Male and Female Reproductive Systems Mrs. Bishop.
-
Upload
noel-evans -
Category
Documents
-
view
213 -
download
1
Transcript of Male and Female Reproductive Systems Mrs. Bishop.

Male and Female Reproductive Systems
Mrs. Bishop

Gametes – Sex Cells• What are the male and female sex cells?
– Female produce an egg, a haploid cell that contains 23 chromosomes in its nucleus.
– Males produce sperm, which is composed of a head that contains 23 chromosomes and a tail that helps it move. Sperm mixes with other fluids to make semen.
– Semen is the environment in which 5 to 10 million sperm per drop can swim in.

Fertilization
• What is the product of fertilization?
– A zygote, a diploid cell, is formed when an egg is fertilized by a sperm.
– Fertilization is an important part of the process by which organisms produce organisms of the same type (Reproduction).

Inherited Characteristics
• What carries the information that controls inherited characteristics?– Chromosomes, which are found in the nuclei
of the sex cells.
• How many chromosomes are there in each sex cell?– Sperm (haploid cells) have 23, eggs (haploid
cells) have 23, and a zygotes (diploid cells) have 46. Therefore, zygotes has all the information to produce a new human being.

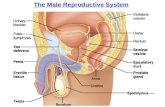
The male reproductive system
• What is the male reproductive system composed of?– Testes - oval shaped organs that have clusters of
hundreds of tiny coiled tubes, where sperm is formed.– Scrotum - an external pouch of skin where the testes
are located. The scrotum keeps testes about 2 to 3 degrees cooler than the body temperature which is 37 degrees Celsius.
– Penis - an organ that contains the urethra , the channel through which urine and semen pass to the exterior.

The male reproductive system
• What does the male reproductive system produce?
– Sperm - male gamete (sex cells)
– Testosterone - the hormone that controls the development of adult physical characteristics in men such as facial hair, deep voice, broad shoulders, and the production of sperm.

The female reproductive system
• What is the female reproductive system composed of?– Ovaries - organs that are located slightly
below the waist on each side of the body, where egg cells are produced.
– Oviduct (fallopian tube) - a passage way for the egg to travel to the uterus. This is where fertilization usually occurs.

The female reproductive system
– Uterus (womb) - a hollow muscular organ where a zygote begins to develop.
– Vagina (birth canal) - a muscular passageway leading to the outside of the body, where an egg or a baby leave the female body.

The female reproductive system
• What does the female reproductive system produce?
– Eggs - female gamete (sex cell). If an egg is fertilized, the reproductive system will nourish the developing baby until birth.
– Estrogen - the hormone that controls the development of adult physical characteristics in women such as the widening of hips, development of breast, and the production of eggs during the menstrual cycle.

The Menstrual cycle• What controls the menstrual cycle?
– The hormones of the endocrine system.
• What occurs during the menstrual cycle?– Once a month an egg matures in an ovary.– The uterus prepares for the arrival of a zygote
(fertilized egg).– Ovulation usually occurs halfway though a
typical cycle. This is where the egg is released from the ovary into the oviduct and the lining of the uterus begins to thicken.

The Menstrual cycle
– If the egg is not fertilized when it reaches the uterus, it will begin to break down along with the lining.
– The extra blood and tissue that lined the uterus will pass out the body through the vagina, which last about 4 to 6 days. This process is called menstruation.
– Menstruation usually begins between the ages of 10 and 14 years and continues until about the age of 50.

And now some advice from Mean Girls….