Lesson Four Structure of a Gene. Gene Structure What is a gene? Gene: a unit of DNA on a chromosome...
-
Upload
brett-carson -
Category
Documents
-
view
268 -
download
0
description
Transcript of Lesson Four Structure of a Gene. Gene Structure What is a gene? Gene: a unit of DNA on a chromosome...

Lesson Four
Structure of a Gene

Gene Structure What is a gene? Gene: a unit of DNA on a chromosome
that codes for a protein(s)– Exons– Introns– Promoter sequences– Terminator sequences
Other regulatory sequences (enhancers, silencers), which may be far from major components of a gene

Gene Structure
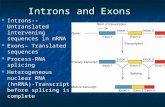
Exons: contain the bases that are utilized in coding for the protein
Introns: contain bases that are not utilized in coding for proteins and intervene between the exons – Introns are spliced out

Gene Structure Promoter: bases that provide a signal
to tell the cell’s machinery where to begin transcription, usually before or within a gene
Terminator: bases that provide a signal to tell the cell’s machinery where to stop transcription, usually at the end of a gene

Gene Structure A typical gene might look something like this:
This gene has 3 exons and 2 introns
----------
----------
= exon= intron
= promoter
= terminator

Lesson Five
Transcription

Transcription The process of using DNA (a gene) as a template to produce
messenger RNA (mRNA)
Occurs in the nucleus
Template strand – the strand of DNA that is accessed to make mRNA
Coding strand – the strand of DNA that is NOT accessed to make mRNA. The mRNA that is made from the template strand will be identical to the coding strand (with the exception of U’s for T’s)


RNA Modification Trimming: removing bases from the 5’ and 3’
ends
Capping: adding a methylated G to the 5’ end– Necessary for RNA localization to the ribosome
Tailing: addition of A’s to the 3’ end of the mRNA– More A’s = more stabile mRNA
Splicing: removing introns prior to mRNA transport to the nucleus


Lesson Six
Translation

Translation The process of using mRNA as a
template to generate a polypeptide that will eventually become a mature protein
Also called protein synthesis Requires the ‘genetic code’
– Based on 64 codons, each with 3 nucleotides
– Provides the link between DNA and protein sequence

Translation Requires Different Types of DNA
mRNA: messenger RNA; major product of transcription– Represents the code for the primary amino acid sequence
of a protein– Only type of RNA that is translated
tRNA: transfer RNA– Recognizes the mRNA code (tri-nucleotide) and brings
with it (or transfers) the appropriate amino acid to the protein
– Link between mRNA and protein rRNA: ribosomal RNA
– Part of the ribosomes – Involved with translation by helping to align the mRNAs
and tRNAs







Protein Processing
Final transport

Primary control of gene expression
Genomics to Proteomics

Lesson Seven
Mutations

Point Mutations Involves a single base pair
– Substitution, insertion, deletion– SNPs
May not affect amino acid sequence– Same sense (silent, neutral, synonymous, same sense)– Due to redundancy of the genetic code
May affect amino acid sequence (nonsynonymous)– Missense (results from a change in an amino acid)– Nonsense (results from a change to a stop codon –
truncated protein)– Frame shift mutations (insertion or deletion of 1+ bases
- alters the reading frame)

Missense MutationSickle Cell Anemia