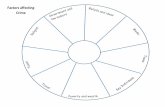
Market Factors Affecting Price How do we get to $9.99?
-
Upload
cory-atkinson -
Category
Documents
-
view
217 -
download
0
Transcript of Market Factors Affecting Price How do we get to $9.99?

Market Factors Affecting Price
How do we get to $9.99?

Objectives
Define Price and Pricing List the four market factors that affect price Identify and discuss each market factor Define elastic demand and inelastic demand List the 5 factors that contribute to demand
elasticity Identify and discuss each factor

Price & Pricing
Price: the money a customer must pay for a product or service. – Part of the Marketing Mix
Pricing: establishing and communicating the value of products and services to potential customers.

Four Major Market Factors That Affect Price
1. Costs and Expenses
2. Supply and Demand
3. Consumer Perceptions
4. Competition

1. Costs and Expenses
Sales – (Costs + Expenses) = Profit Increasing costs and expenses lead
companies to:– Increase price of product or service– Reduce size of product or service– Drop service that is not valued– Add to their product or service

1. Costs and Expenses
Lower costs and expenses lead companies to:– Decrease prices of products and services
Improved technology and less expensive materials help companies produce better-quality products at lower prices.– Example: the price of computers

2. Supply and Demand
With most products:– Demand increases with lower prices– Demand decreases with higher prices
This does not apply to some products Demand Elasticity
– The degree to which demand for a product is affected by its price
Products have either elastic or inelastic demand

Elastic Demand
When a change in price creates a change in demand.– Example: Price of Steak
Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility– Consumers will only buy so much of a product
even if the price is low.– Example: Price of Laundry Detergent

Inelastic Demand
When a change in price has very little effect on demand for a product
Example:– Milk– Bread– Gas (?)

Demand Elasticity
The demand elasticity depends on five factors:– Brand Loyalty – Availability of Substitutes– Price Relative to Income– Luxury vs. Necessity– Urgency of Purchase.

Brand Loyalty
When a customer will not buy a substitute product over a brand name of their choice.
In this case brand is inelastic.

Availability of Substitutes
When there are a variety of substitutes that will do the same job, the demand becomes elastic.
Example: – Laundry Detergent

Price Relative to Income
If a price increases dramatically and it is beyond a customer’s budget, they are less likely to buy it.
In this situation the demand will be elastic.
Example:– A diamond ring

Luxury vs. Necessity
When a consumer feels that a product is a necessity, the demand becomes inelastic.
Example:– medicine
When a consumer feels that a product is a luxury, the demand becomes elastic.
Example:– automobile

Urgency of Purchase
If a purchase must be made immediately then the demand will be inelastic.
Example:– Running out of gas

3. Consumer Perceptions
Price planning involves what the consumers perceive
Some consumers associate quality with price– High price equals high
quality– High price equals status,
prestige, and exclusiveness

3. Consumer Perceptions
Businesses limit market supply to make the consumer think it is worth more.
Example:– Limited Edition
Personalized service can also add to a customer’s perception.

4. Competition
2 Forms:– Non-Price Competition– Price Competition
Non-price Competition – minimizes price as a reason for purchase – The more unusual a product, the greater the
freedom to set prices above competitor’s. Price Competition
– allows a company to gain target market appeal by lowering prices.

4. Competition
Companies are constantly watching each other. If one lowers their price, their competitors will lower their price too.
The benefit is lower prices for consumers.
Price Wars:– When a company lowers their price to the point that
they lose profits. Can cause financial trouble.

Price Assignment
Using what you now know about pricing, source items for a school store– Find the best price for each item– Name brands or knock-offs?– Add in your margin
Determine how many items you must sell to make a weekly profit of $1000

Summary
Defined Price and Pricing Listed the four market factors that affect price Identified and discussed each market factor Defined elastic demand and inelastic
demand Listed the 5 factors that contribute to demand
elasticity Identified and discussed each factor

References
Boone, Louis E. & Kurtz, David L. (2001) Contemporary Marketing (10th Edition). USA: South-Western Thomason Learning.
Burrow, James L. (2002). Marketing (Instructor’s Wraparound Edition). USA: South-Western Thomason Learning.
Farese, L.S, Kimbrell, G. & Woloszyk, C.A (2002). Marketing Essentials (3rd Edition). New York: McGraw-Hill.