Lung structure function_and_cellular_function
-
Upload
hscteacher04 -
Category
Education
-
view
314 -
download
0
Transcript of Lung structure function_and_cellular_function

P3 outline the gross structure of all the main body systems
Structure and Function of the Major Body Systems.You have been employed by a local hospital to help develop resources for a group of trainee nurses. You are required to produce a detailed booklet outlining the structure and function of the major body systems.The booklet should cover the following areas;
• Respiratory system• Cardiovascular system• Digestive system• Renal system• Nervous system• Endocrine system• Musculo-skeletal
system• Immune system• Reproductive system
(male and female)• Lymphatic system.

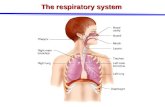
Human Gas Exchange System
• Describe the structure and function of the human gas exchange system
• Investigate the structure of the walls of the: – Trachea– Bronchioles– Alveoli
• Explain how, at cellular level, each structure is adapted to its function

The Lungs
• Gas exchange occurs within the lungs.• Connected to the outside air with a set
of tubes.• The trachea starts at the back of the
moth and branches to form 2 bronchi.• One bronchus goes into each lung.• Each bronchus branches many times
getting smaller and smaller form tubes called bronchioles.
• All of these tubes have cartilage rings for support, except the microscopic ones.
• At the end of the bronchioles are the alveoli.
• Each alveolus is folded top for a set of interconnected spaces.
• There are many alveoli, providing a very large surface area for gas exchange.
• The alveoli are surrounded by blood capillaries transporting blood to and from the lungs
• Describe the structure and function of the human gas exchange system
• Investigate the structure of the walls of the:– Trachea– Bronchioles– Alveoli
• Explain how, at cellular level, each structure is adapted to its function

• Describe the structure and function of the human gas exchange system• Investigate the structure of the walls of the:
– Trachea– Bronchioles– Alveoli
• Explain how, at cellular level, each structure is adapted to its function
Structure Function and Adaptation
Trachea
Bronchioles
Alveoli
For each structure of the breathing system, describe what it does and how
it is adapted to perform it’s function

BronchioleTrachea
• Cartilage – airways open / air resistance low• Trachea – ‘C’ shaped• Bronchi – blocks• Bronchioles smooth muscle
• Warming / moistening• Hairs – traps large particles• Trachea / Bronchi – goblet cells trap small particles (very few in
bronchiole)• Ciliated cells – beat to remove trapped mucus into the throat• Macrophages – Bacterial scavengers



• Inner surface moist –prevents drying from air.
• Surfactant – prevents surfaces sticking• Macrophages.• Epithelium cells – flattened for easy
diffusion.• Single layer cells in capillaries.• LSA.• Large diffusion gradient for both gases
Alveoli

Investigating at Cellular Level

Lung Structure – Cellular Level• Ciliated
epithelial cells line the airways with goblet cells
• Goblet cells produce the mucus
• Cilia, hair like structures, beat and move the mucus
• Basement membrane holds it in position
• Describe the structure and function of the human gas exchange system• Investigate the structure of the walls of the:
– Trachea– Bronchioles– Alveoli
• Explain how, at cellular level, each structure is adapted to its function

Epithelial Cells• Squamous
(pavement) . epithelial cells - work together to make an epithelium.
• Epithelium sits on a basement membrane (protein fibres)
• Epithelium in the walls of the alveoli is squamous.

Ciliated Epithelium• Trachea, bronchi,
bronchioles – ciliated epithelial cells with cilia on the free surface.
• Ciliated columnar epithelium appears to be stratified ! But each cell is in contact with the basement membrane. Nucleus on different levels – pseudostratified.


Rate of diffusion – 3 properties of gas exchange surface
1. Surface area – rate of diffusion is directly proportional.
2. Concentration gradient- rate of diffusion is directly proportional to the difference in concentration across the GE surface.
3. Thickness of the GE surface- rate of diffusion is inversely proportional to the thickness of the GE surface. Thicker surface, slower the diffusion.








![Speaker: Lung-Sheng Chienoz.nthu.edu.tw/~d947207/chap6.pdf · 2008. 7. 7. · Structure representation of 2D point [1] point is called structure tag pt =(4,3) (0,0)x and y in structure](https://static.fdocuments.us/doc/165x107/60d45c315d49e4101a79de24/speaker-lung-sheng-d947207chap6pdf-2008-7-7-structure-representation-of.jpg)
![[OS 213] LEC 03 Review of Normal Lung Structure and Function](https://static.fdocuments.us/doc/165x107/563db912550346aa9a99b6fe/os-213-lec-03-review-of-normal-lung-structure-and-function.jpg)








