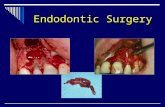
Lecture 6 Periapical Periodontitis (Slide)
Transcript of Lecture 6 Periapical Periodontitis (Slide)
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 6 Periapical Periodontitis (Slide)
1/25
Periapical PeriodontitisPeriapical Periodontitis
Dr. Rima SafadiDr. Rima Safadi
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 6 Periapical Periodontitis (Slide)
2/25
Periapical PeriodontitisPeriapical Periodontitis
Acute and chronic periapical periododntitisAcute and chronic periapical periododntitis
Dynamic processDynamic process
Rich periapical collateral circulationRich periapical collateral circulation Enhances ability of tissue to healEnhances ability of tissue to heal
Often accompanied by resorption of boneOften accompanied by resorption of bone
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 6 Periapical Periodontitis (Slide)
3/25
Etiology/ Periapical PeriodontitisEtiology/ Periapical Periodontitis
Pulpitis and pulpPulpitis and pulp
necrosisnecrosis
Bacterial toxinsBacterial toxins
Products ofProducts ofinflammationinflammation
TraumaTrauma
Occlusal traumaOcclusal trauma
Orthodontic treatmentOrthodontic treatment
Biting on a hard bodyBiting on a hard body
Often acute, transientOften acute, transient
Endodontic treatmentEndodontic treatment::
MechanicalMechanical
ChemicalChemical
BacterialBacterial
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 6 Periapical Periodontitis (Slide)
4/25
Acute Periapical PeriodontitisAcute Periapical Periodontitis
Acute exudateAcute exudate
Confined spaceConfined space
Thermal stimuli and painThermal stimuli and painLocalized painLocalized pain
Proprioceptive nerve endings in PDLProprioceptive nerve endings in PDL
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 6 Periapical Periodontitis (Slide)
5/25
Acute Periapical PeriodontitisAcute Periapical Periodontitis
Radiographically:Radiographically:
normalnormal
Or slight widening ofOr slight widening of
PDLPDL Less well definedLess well defined
lamina duralamina dura
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 6 Periapical Periodontitis (Slide)
6/25
Acute Periapical PeriodontitisAcute Periapical Periodontitis
Out comes:Out comes:
Resolve if trauma is transientResolve if trauma is transient
Chronic periapical periodontitis: if irritationChronic periapical periodontitis: if irritation
persistspersists
Acute periapical abscess (massive exudate)Acute periapical abscess (massive exudate)
If severe irritation persists like tissue necrosisIf severe irritation persists like tissue necrosis
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 6 Periapical Periodontitis (Slide)
7/25
Chronic periapical periodontitisChronic periapical periodontitis
Persistent irritationPersistent irritation
Resorption of periapicalResorption of periapical
alveolar bonealveolar bone
Replaced by inflamedReplaced by inflamed
granulation tissuegranulation tissue
Dense bundles of collagenDense bundles of collagen
fibers at peripheryfibers at periphery
Capsule likeCapsule like
Attached to root apeAttached to root apexx
Asymptomatic or mildAsymptomatic or mild
tenderness to percussiontenderness to percussion
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 6 Periapical Periodontitis (Slide)
8/25
Chronic periapical periodontitisChronic periapical periodontitis
Radiographically:Radiographically:
Widening of PDLWidening of PDL
Well circumscribed RLWell circumscribed RL
with or withoutwith or withoutcorticationcortication
Based on cellularBased on cellular
activity of marginactivity of margin
Resorption ofResorption of
cementum or dentinecementum or dentine
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 6 Periapical Periodontitis (Slide)
9/25
Periapical GranulomaPeriapical Granuloma
A localized mass of chronically inflamedA localized mass of chronically inflamed
granulation tissue that forms at the apex of agranulation tissue that forms at the apex of a
non-vital tooth root.non-vital tooth root.
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 6 Periapical Periodontitis (Slide)
10/25
Periapical granulomaPeriapical granuloma
HistologicallyHistologicallyGranulation tissue: infiltratedGranulation tissue: infiltratedmainly by lymphocytes,mainly by lymphocytes,macrophages and plasmamacrophages and plasmacellscells
Antigenic stimulation from theAntigenic stimulation from thepulppulp
Cholesterol clefts formationCholesterol clefts formation
Haemosidren depositsHaemosidren deposits
Multinucleated giant cellsMultinucleated giant cells
Foam cells-lipid ladenFoam cells-lipid ladenmacrophagesmacrophages
Proliferation of epithelial restsProliferation of epithelial restsof Malassezof Malassez
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 6 Periapical Periodontitis (Slide)
11/25
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 6 Periapical Periodontitis (Slide)
12/25
Proliferation of epithelial cell rest ofProliferation of epithelial cell rest of
MalassezMalassez
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 6 Periapical Periodontitis (Slide)
13/25
Sequelae of Periapical GranulomaSequelae of Periapical Granuloma
1. Equilibrium with host immunlogic response:1. Equilibrium with host immunlogic response:static for yearsstatic for years
2. Acute exacerbation2. Acute exacerbation
Patient with acute symptomsPatient with acute symptoms3. Suppuration:3. Suppuration:
AcuteAcute periapical abscessperiapical abscessRapid onset of pain and swelling, tenderness to percussionRapid onset of pain and swelling, tenderness to percussion
ChronicChronic Abscess: little tendency to enlalrge or spreadAbscess: little tendency to enlalrge or spread4. Proliferation of epithelial cell rests of Malassez4. Proliferation of epithelial cell rests of Malassez
Radicular cystRadicular cyst
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 6 Periapical Periodontitis (Slide)
14/25
Sequelae of Periapical GranulomaSequelae of Periapical Granuloma
5. Osteosclerosis: low5. Osteosclerosis: low
grade irritationgrade irritation
6. Hypercementosis6. Hypercementosis
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 6 Periapical Periodontitis (Slide)
15/25
Periapical AbscessPeriapical AbscessRadiographic FeaturesRadiographic Features
If abscess develops directlyIf abscess develops directlyfrom pulp inflammation andfrom pulp inflammation andnecrosis, there may be nonecrosis, there may be noradiographic changes initially,radiographic changes initially,
except forexcept forslight widening ofslight widening ofthe PDL space.the PDL space.
If the abscess developsIf the abscess develops
through acute exacerbation inthrough acute exacerbation inan area of previously existingan area of previously existingchronic inflammation, achronic inflammation, a distinctdistinctradiolucent area is seen at theradiolucent area is seen at theapex.apex.
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 6 Periapical Periodontitis (Slide)
16/25
Acute periapical abscess andAcute periapical abscess and
spread of inflammationspread of inflammation
From acute PAFrom acute PA
periodontitisperiodontitis
Or chronic PAOr chronic PA
granulomagranulomaBacteriology: mixedBacteriology: mixed
infection mainlyinfection mainly
anaerobesanaerobes
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 6 Periapical Periodontitis (Slide)
17/25
Acute periapical abscess andAcute periapical abscess and
spread of inflammationspread of inflammation
Routes of Spread:Routes of Spread:
Through root canalThrough root canal
PDL into gingival sulcusPDL into gingival sulcusThrough Cancellous bone and perforatesThrough Cancellous bone and perforates
cortexcortex
Lingual plates are denser than buccalLingual plates are denser than buccal Origin of muscles guides spread of pusOrigin of muscles guides spread of pus
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 6 Periapical Periodontitis (Slide)
18/25
Acute periapical abscess andAcute periapical abscess and
spread of inflammationspread of inflammation
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 6 Periapical Periodontitis (Slide)
19/25
Acute periapical abscess andAcute periapical abscess and
spread of inflammationspread of inflammation
Drain into oral cavity via a sinusDrain into oral cavity via a sinus
Small swelling may develop before openingSmall swelling may develop before opening
A nodule of granulation tissue marks theA nodule of granulation tissue marks the
opening of sinusopening of sinus
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 6 Periapical Periodontitis (Slide)
20/25
Acute periapical abscess andAcute periapical abscess and
spread of inflammationspread of inflammation
Palatal abscessPalatal abscess
Molar regions of bothMolar regions of both
jaws:jaws:
Penetrate above orPenetrate above orbelow buccinatorbelow buccinator
muscle attachments:muscle attachments:
CellulitisCellulitis
Localized soft tissueLocalized soft tissueabscessabscess
Drain on skinDrain on skin
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 6 Periapical Periodontitis (Slide)
21/25
Acute periapical abscess andAcute periapical abscess and
spread of inflammationspread of inflammation
Anterior maxillary teeth:Anterior maxillary teeth:
Upper lipUpper lip
Perforate abovePerforate above
attachment of lip muscles:attachment of lip muscles:
infection passes to innerinfection passes to innereye canthus, nasolabialeye canthus, nasolabial
fold, lower eyelidfold, lower eyelid
Maxillary molars:Maxillary molars:
discharge into thedischarge into the
maxillary sinusmaxillary sinus
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 6 Periapical Periodontitis (Slide)
22/25
Acute periapical abscess andAcute periapical abscess and
spread of inflammationspread of inflammation
Mandibular premolarMandibular premolaror molar: belowor molar: belowattachment of MHattachment of MHmusclemuscle Submandibular space,Submandibular space,
communicates withcommunicates withlateral pharyngeallateral pharyngealspacesspaces
Mandibular incisor:Mandibular incisor:subcutaneoussubcutaneousabscessabscess
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 6 Periapical Periodontitis (Slide)
23/25
CellulitisCellulitis
Rapid spread of inflammationRapid spread of inflammationof the soft tissues associatedof the soft tissues associatedwith streptococcal infectionwith streptococcal infection
Large amounts ofLarge amounts ofstreptokinase andstreptokinase and
hyaluronidasehyaluronidase Mainly: InflammatoryMainly: Inflammatory
edemaedema
ClinicallyClinically
Poorly localizedPoorly localized PainfulPainful
MalaiseMalaise
Elevated temperatureElevated temperature
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 6 Periapical Periodontitis (Slide)
24/25
Complications: Cavernous sinusComplications: Cavernous sinus
thrombosis due to involvement of veins atthrombosis due to involvement of veins at
inner canthus of the eyeinner canthus of the eye
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 6 Periapical Periodontitis (Slide)
25/25
Ludwig`s anginaLudwig`s angina
Severe cellulitis initially involvingSevere cellulitis initially involving
submandibular spacesubmandibular space
SwellingSwelling inin floor of the mouth, elevatedfloor of the mouth, elevated
tonguetongue
edema of glottis may occuredema of glottis may occur