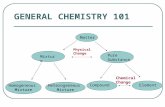
Classification of Matter Matter Flowchart Pure Substances Mixtures.
Matter. “Food Matters” Is it a Pure Substance or a Mixture? Matter can be divided into two main...
-
Upload
simon-lawrence -
Category
Documents
-
view
217 -
download
2
Transcript of Matter. “Food Matters” Is it a Pure Substance or a Mixture? Matter can be divided into two main...

Matter

“Food Matters” Is it a Pure Substance or a Mixture? • Matter can be divided into two main
categories: – Pure substances are homogeneous throughout.
They have the same chemical properties no matter where the sample is obtained or how large the sample is.
– Mixtures are combinations of two or more substances, with each substance retaining its chemical identity.

“Food Matters”
Is it a Pure Substance or a Mixture? • Distilled Water – PS Corn Flakes - M• Bottled Water – M White Vinegar - M• Tap Water – M Corn Starch - PS• OJ – M Plain Choc - M• Milk – M Crunch Bar - M• Sugar – PS• Salt - PS


Chemistry is the study of …
• ….Matter• Matter is
anything that takes up space and has mass.• Light and
sound are NOT matter!!

MATTER IS MADE UP OF…• …Atoms• The smallest
particle of an element
• Indivisible
….that guy is Democritus– Greek philosopher– “atomos”

What Does an Atom Look Like?
• Atoms are too small to see with the eye, but if we could see them, they would look like this….
• But we can see GROUPS of atoms.

Groups of Atoms are Called…
• …Elements• …made of IDENTICAL
atoms.
• Examples: Anything on the Periodic Table

Elements can combine to form…• …Compounds • …contain 2 OR MORE DIFFERENT
ELEMENTS (atoms) and are BONDED (attached) or joined in a fixed proportion
• Compounds are NOT on the Periodic Table;
• Compounds are NOT MIXTURES (we’ll get to those later…)

Identify these as Element(s) or Compound(s).
A B C D

1 Element 1 Compound 2 Elements 2 Elements

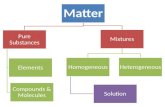
Classifying Matter
• All matter is made out of atoms…• And all matter can be classified into different
categories!– Pure Substances– Mixtures

Mixture• MIXTURES CAN BE SEPARATED!• Made up of 2 or more elements or compounds
– Yellow – an ELEMENT– Red/Blue – a COMPOUND
(Atoms are not really colored. The different colors represent different elements.)

Pure Substances (or simply, a substance)
• CANNOT BE SEPARATED • Can be made up of all one element OR all one
compound• Examples: – table salt – table sugar
• Element
• Compound

Identify these as Pure Substances or Mixtures.
A B C D

Pure Pure Mixture Mixture
1 element 1 compound 2 elements 2 elements

Pure Substances v. Mixtures
Video

Mixtures• A combination of more than one
type of substance• The properties of a mixture can
vary because the make up of a mixture is not fixed (unlike compounds which have a fixed proportion)
• 2 Types of Mixtures:– Heterogeneous – the parts of the mixture are noticeably different from one another
– Homogeneous – the parts of the mixture are so evenly distributed that it appears to be all the same substance (but a mixture is more than one substance!)

Solutions and Suspensions and Colloids…Oh My!
• A mixture can be further classified into 3 categories based on the size its largest particles– Solutions– Suspensions– Colloids

Solutions and Suspensions and Colloids…Oh My!
• Solutions – homogeneous mixtures– Examples: Sugar dissolved in water, tap water
– Properties of solutions:• DO NOT separate into layers over time• If liquid solutions are poured through a filter
none of the substance gets trapped in the filter.• You can see through liquid solutions
– All of these relate to the size of the particles - in a solution, they are tiny!

Homogeneous Mixture
• Substances are evenly distributed
• Appears to contain only one substance
• Solutions – homogeneous mixtures in which one substance dissolves in another

Solutions and Suspensions and Colloids…Oh My!
• Suspensions – heterogeneous mixtures– Example: sandy water– Properties of solutions:• DO separate into layers over time• If you pour a suspension through a filter some of
the substance in the mixture gets trapped in the filter.• Suspensions are cloudy because light gets
scattered in all directions as it hits larger particles.
– All of these relate to the size of the particles - in a suspension, they are bigger!

Heterogeneous Mixture
• The parts of the mixture are noticeably different from one another
• Suspensions– Separate into
layers

Heterogeneous Mixture
• Suspensions can be mixed (“Shake before serving) but eventually separate out.

Solutions and Suspensions and Colloids…Oh My!
• Colloids– somewhere in between homogeneous and heterogeneous
mixtures– Examples: milk and fog– Properties of colloids:
• DO NOT separate into layers over time.• Cannot use a filter to separate the parts of a colloid• Light gets scattered when it passes into a colloid
– Contain intermediate sized particles


How Do You Separate A Mixture?
• REMEMBER THE LAB?• Here are a few other ways to separate
mixtures….

Separation of Mixtures
• Compounds and mixtures differ in another way.
• It is difficult to separate a compound into each element.
• Mixtures can be easy to separate into its components because each component keeps its own properties.

Separation of Mixtures
1. Magnetic attraction: The magnetic components of a mixture can be separated by using a magnet.

Separation of Mixtures2. Filtration: separates parts of a
heterogeneous mixture by pouring it though a filter, the larger particles (residue) will be held in the filter while the smaller ones (filtrate) will pass through.

Separation of Mixtures
3. Distillation: used to separate components of a homogeneous mixture based on their different boiling points. Solution is heated and substance with lower boiling points evaporates and passes through a tube where it cools and turns back into water in another container.

Separation of Mixtures
4. Evaporation: When a mixture contains a solvent such as water and a solute such as salt, the solvent can be allowed to evaporate, leaving behind the solute.

Separation of Mixtures
5. Sedimentation: occurs naturally when solid substances that are heavier than their solvent deposit at the bottom of the mixture.

Separation of Mixtures
6. Decantation: a heterogeneous mixture that has distinct layers can be separated by slowly pouring one of the layers into another container.