callus formation is delayed
Blood supply is hampered
mipo orif
Low infection rate due to smaller incision and decrease soft tisuedamage
decreased need for bone grafting
High infection rate due to poor soft tissue handling over large incised wound
Bone grafting is required sometimes
conclusion
Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis(MIPO) of the distal tibia offers several theoretical advantages compared to classic open reduction and internal fixation A mechanically stable fracture-bridging osteosynthesis can be obtained without significant dissection and surgical trauma to the bone and surrounding soft tissues
MIPO has a high union rate and less complication rate
Thank you

REVIEW OF WORK
THE VARIOUS STUDY DONE TO CHECK THE EFFECTIVENESS OF MIPO TECHNIQUE FOR DISTAL END TIBIA FRACTURES ARE AS FOLLOWS
REVIEW OF WORK
STUDY NO OF FRACTURE
FIXATION OUTCOME COMPLICATION
Ronga M et al2010
19 MIPO Union 18 (223 wks range 12-24)
Nonunion1 No malunion ( ge7deg deformity or ge1 cm LLD) Deep infection3
Ahmad MA et al 2010
18 MIPO Union 15 (212 wks)
Delayed union 3 Superficial wound infarction 1 Chronic wound infection 1 Implant failure 1
Ronga M Longo UG Maffulli N Minimally invasive locked plating of distal tibia fractures is safe and effective Clin Orthop Relat Res 2010
Ahmad MA Sivaraman A Zia A Rai A Patel AD Percutaneouslocking plates for fractures of the distal tibia Our experience and a review of the literature J Trauma 2010
HasenbohehlerE et al (2007)
32 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 29 ( 277 wks range 24ndash60)
Nonunion 2 No malunion (ge 5deg deformity or ge 1 cm LLD) Plate bending (18deg) 1 Pseudoarthrosis 2
Hazarika S et al (2006)
20 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 18 ( 285 wks range 9ndash68)
Nonunion 2 Delayed wound break down 2 Wound infection 1 Implant failure 1 Secondary procedure 2
Hasenboehler E RikliD Babst R Locking compression plate with minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in diaphyseal and distal tibial fracture a retrospective study of 32 patients Injury 2007
Hazarika S Chakravarthy J Cooper J Minimally invasive locking plate osteosynthesis for fractures of the distal tibia-results in 20 patients Injury 2006
Bahari S et al (2007)
42 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 42 (224 wks)
No malunionSuperficial wound infection 2 Deep infection 1 Implant failure 1
Collinge C et al(2010)
38 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 38 (21 wks range 9ndash48)
Malunion ( ge 5degdeformity) 1 Secondary procedure 3
Mushtaq A et al (2009)
21 (open fracture 4)
MIPO Union 21( 55 months range 3ndash13)
Delayed union 1 Non union 1 Wound infection 2 Secondary procedure 2
Bahari S LenehanB Khan H Mcelwain JP Minimally invasive percutaneous plate fixation of distal tibia fractures Acta Orthop Belg2007
Collinge C Protzman R Outcomes of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis for metaphyseal distal tibia fractures J OrthopTrauma 2010
Mushtaq A Shahid R AsifM Maqsood M Distal tibialfracture fixation with locking compression plate (LCP) using the minimally invasive percutaneousosteosynthesis (MIPO) technique Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg 2009
Lau TW et al (2008)
48 (open fracture 9)
MIPO Union 47 ( 187 wks range 12-44 wks)
Delayed union 5 Wound infection 8 Secondary procedure1
Gupta RK et al(2010)
80 (open fracture19)
MIPO Union 77 (19 wks range 16-32)
Delayed union 7 Non union 3 Malunion (ge 5degdeformity or ge 1 cm LLD) 2 Wound infection1 Wound breakdown 2 Secondary procedure 2
Lau TW Leung F Chan CF Chow SP Wound complication of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in distal tibia fractures Inter Orthop 2008
Gupta RK RohillaRK Sangwan K Singh V Walia S Locking plate fixation in distal metaphysealtibial fractures series of 79 patients Inter Orthop 2010
Shreshta et al(2011)
20 MIPO Union 20 (185 wks range 14-28)
Delayed union 1 No malunion (ge 5deg deformity or ge 1 cm LLD) Superficial wound infection 2 Deep infection 1 Secondary procedure 1
Oog Jin et al 10 MIPO Union10(21 wksrange17-28)
no non-union no angular deformity gt 5deg shortening gt 10 mm no infection
Shrestha D Acharya BM Shrestha PM Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis with locking compression plate for distal diametaphyseal tibia fracture Kathmandu Univ Med J 2011
hong et al
Fractures of the Distal Tibia Treated with PolyaxialLocking Plating
Hong Gao MD Chang-Qing Zhang MD PhD Cong-FengLuo MD PhD Zu-Bin Zhou MD and Bing-Fang Zeng
MDClin Orthop Relat Res 2009 March 467(3) 831ndash837 Total pts 32 The average healing time was 13 weeks (range 10ndash18 weeks)
for fractures using the MIPO technique and 156 weeks (range 10ndash20 weeks p = 00045) for fractures using the ORIF technique
The fracture healing time was shorter in the MIPO technique group than in the ORIF technique group which might be related to minimizing soft tissue trauma to the injured zone and preserving better blood supply around the fracture area
ADVANTAGE OF MIPPO OVER
ORIF
mipo orif
Smaller incision
Fracture site is undisturbed
Better callus formation
Blood supply to fracture fragments maintained
Larger incision
Fracture site explored
Callus formation is delayed
Blood supply is hampered
mipo orif
Low infection rate due to smaller incision and decrease soft tisuedamage
decreased need for bone grafting
High infection rate due to poor soft tissue handling over large incised wound
Bone grafting is required sometimes
conclusion
Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis(MIPO) of the distal tibia offers several theoretical advantages compared to classic open reduction and internal fixation A mechanically stable fracture-bridging osteosynthesis can be obtained without significant dissection and surgical trauma to the bone and surrounding soft tissues
MIPO has a high union rate and less complication rate
Thank you

REVIEW OF WORK
STUDY NO OF FRACTURE
FIXATION OUTCOME COMPLICATION
Ronga M et al2010
19 MIPO Union 18 (223 wks range 12-24)
Nonunion1 No malunion ( ge7deg deformity or ge1 cm LLD) Deep infection3
Ahmad MA et al 2010
18 MIPO Union 15 (212 wks)
Delayed union 3 Superficial wound infarction 1 Chronic wound infection 1 Implant failure 1
Ronga M Longo UG Maffulli N Minimally invasive locked plating of distal tibia fractures is safe and effective Clin Orthop Relat Res 2010
Ahmad MA Sivaraman A Zia A Rai A Patel AD Percutaneouslocking plates for fractures of the distal tibia Our experience and a review of the literature J Trauma 2010
HasenbohehlerE et al (2007)
32 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 29 ( 277 wks range 24ndash60)
Nonunion 2 No malunion (ge 5deg deformity or ge 1 cm LLD) Plate bending (18deg) 1 Pseudoarthrosis 2
Hazarika S et al (2006)
20 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 18 ( 285 wks range 9ndash68)
Nonunion 2 Delayed wound break down 2 Wound infection 1 Implant failure 1 Secondary procedure 2
Hasenboehler E RikliD Babst R Locking compression plate with minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in diaphyseal and distal tibial fracture a retrospective study of 32 patients Injury 2007
Hazarika S Chakravarthy J Cooper J Minimally invasive locking plate osteosynthesis for fractures of the distal tibia-results in 20 patients Injury 2006
Bahari S et al (2007)
42 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 42 (224 wks)
No malunionSuperficial wound infection 2 Deep infection 1 Implant failure 1
Collinge C et al(2010)
38 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 38 (21 wks range 9ndash48)
Malunion ( ge 5degdeformity) 1 Secondary procedure 3
Mushtaq A et al (2009)
21 (open fracture 4)
MIPO Union 21( 55 months range 3ndash13)
Delayed union 1 Non union 1 Wound infection 2 Secondary procedure 2
Bahari S LenehanB Khan H Mcelwain JP Minimally invasive percutaneous plate fixation of distal tibia fractures Acta Orthop Belg2007
Collinge C Protzman R Outcomes of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis for metaphyseal distal tibia fractures J OrthopTrauma 2010
Mushtaq A Shahid R AsifM Maqsood M Distal tibialfracture fixation with locking compression plate (LCP) using the minimally invasive percutaneousosteosynthesis (MIPO) technique Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg 2009
Lau TW et al (2008)
48 (open fracture 9)
MIPO Union 47 ( 187 wks range 12-44 wks)
Delayed union 5 Wound infection 8 Secondary procedure1
Gupta RK et al(2010)
80 (open fracture19)
MIPO Union 77 (19 wks range 16-32)
Delayed union 7 Non union 3 Malunion (ge 5degdeformity or ge 1 cm LLD) 2 Wound infection1 Wound breakdown 2 Secondary procedure 2
Lau TW Leung F Chan CF Chow SP Wound complication of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in distal tibia fractures Inter Orthop 2008
Gupta RK RohillaRK Sangwan K Singh V Walia S Locking plate fixation in distal metaphysealtibial fractures series of 79 patients Inter Orthop 2010
Shreshta et al(2011)
20 MIPO Union 20 (185 wks range 14-28)
Delayed union 1 No malunion (ge 5deg deformity or ge 1 cm LLD) Superficial wound infection 2 Deep infection 1 Secondary procedure 1
Oog Jin et al 10 MIPO Union10(21 wksrange17-28)
no non-union no angular deformity gt 5deg shortening gt 10 mm no infection
Shrestha D Acharya BM Shrestha PM Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis with locking compression plate for distal diametaphyseal tibia fracture Kathmandu Univ Med J 2011
hong et al
Fractures of the Distal Tibia Treated with PolyaxialLocking Plating
Hong Gao MD Chang-Qing Zhang MD PhD Cong-FengLuo MD PhD Zu-Bin Zhou MD and Bing-Fang Zeng
MDClin Orthop Relat Res 2009 March 467(3) 831ndash837 Total pts 32 The average healing time was 13 weeks (range 10ndash18 weeks)
for fractures using the MIPO technique and 156 weeks (range 10ndash20 weeks p = 00045) for fractures using the ORIF technique
The fracture healing time was shorter in the MIPO technique group than in the ORIF technique group which might be related to minimizing soft tissue trauma to the injured zone and preserving better blood supply around the fracture area
ADVANTAGE OF MIPPO OVER
ORIF
mipo orif
Smaller incision
Fracture site is undisturbed
Better callus formation
Blood supply to fracture fragments maintained
Larger incision
Fracture site explored
Callus formation is delayed
Blood supply is hampered
mipo orif
Low infection rate due to smaller incision and decrease soft tisuedamage
decreased need for bone grafting
High infection rate due to poor soft tissue handling over large incised wound
Bone grafting is required sometimes
conclusion
Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis(MIPO) of the distal tibia offers several theoretical advantages compared to classic open reduction and internal fixation A mechanically stable fracture-bridging osteosynthesis can be obtained without significant dissection and surgical trauma to the bone and surrounding soft tissues
MIPO has a high union rate and less complication rate
Thank you

HasenbohehlerE et al (2007)
32 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 29 ( 277 wks range 24ndash60)
Nonunion 2 No malunion (ge 5deg deformity or ge 1 cm LLD) Plate bending (18deg) 1 Pseudoarthrosis 2
Hazarika S et al (2006)
20 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 18 ( 285 wks range 9ndash68)
Nonunion 2 Delayed wound break down 2 Wound infection 1 Implant failure 1 Secondary procedure 2
Hasenboehler E RikliD Babst R Locking compression plate with minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in diaphyseal and distal tibial fracture a retrospective study of 32 patients Injury 2007
Hazarika S Chakravarthy J Cooper J Minimally invasive locking plate osteosynthesis for fractures of the distal tibia-results in 20 patients Injury 2006
Bahari S et al (2007)
42 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 42 (224 wks)
No malunionSuperficial wound infection 2 Deep infection 1 Implant failure 1
Collinge C et al(2010)
38 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 38 (21 wks range 9ndash48)
Malunion ( ge 5degdeformity) 1 Secondary procedure 3
Mushtaq A et al (2009)
21 (open fracture 4)
MIPO Union 21( 55 months range 3ndash13)
Delayed union 1 Non union 1 Wound infection 2 Secondary procedure 2
Bahari S LenehanB Khan H Mcelwain JP Minimally invasive percutaneous plate fixation of distal tibia fractures Acta Orthop Belg2007
Collinge C Protzman R Outcomes of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis for metaphyseal distal tibia fractures J OrthopTrauma 2010
Mushtaq A Shahid R AsifM Maqsood M Distal tibialfracture fixation with locking compression plate (LCP) using the minimally invasive percutaneousosteosynthesis (MIPO) technique Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg 2009
Lau TW et al (2008)
48 (open fracture 9)
MIPO Union 47 ( 187 wks range 12-44 wks)
Delayed union 5 Wound infection 8 Secondary procedure1
Gupta RK et al(2010)
80 (open fracture19)
MIPO Union 77 (19 wks range 16-32)
Delayed union 7 Non union 3 Malunion (ge 5degdeformity or ge 1 cm LLD) 2 Wound infection1 Wound breakdown 2 Secondary procedure 2
Lau TW Leung F Chan CF Chow SP Wound complication of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in distal tibia fractures Inter Orthop 2008
Gupta RK RohillaRK Sangwan K Singh V Walia S Locking plate fixation in distal metaphysealtibial fractures series of 79 patients Inter Orthop 2010
Shreshta et al(2011)
20 MIPO Union 20 (185 wks range 14-28)
Delayed union 1 No malunion (ge 5deg deformity or ge 1 cm LLD) Superficial wound infection 2 Deep infection 1 Secondary procedure 1
Oog Jin et al 10 MIPO Union10(21 wksrange17-28)
no non-union no angular deformity gt 5deg shortening gt 10 mm no infection
Shrestha D Acharya BM Shrestha PM Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis with locking compression plate for distal diametaphyseal tibia fracture Kathmandu Univ Med J 2011
hong et al
Fractures of the Distal Tibia Treated with PolyaxialLocking Plating
Hong Gao MD Chang-Qing Zhang MD PhD Cong-FengLuo MD PhD Zu-Bin Zhou MD and Bing-Fang Zeng
MDClin Orthop Relat Res 2009 March 467(3) 831ndash837 Total pts 32 The average healing time was 13 weeks (range 10ndash18 weeks)
for fractures using the MIPO technique and 156 weeks (range 10ndash20 weeks p = 00045) for fractures using the ORIF technique
The fracture healing time was shorter in the MIPO technique group than in the ORIF technique group which might be related to minimizing soft tissue trauma to the injured zone and preserving better blood supply around the fracture area
ADVANTAGE OF MIPPO OVER
ORIF
mipo orif
Smaller incision
Fracture site is undisturbed
Better callus formation
Blood supply to fracture fragments maintained
Larger incision
Fracture site explored
Callus formation is delayed
Blood supply is hampered
mipo orif
Low infection rate due to smaller incision and decrease soft tisuedamage
decreased need for bone grafting
High infection rate due to poor soft tissue handling over large incised wound
Bone grafting is required sometimes
conclusion
Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis(MIPO) of the distal tibia offers several theoretical advantages compared to classic open reduction and internal fixation A mechanically stable fracture-bridging osteosynthesis can be obtained without significant dissection and surgical trauma to the bone and surrounding soft tissues
MIPO has a high union rate and less complication rate
Thank you

Bahari S et al (2007)
42 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 42 (224 wks)
No malunionSuperficial wound infection 2 Deep infection 1 Implant failure 1
Collinge C et al(2010)
38 (open fracture 8)
MIPO Union 38 (21 wks range 9ndash48)
Malunion ( ge 5degdeformity) 1 Secondary procedure 3
Mushtaq A et al (2009)
21 (open fracture 4)
MIPO Union 21( 55 months range 3ndash13)
Delayed union 1 Non union 1 Wound infection 2 Secondary procedure 2
Bahari S LenehanB Khan H Mcelwain JP Minimally invasive percutaneous plate fixation of distal tibia fractures Acta Orthop Belg2007
Collinge C Protzman R Outcomes of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis for metaphyseal distal tibia fractures J OrthopTrauma 2010
Mushtaq A Shahid R AsifM Maqsood M Distal tibialfracture fixation with locking compression plate (LCP) using the minimally invasive percutaneousosteosynthesis (MIPO) technique Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg 2009
Lau TW et al (2008)
48 (open fracture 9)
MIPO Union 47 ( 187 wks range 12-44 wks)
Delayed union 5 Wound infection 8 Secondary procedure1
Gupta RK et al(2010)
80 (open fracture19)
MIPO Union 77 (19 wks range 16-32)
Delayed union 7 Non union 3 Malunion (ge 5degdeformity or ge 1 cm LLD) 2 Wound infection1 Wound breakdown 2 Secondary procedure 2
Lau TW Leung F Chan CF Chow SP Wound complication of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in distal tibia fractures Inter Orthop 2008
Gupta RK RohillaRK Sangwan K Singh V Walia S Locking plate fixation in distal metaphysealtibial fractures series of 79 patients Inter Orthop 2010
Shreshta et al(2011)
20 MIPO Union 20 (185 wks range 14-28)
Delayed union 1 No malunion (ge 5deg deformity or ge 1 cm LLD) Superficial wound infection 2 Deep infection 1 Secondary procedure 1
Oog Jin et al 10 MIPO Union10(21 wksrange17-28)
no non-union no angular deformity gt 5deg shortening gt 10 mm no infection
Shrestha D Acharya BM Shrestha PM Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis with locking compression plate for distal diametaphyseal tibia fracture Kathmandu Univ Med J 2011
hong et al
Fractures of the Distal Tibia Treated with PolyaxialLocking Plating
Hong Gao MD Chang-Qing Zhang MD PhD Cong-FengLuo MD PhD Zu-Bin Zhou MD and Bing-Fang Zeng
MDClin Orthop Relat Res 2009 March 467(3) 831ndash837 Total pts 32 The average healing time was 13 weeks (range 10ndash18 weeks)
for fractures using the MIPO technique and 156 weeks (range 10ndash20 weeks p = 00045) for fractures using the ORIF technique
The fracture healing time was shorter in the MIPO technique group than in the ORIF technique group which might be related to minimizing soft tissue trauma to the injured zone and preserving better blood supply around the fracture area
ADVANTAGE OF MIPPO OVER
ORIF
mipo orif
Smaller incision
Fracture site is undisturbed
Better callus formation
Blood supply to fracture fragments maintained
Larger incision
Fracture site explored
Callus formation is delayed
Blood supply is hampered
mipo orif
Low infection rate due to smaller incision and decrease soft tisuedamage
decreased need for bone grafting
High infection rate due to poor soft tissue handling over large incised wound
Bone grafting is required sometimes
conclusion
Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis(MIPO) of the distal tibia offers several theoretical advantages compared to classic open reduction and internal fixation A mechanically stable fracture-bridging osteosynthesis can be obtained without significant dissection and surgical trauma to the bone and surrounding soft tissues
MIPO has a high union rate and less complication rate
Thank you

Lau TW et al (2008)
48 (open fracture 9)
MIPO Union 47 ( 187 wks range 12-44 wks)
Delayed union 5 Wound infection 8 Secondary procedure1
Gupta RK et al(2010)
80 (open fracture19)
MIPO Union 77 (19 wks range 16-32)
Delayed union 7 Non union 3 Malunion (ge 5degdeformity or ge 1 cm LLD) 2 Wound infection1 Wound breakdown 2 Secondary procedure 2
Lau TW Leung F Chan CF Chow SP Wound complication of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in distal tibia fractures Inter Orthop 2008
Gupta RK RohillaRK Sangwan K Singh V Walia S Locking plate fixation in distal metaphysealtibial fractures series of 79 patients Inter Orthop 2010
Shreshta et al(2011)
20 MIPO Union 20 (185 wks range 14-28)
Delayed union 1 No malunion (ge 5deg deformity or ge 1 cm LLD) Superficial wound infection 2 Deep infection 1 Secondary procedure 1
Oog Jin et al 10 MIPO Union10(21 wksrange17-28)
no non-union no angular deformity gt 5deg shortening gt 10 mm no infection
Shrestha D Acharya BM Shrestha PM Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis with locking compression plate for distal diametaphyseal tibia fracture Kathmandu Univ Med J 2011
hong et al
Fractures of the Distal Tibia Treated with PolyaxialLocking Plating
Hong Gao MD Chang-Qing Zhang MD PhD Cong-FengLuo MD PhD Zu-Bin Zhou MD and Bing-Fang Zeng
MDClin Orthop Relat Res 2009 March 467(3) 831ndash837 Total pts 32 The average healing time was 13 weeks (range 10ndash18 weeks)
for fractures using the MIPO technique and 156 weeks (range 10ndash20 weeks p = 00045) for fractures using the ORIF technique
The fracture healing time was shorter in the MIPO technique group than in the ORIF technique group which might be related to minimizing soft tissue trauma to the injured zone and preserving better blood supply around the fracture area
ADVANTAGE OF MIPPO OVER
ORIF
mipo orif
Smaller incision
Fracture site is undisturbed
Better callus formation
Blood supply to fracture fragments maintained
Larger incision
Fracture site explored
Callus formation is delayed
Blood supply is hampered
mipo orif
Low infection rate due to smaller incision and decrease soft tisuedamage
decreased need for bone grafting
High infection rate due to poor soft tissue handling over large incised wound
Bone grafting is required sometimes
conclusion
Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis(MIPO) of the distal tibia offers several theoretical advantages compared to classic open reduction and internal fixation A mechanically stable fracture-bridging osteosynthesis can be obtained without significant dissection and surgical trauma to the bone and surrounding soft tissues
MIPO has a high union rate and less complication rate
Thank you

Shreshta et al(2011)
20 MIPO Union 20 (185 wks range 14-28)
Delayed union 1 No malunion (ge 5deg deformity or ge 1 cm LLD) Superficial wound infection 2 Deep infection 1 Secondary procedure 1
Oog Jin et al 10 MIPO Union10(21 wksrange17-28)
no non-union no angular deformity gt 5deg shortening gt 10 mm no infection
Shrestha D Acharya BM Shrestha PM Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis with locking compression plate for distal diametaphyseal tibia fracture Kathmandu Univ Med J 2011
hong et al
Fractures of the Distal Tibia Treated with PolyaxialLocking Plating
Hong Gao MD Chang-Qing Zhang MD PhD Cong-FengLuo MD PhD Zu-Bin Zhou MD and Bing-Fang Zeng
MDClin Orthop Relat Res 2009 March 467(3) 831ndash837 Total pts 32 The average healing time was 13 weeks (range 10ndash18 weeks)
for fractures using the MIPO technique and 156 weeks (range 10ndash20 weeks p = 00045) for fractures using the ORIF technique
The fracture healing time was shorter in the MIPO technique group than in the ORIF technique group which might be related to minimizing soft tissue trauma to the injured zone and preserving better blood supply around the fracture area
ADVANTAGE OF MIPPO OVER
ORIF
mipo orif
Smaller incision
Fracture site is undisturbed
Better callus formation
Blood supply to fracture fragments maintained
Larger incision
Fracture site explored
Callus formation is delayed
Blood supply is hampered
mipo orif
Low infection rate due to smaller incision and decrease soft tisuedamage
decreased need for bone grafting
High infection rate due to poor soft tissue handling over large incised wound
Bone grafting is required sometimes
conclusion
Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis(MIPO) of the distal tibia offers several theoretical advantages compared to classic open reduction and internal fixation A mechanically stable fracture-bridging osteosynthesis can be obtained without significant dissection and surgical trauma to the bone and surrounding soft tissues
MIPO has a high union rate and less complication rate
Thank you

hong et al
Fractures of the Distal Tibia Treated with PolyaxialLocking Plating
Hong Gao MD Chang-Qing Zhang MD PhD Cong-FengLuo MD PhD Zu-Bin Zhou MD and Bing-Fang Zeng
MDClin Orthop Relat Res 2009 March 467(3) 831ndash837 Total pts 32 The average healing time was 13 weeks (range 10ndash18 weeks)
for fractures using the MIPO technique and 156 weeks (range 10ndash20 weeks p = 00045) for fractures using the ORIF technique
The fracture healing time was shorter in the MIPO technique group than in the ORIF technique group which might be related to minimizing soft tissue trauma to the injured zone and preserving better blood supply around the fracture area
ADVANTAGE OF MIPPO OVER
ORIF
mipo orif
Smaller incision
Fracture site is undisturbed
Better callus formation
Blood supply to fracture fragments maintained
Larger incision
Fracture site explored
Callus formation is delayed
Blood supply is hampered
mipo orif
Low infection rate due to smaller incision and decrease soft tisuedamage
decreased need for bone grafting
High infection rate due to poor soft tissue handling over large incised wound
Bone grafting is required sometimes
conclusion
Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis(MIPO) of the distal tibia offers several theoretical advantages compared to classic open reduction and internal fixation A mechanically stable fracture-bridging osteosynthesis can be obtained without significant dissection and surgical trauma to the bone and surrounding soft tissues
MIPO has a high union rate and less complication rate
Thank you

ADVANTAGE OF MIPPO OVER
ORIF
mipo orif
Smaller incision
Fracture site is undisturbed
Better callus formation
Blood supply to fracture fragments maintained
Larger incision
Fracture site explored
Callus formation is delayed
Blood supply is hampered
mipo orif
Low infection rate due to smaller incision and decrease soft tisuedamage
decreased need for bone grafting
High infection rate due to poor soft tissue handling over large incised wound
Bone grafting is required sometimes
conclusion
Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis(MIPO) of the distal tibia offers several theoretical advantages compared to classic open reduction and internal fixation A mechanically stable fracture-bridging osteosynthesis can be obtained without significant dissection and surgical trauma to the bone and surrounding soft tissues
MIPO has a high union rate and less complication rate
Thank you

mipo orif
Smaller incision
Fracture site is undisturbed
Better callus formation
Blood supply to fracture fragments maintained
Larger incision
Fracture site explored
Callus formation is delayed
Blood supply is hampered
mipo orif
Low infection rate due to smaller incision and decrease soft tisuedamage
decreased need for bone grafting
High infection rate due to poor soft tissue handling over large incised wound
Bone grafting is required sometimes
conclusion
Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis(MIPO) of the distal tibia offers several theoretical advantages compared to classic open reduction and internal fixation A mechanically stable fracture-bridging osteosynthesis can be obtained without significant dissection and surgical trauma to the bone and surrounding soft tissues
MIPO has a high union rate and less complication rate
Thank you

mipo orif
Low infection rate due to smaller incision and decrease soft tisuedamage
decreased need for bone grafting
High infection rate due to poor soft tissue handling over large incised wound
Bone grafting is required sometimes
conclusion
Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis(MIPO) of the distal tibia offers several theoretical advantages compared to classic open reduction and internal fixation A mechanically stable fracture-bridging osteosynthesis can be obtained without significant dissection and surgical trauma to the bone and surrounding soft tissues
MIPO has a high union rate and less complication rate
Thank you

conclusion
Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis(MIPO) of the distal tibia offers several theoretical advantages compared to classic open reduction and internal fixation A mechanically stable fracture-bridging osteosynthesis can be obtained without significant dissection and surgical trauma to the bone and surrounding soft tissues
MIPO has a high union rate and less complication rate
Thank you

Thank you









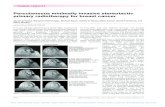








![Analysis of Tibial Condyle Fractures Treated by minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis [MIPO]](https://static.fdocuments.us/doc/165x107/587d03a51a28ab1e7e8b6f45/analysis-of-tibial-condyle-fractures-treated-by-minimally-invasive-plate-osteosynthesis.jpg)
