Membrane Different membranes –All have similar functions & structures –Plasma membrane separates...
-
Upload
juliet-james -
Category
Documents
-
view
212 -
download
0
Transcript of Membrane Different membranes –All have similar functions & structures –Plasma membrane separates...


Membrane
• Different membranes –All have similar functions & structures–Plasma membrane separates inside of cell
from outside of cell–Other membrane define organelles to form
compartments of eukaryotic cells
• Forms a selectively permeable layer–Lets some things in or out but not all–Like a window screen

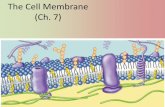
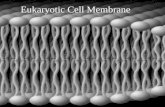
Membrane • Phospholipid bilayer
– Phosphate group facing outward• hydrophillic
– Fatty acid tails face each other • hydrophobic
• Proteins also in membrane– Lots of functions
• Signaling • Transport • Enzymatic
– Peripheral- on inside or outside surface– Integral- proteins stick out on both sides

Permeability in membranes
• Selectively permeable – Some move easily through the lipid layer
• Non polar molecules (O2, alcohols)
• Small polar molecules (H2O, CO2)
• Move with (or down) a concentration gradient– From areas of high to low concentration
– Some need help to get through• Like ions and larger polar molecules (sugar, a.a.)• Transport proteins assist
– Channel proteins - allow passage of charged particles
– Carrier proteins- transport specific molecules

Diffusion
Defined as passive movement of molecules down a concentration gradient
from areas of high to low conc.
This does not require energy - (passive)
Eventually the molecules will be equally distributed (equillibrium is reached)

Osmosis• Movement of water molecules from high to low concentration across a
semi-permeable membrane• Or diffusion of water• Hypotonic Hypotonic solution outside cell
– Low solute concentration– High water concentration– Water moves into cell
• HypertonicHypertonic solution outside cell– High solute concentration– Low water concentration– Water leaves cell
• IsotonicIsotonic solution– Concentration of water equal on both sides of membrane– No change in concentration will occur

Water in Plants
• Plant cells normally in hypotonic environment– Central vacuole full– Puts pressure on cell wall– Cell doesn’t burst because of cell wall
• Plants in hypertonic solution– Lose water and usually kills cell

Passive transport
• Involves movement of molecules across a membrane
• From areas of high concentration to areas of lower concentration across a membrane–Spilled perfume example
• Without energy

Facilitated transport
• Like passive transport but requires a membrane protein to help (facilitate) the movement
• Does not require energy
• Moves with concentration gradient

Active Transport
• Moves molecules across a membrane – Via a membrane protein– Can move molecules against their
concentration gradient• From low to high concentration• Not easy to put spilled perfume back into bottle
– Requires energy (ATP)

Exo or endocytosis
• Exocytosis- molecules exiting cell– Ex. Transport vesicle releasing contents outside
cell
• Endocytosis- molecules entering cell– Phagocytosis - cell eating
• Ex. White blood cell eating bacteria
– Pinocytosis - cell drinking– Receptor mediated endocytosis
• Molecule binds to protein receptor
Ex. Cholesterol in liver cells


Cell signaling
• Signal transduction pathway– How cells talk to each other– Reception
• Outside molecule binds to receptor• Ex. Adrenaline to muscle cells
– Transduction• Message relayed inside cell via chemicals
– Response• Chemical action• Ex. Breakdown glycogen to release glucose