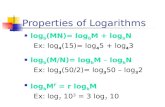
log mar2
-
Upload
ristaniatauhid -
Category
Documents
-
view
230 -
download
0
description
Transcript of log mar2
-
LOGMAR BAILEY-LOVIE CHART* Founded by Ian Bailey and Jan Lovie in 1980
The chart has the shape of an inverted triangle
The character size change is a logarithmic progression of letter sizes
D,E,F,H,N,P,R,U,V,Z
-
*LOGMAR CHART LogMAR is the base Logarithm of the minimum angle of resolution
LogMAR chart is used when precision is required in the examination of visual acuity
LogMAR visual acuity, usually used in research studies
-
*Assessment LogMAR visual acuity was 0.1 LogMAR for each row
0.02 LogMAR for each letter correctly identified.
-
*Positioning patient on 4 m from chartInstruct to cover his left eye and not to squintInstruct to read letters from top to bottomUse a score sheet : identify the correct letters and note it Continue read the letter until the patien unable read any letter.Do to the right eye tooNote the score of visual acuityIf, the patien can not read any letter on the top line Move the chart to be 2 metersStep by Step Procedure
-
*LOGMAR VISUAL ACUITY RECORDING FORM
-
*
-
*Visual acuity conversion :EXAMPLE
-
ETDRS* Rick Ferris et al. of the National Eye Institute in 1982
chose the Bailey-Lovie layout
Sloan letters (C,D,H,K,N,O,R,S,V,Z)
a standarized method of visual acuity measurement for the Early Treatment of Diabetic Retinopathy Study (ETDRS)..
-
ETDRS Acuity Testing
-
Same number of letters per row (five letters per row)Equal spacing of the rows on a log scale (the rows are separated by 0.1. log unit)Equal spacing of the letters on a log scaleIndividual rows balanced for letter difficultyTo prevent memorization, different versions of the ETDRS test chart are available. The three standard versions of the ETDRS chart are R, 1 and 2.
ETDRS Design
-
What is a visual impairment?
-
Levels of visual impairmentWorld Health Organization has a classification system:When the vision in the better eye withbest possible glassescorrection is:20/30 to 20/60 Mild 20/70 to 20/160 Moderate20/200 to 20/400 Severe20/500 to 20/1,000 Profound
-
Levels of visual impairment cont.less than 20/1,000 Near-total visual impairment, ornear total blindnessNo light perception Total impairment, or total blindnessThere are also levels of visual impairment based on visual field loss (loss of peripheral vision). Visual acuity alone is not a good predictorSomeone with relatively good acuity (e.g., 20/40) can have difficulty functioning, while someone with worse acuity (e.g., 20/200) might not be having any real problems.
-
VA alone not a good predictorVisual acuity 20/40With visual field lossVisual acuity 20/200With no visual field loss
*ETDRS stands for Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study. The ETDRS test is designed to eliminate inaccuracies in the Snellen and Sloan tests.The ETDRS acuity test was developed to aid in evaluating the changes in vision following panretinal photocoagulation in patients with diabetic retinopathy.Previous studies had somewhat confusing results due to inadequacies of the acuity tests used in those early studies. For example, the Snellen acuity test has a different number of letters per row, e.g. 10 letters on the 20/20 line, but only 3 letters on the 20/70 line.Therefore, if the results of a study showed that the patients gained three letters of acuity, the results could indicate the gain of a full acuity line, as in the 20/70 line, or only a portion of an acuity line, as in the 20/20 line.Also, the individual lines on the Snellen acuity test are not equally spaced. For example, the change from the 20/25 line to the 20/20 line is a 20% change, while the change from the 20/30 line to the 20/25 line is a 16% change.
*