Lungs
description
Transcript of Lungs

Lungs
Gaseous Exchange
Breathing

Learning objectives:
1. Must say what the job of the lungs is and name the main parts
2. Should describe the special features the lungs have to do their job really well
3. Could explain how the alveoli work

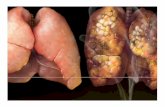
What are the lungs?Lungs are the organs of respiration.
What is gas exchange?
The right lung is a little bigger than the left lung. This the left lung has to fit around the heart making it slightly smaller.
The lungs are split into lobesThe left lung is split into 2 lobes while the right lung is split into 3
lobes. Lungs have a very spongy texture and have a large surface area.
The process of oxygen and carbon dioxide moving between the lungs and the blood.

Task:1.Label the different parts of the respiratory
system
2.Match up the parts of the respiratory system with the correct description.

Trachea
Lung
Diaphragm
Ribs
Alveoli
Intercostal Muscles
Bronchi
Bronchioles

Breathing
Ventilation
When your muscles change the size of your lungs.
The movement of air into and out of your lungs


What is breathing?The process by which you take IN oxygen and
give OUT carbon dioxide. When you breathe in:
Your diaphragm muscles contracts and goes downExternal intercostal muscles contract and pull rib cage upwards and outwardsIncreasing the volume of the thoraxIt decreases the air pressure in the thoracic cavity

• When you breathe in:• Your diaphragm muscles contracts and goes
down• External intercostal muscles contract and pull
rib cage upwards and outwards• Increasing the volume of the thorax• It decreases the air pressure in the thoracic
cavity

Where does gas exchange occur?The alveoli are adapted to make gas exchange in lungs happen easily and efficiently.
Features of the alveoli that allow gas exchange
They have a thin epithelium (just one cell thick)
They have a large surface area
They have a rich supply of blood capillaries
Ventilation of lungs maintains a steep diffusion gradient

The gases move by diffusion.
Diffusion is the process by where gases move from a high concentration to a low concentration:
Oxygen diffuses from the air in the alveoli into the blood.
Carbon dioxide diffuses from the blood into the air in the alveoli.
How do the gases move?
Capillary

http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/ks3bitesize/science/organisms_behaviour_health/life_processes/revise5.shtml

Collect information and pictures about the heart or the lungs so that we can make information posters for display work.
To be handed in next lesson – Tuesday 1st December

List 3 ways that the lungs are adapted for gas exchange.
Capillary

The passage of air through the body:
The lungs are positioned inside the ………….. …………….. The ………… form a cage protecting them. The ………..lung has ………… cavities is bigger than the ………… lung which only has ……….. The action of breathing means that the lungs are constantly moving in and out. In order to prevent friction, the lungs are surrounded by the ………………. ………………… This is a complete lining which is smooth and has a moist, slimy mucus.
two three right left chest cavity pleural membrane