Lipids
-
Upload
romy-friedman -
Category
Environment
-
view
78 -
download
0
Transcript of Lipids

LipidsHL Biology
Cells & Biomolecules

Homework review
• Are fats part of a healthy diet??

Lipids
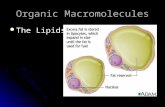
• A group of compounds that mix poorly with water.
• Varied in form of function• Three main types:– Triglycerides (fats)– Phospholipids– Steroids
This lesson will focus on Triglycerides (fats)

Triglycerides (fats)• Triglycerides are made from two kinds of
smaller molecules: • One glycerol and three fatty acids.• Formed by condensation reactions

Fatty Acids
• There are two parts to a fatty acid:– A carboxyl group (COOH)– An unbranched hydrocarbon chain.
Fatty acids can be saturated, monounsaturated and polyunsaturated.

Spot the difference?

Types of Fatty Acids
• Saturated = all of the carbon atoms in the chain are connected by single covalent bond, meaning there is no more room for Hydrogen atoms (It is saturated with hydrogen!)
• Monounsaturated = only one double bond• Polyunsaturated = two or more double bonds


Saturated Fats
• A fat made from saturated fatty acids is called a saturated fat
• Most animal fats are saturated• The lack of double bonds and their flexibility
allow the fat molecules to pack together tightly, forming solids at room temperature.
• Eg. Lard or butter


Unsaturated fats
• The fats of plants and fish are normally unsaturated
• They are usually liquid at room temperature and referred to as oils,
• Eg. Olive oil, fish oil• Nearly all natural occurring unsaturated fats
have Cis double bonds.

Cis or Trans Unsaturated Fats
• Double bonds can be cis or trans bonds.• Cis bonds – all hydrogen atoms are bonded to
carbon atoms on the same side. Results in a “bent” structure.
• Trans bonds – hydrogen atoms are bonded to carbon atoms on opposite sides of a double bond. Results in a “straight” structure.

Spot the difference?
How do you think this affects the melting point of the fat?

Cis or Trans
• The kinks where the cis double bonds are located prevent the molecules from packing together closely enough to solidify at room temperature.
• This is why most natural unsaturated fats are liquid at room temperature (oils)

Trans Fats

Trans fats
• Unsaturated fats can be synthetically converted to trans fats to make them a solid at room temperature.
• Eg, margarine and peanut butter.• Trans-fats are normally found in heavily
processed food.
What are the effects of trans-fats in diet?

Lipids for Energy storage

Lipids for Energy Storage
• Lipids are better for long-term energy storage compared to carbohydrates.
• Lipids store twice as much as carbohydrates energy per gram.
• Glycogen is stored with water, making it even heavier.
• Lipids can store 6 times more energy per gram than carbohydrates.