Lesson 5 the human nervous system
-
Upload
coburgpsych -
Category
Education
-
view
539 -
download
2
Transcript of Lesson 5 the human nervous system
Lesson 1: The Human Nervous System
Learning Intentions:
• Describe the role and function of the two major divisions of the nervous system: CNS and PNS • Describe the role and function of the Somatic Nervous System including
the roles of the motor, sensory and interneurons
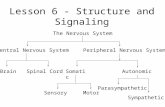
Today’s lesson -Central Nervous System CNS -Peripheral Nervous System PNS -Somatic division of PNS
Next Lesson -Autonomic division of PNS (sympathetic and parasympathetic)
Central Nervous System CNS
- The central nervous system is that part of the nervous system that consists of the brain and spinal cord.- The brain is the centre of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. The brain controls the other organ systems of the body, either by activating muscles or by causing secretion of chemicals such as hormones and neurotransmitters.- The spinal cord is the main pathway for information connecting the brain and peripheral nervous system.
Peripheral Nervous System PNS
-Peripheral means outside the centre or in the surrounding areas.
-The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is comprised of all the neurons outside the central nervous system.
-It is located mainly in the body (with the exception of the spinal cord), although the cranial nerves in the head (outside the skull) are also part of the peripheral nervous system. These are the only nerves in the PNS that enter the brain (CNS) without going via the spinal cord.
-The PNS provides the pathway from the brain and spinal cord to all other parts of the body (including the internal organs and glands).
-It allows two-way communication between the CNS and all other areas. -The peripheral nervous system is separated into two other divisions, which are distinguished by their different functions. These are the somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system.
Somatic Nervous System SNS
The somatic nervous system is involved in all skeletal muscle activity enabling you to perform voluntary actions such as writing, texting,
chewing, talking, goal-shooting, riding a surfboard and dancing.
Sensory neurons (also called afferent neurons) are specialised nerve cells that receive and carry sensory messages. These neurons generally respond only to a particular type of stimulation. For example, sensory neurons in the eyes respond only to light, but not to other types of stimulation such as mechanical energy (sound), odours (smell) or pressure (touch).
Sensory Neuron
Motor neurons (also called efferent neurons) are specialised nerve cells that carry messages to skeletal muscles causing them to contract or relax
Motor Neuron
Interneurons (also called connecting neurons) perform the important function of making the connection between sensory and motor neurons, which rarely ever connect directly. They are found only in the CNS and they are the most abundant type of neuron in the brain.
Interneuron