LIPIDS
description
Transcript of LIPIDS

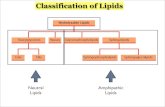
LIPIDS

Lipids
Triglycerides fats and oils
Phospholipids Sterol derivatives

Storage
Adipose tissueFat storingCan expand indefinitely
by number by size

Lipids
Provides energy stored fat supplies 60% of energy
during rest prolonged exercise starvation

Lipids
Provide insulation vital organ protection nerve impulse transmission
Cell structure Enhance fat soluble vitamin
absorption

Lipids
Facilitate weight gain Found in plants and animals Visible and invisible (hidden) fats Body synthesizes all fatty acids
except two 9 kcal/g

Lipids
Supply taste and flavor to foods Post-prandial satiety
Can stay 3 - 4 hours in stomach

Lipids
Precursor for synthesis of steroid hormones prostalandins and actylcholine

Triglycerides
Fats and oils 95% of total fat intake 3 fatty acids attached to 3 carbon
based glycerol Glycerol is an alcohol Straight chains
C2 to C20+


Fatty Acids
Differ in two ways Chain length
short- not usually in foods medium- milk fat, non-dairy creamers long- meat fats, olive oil, peanut oil very long- fish oils, some plant oils

Fatty Acids
Degree of saturation Partially determines health impact Chemical structure
saturated-all single bonds monounsaturated-one double bond polyunsaturated-two or more double
bonds

Essential Fatty Acids Linoleic Plant oils Omega 6 Rare deficiency Hormone-like Part of clotting
process and immune response
Linolenic Fish oils Omega 3 Rare deficiency Hormone-like Part of clotting
process and immune response

Linolenic -Omega 3 In the news Research on
preventing heart disease
Fish oil supplements?
Eat the fish!
Too much fish oil acts a blood thinner.
Dark meat fish or cold water fish.
Bass, cod, salmon

Phospholipids
Glycerol with 2 fatty acids plus choline or similar compound
Lecithin Supplement not needed Enough made in liver Emulsifiers Major part of cell membrane

2 fatty acids & 1 choline
Phospholipid formed

Sterols
Cholesterol Vitamin D Sex hormones Adrenocortical hormones

Plant sterols
Poorly absorbed Compete with CHOL absorption Can decrease CHOL absorption up
to 50% Subject of research & TV ads Phytoestrogens-hot topic in
women’s health

Sterols
Cholesterol made in liver, not essential part of cell membranes precursor of bile acids helps vitamin D be formed part of hormones

Cholesterol
Bile is made from cholesterol stored in gall bladder prepares fat for digestion after fat digestion,some is excreted
and some is reabsorbed CHOL in reabsorbed bile is reused Medications and dietary fiber is used
to bind bile-reduces total CHOL

Cholesterol
Some travels in bloodstream as part of lipoproteins
Can become trapped in arteries and contribute to heart disease
High CHOL and high fat diet increased risk of LDL elevation

Dietary Fat
Excessive intakes =obesity =diabetes mellitus =cancer =heart disease

Obesity
Imbalance Too many kcal in Not enough energy expenditure
Percentage of fat in diet varies Do not restrict fat until age 2 Gradually change diet to match
dietary guidelines during childhood

Cancer Fat may promote, but does not
cause cancer High fat diets linked to increased
risk for Colon and rectum Prostate Endometrium
More research needed

Cardiovascular Disease Leading cause of death Plaque development causes
increased incidence of blood clots Strongest diet connection
Too much saturated fat in the diet Polyunsaturated fats have both +/-
effects Monounsaturated fats more beneficial

Saturated Fat
Associated with serum CHOL elevation
Main dietary determinant of blood CHOL levels
Omega 3 fatty acids reduce CHOL most delay cancer development?

Polyunsaturated Fat
Associated with total serum CHOL reduction
Reduction LDL-C Shorter chained, unsaturated fats
are softer and melt more easily. Lard is hard.

Monounsaturated Fat
Associated with serum TG reduction
Maintenance of HDL-C Serum CHOL neutral

Fat substitutes
Instead of, not in addition Long term health effects not
known Simplesse Olestra Oatrim

Sources
Meats, nuts, seeds, olives, avocados
Ice cream Bakery products Salad dressing Milk Fried foods

Hydrogenated Fats
Unsaturated vegetable oils Hydrogen bonds have been added More stable products More solid products

Trans and CIS fatty acids
CIS fatty acid-naturally occurring bond H2 on same side of chain
Trans fatty acid-commercially made bond H2 on opposite sides makes more solid texture research says too much will raise
serum lipid levels limit to 5-10% of fat

Kcal and Grams Kcal from fat confusing for many
persons Count fat grams 20-30% of kcal from fat usually
appropriate X number of kcal by percent of kcal
from fat wanted Divide by 9

Dietary guidelines
Total fat <30% Saturated fat <10% Polyunsaturated <10% Monounsaturated <10% CHOL <300 mg New TLC diet: 200 mg CHOL, up to
35% fat if mostly monounsaturated