LASER THERAPY IN GINGIVAL HYPERPLASIA: A CASE REPORT · - from a gingival cyst - erupting We...
Transcript of LASER THERAPY IN GINGIVAL HYPERPLASIA: A CASE REPORT · - from a gingival cyst - erupting We...
:
ReferencesReferences
Covani U., Crespi R., Grassi R.: Covani U., Crespi R., Grassi R.: L’utilizzo clinico del laser
in odontoiatria. SEE-Firenze, 2004
TamaritTamarit--Borrás M., DelgadoBorrás M., Delgado--Molina E., BeriniMolina E., Berini--Aytés L., Aytés L.,
GayGay--Escoda C.: Escoda C.: Removal of hyperplastic
lesions of the oral cavity. A retrospective
study of 128 cases. 2005
Kelman MM, Poiman DJ, Jacobson BL.: Kelman MM, Poiman DJ, Jacobson BL.: Laser
gingivectomy for pediatrics. A case report.
2010
Coluzzi DJ, Rice JH, Coleton S.: Coluzzi DJ, Rice JH, Coleton S.: The coming of age of
lasers in dentistry. 1998
ODONTOSTOMATOLOGICHEFIRENZE-SIENA, 14-16 Aprile 2011
University of BariDepartment of Odontostomatology and Surgery MD: Prof. D. Devito
Calabrodental S.r.l. Operative Unit of Maxillofacial Surgery, Calabria Region – Crotone. MD: Dott. M.
W. Marrelli
LASER THERAPY IN GINGIVAL HYPERPLASIA: A CASE REPORT
F. Inchingolo, F. Schinco* G. Dipalma, M. Serafini, S. Di Teodoro, A. M. Inchingolo, M. De Carolis, M. Marrelli,
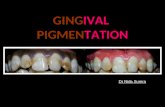
A. Palladino, A. D. InchingoloGingival hyperplasia is an increase in volume of the gingival tiGingival hyperplasia is an increase in volume of the gingival tiGingival hyperplasia is an increase in volume of the gingival tiGingival hyperplasia is an increase in volume of the gingival tissue, together with an increase in the number of ssue, together with an increase in the number of ssue, together with an increase in the number of ssue, together with an increase in the number of cells. The gingiva is reddish or redcells. The gingiva is reddish or redcells. The gingiva is reddish or redcells. The gingiva is reddish or red----bluish, with an increased size both in coronal and buccobluish, with an increased size both in coronal and buccobluish, with an increased size both in coronal and buccobluish, with an increased size both in coronal and bucco----lingual direction. lingual direction. lingual direction. lingual direction. Several etiologic factors are responsible for localized gingivalSeveral etiologic factors are responsible for localized gingivalSeveral etiologic factors are responsible for localized gingivalSeveral etiologic factors are responsible for localized gingival hyperplasia: it can be classified from a topographic hyperplasia: it can be classified from a topographic hyperplasia: it can be classified from a topographic hyperplasia: it can be classified from a topographic and ethiopatogenetic point of view. and ethiopatogenetic point of view. and ethiopatogenetic point of view. and ethiopatogenetic point of view. The therapy varies according to its origin and nature: it rangesThe therapy varies according to its origin and nature: it rangesThe therapy varies according to its origin and nature: it rangesThe therapy varies according to its origin and nature: it ranges from etiologic therapy, which is the removal of the from etiologic therapy, which is the removal of the from etiologic therapy, which is the removal of the from etiologic therapy, which is the removal of the irritating stimulus, like in inflammatory hyperplasia, to surgicirritating stimulus, like in inflammatory hyperplasia, to surgicirritating stimulus, like in inflammatory hyperplasia, to surgicirritating stimulus, like in inflammatory hyperplasia, to surgical therapy. al therapy. al therapy. al therapy. The aim of the present study is to show the advantage of using lThe aim of the present study is to show the advantage of using lThe aim of the present study is to show the advantage of using lThe aim of the present study is to show the advantage of using laser therapy in the treatment of a 14aser therapy in the treatment of a 14aser therapy in the treatment of a 14aser therapy in the treatment of a 14----yearyearyearyear----old old old old female patient, presenting with a reddish gingiva and bleeding ofemale patient, presenting with a reddish gingiva and bleeding ofemale patient, presenting with a reddish gingiva and bleeding ofemale patient, presenting with a reddish gingiva and bleeding on probing in the upper maxilla. Around the teeth n probing in the upper maxilla. Around the teeth n probing in the upper maxilla. Around the teeth n probing in the upper maxilla. Around the teeth number 13 number 13 number 13 number 13 –––– 23 there was a deep23 there was a deep23 there was a deep23 there was a deep----red sessile mass, characterized by easy bleeding. The diagnosticred sessile mass, characterized by easy bleeding. The diagnosticred sessile mass, characterized by easy bleeding. The diagnosticred sessile mass, characterized by easy bleeding. The diagnostic hypothesis hypothesis hypothesis hypothesis was epulis, but there was no histological confirmation so it waswas epulis, but there was no histological confirmation so it waswas epulis, but there was no histological confirmation so it waswas epulis, but there was no histological confirmation so it was identified as gingival hyperplasia.identified as gingival hyperplasia.identified as gingival hyperplasia.identified as gingival hyperplasia.
TOPOGRAPHIC CLASSIFICATION OF
GINGIVAL HYPERPLASIA
marginalmarginal: : limited to the marginal gingiva;
papillary:papillary: limited to the papillary gingiva;
diffused: diffused: affecting both the marginal and
papillary gingiva;
generalized: generalized: affecting the entire gingiva;
discretediscrete: : isolated, sessile or pedunculated.
ETHIOPATOGENETIC CLASSIFICATION
OF GINGIVAL HYPERPLASIA:
- inflammatory
- non inflammatory
- conditioned
- neoplastic
- from a gingival cyst
- erupting
We performed an initial preparation (hygienic phase), revaluatioWe performed an initial preparation (hygienic phase), revaluatioWe performed an initial preparation (hygienic phase), revaluatioWe performed an initial preparation (hygienic phase), revaluation, surgical n, surgical n, surgical n, surgical therapy and maintaining phase. After initial treatment, which cotherapy and maintaining phase. After initial treatment, which cotherapy and maintaining phase. After initial treatment, which cotherapy and maintaining phase. After initial treatment, which consisted in nsisted in nsisted in nsisted in plaque control, surface scaling, root planing and polishing, theplaque control, surface scaling, root planing and polishing, theplaque control, surface scaling, root planing and polishing, theplaque control, surface scaling, root planing and polishing, the clinical clinical clinical clinical examination showed the permanence of an increased gingival volumexamination showed the permanence of an increased gingival volumexamination showed the permanence of an increased gingival volumexamination showed the permanence of an increased gingival volume which e which e which e which caused masticatory disorders. caused masticatory disorders. caused masticatory disorders. caused masticatory disorders. Hyperplastic tissues were removed with laser therapy, which provHyperplastic tissues were removed with laser therapy, which provHyperplastic tissues were removed with laser therapy, which provHyperplastic tissues were removed with laser therapy, which proved ed ed ed advantageous because it was painless for the patient, did not readvantageous because it was painless for the patient, did not readvantageous because it was painless for the patient, did not readvantageous because it was painless for the patient, did not require quire quire quire anesthesia and gingival incisions, and provided better hemostasianesthesia and gingival incisions, and provided better hemostasianesthesia and gingival incisions, and provided better hemostasianesthesia and gingival incisions, and provided better hemostasis. After 15 s. After 15 s. After 15 s. After 15 days, the objective clinical examination revealed perfect healindays, the objective clinical examination revealed perfect healindays, the objective clinical examination revealed perfect healindays, the objective clinical examination revealed perfect healing of gingival g of gingival g of gingival g of gingival lesions.lesions.lesions.lesions.














![Endometrium presentation - Dr Wright[1] · Endometrial Hyperplasia Simple hyperplasia Complex hyperplasia (adenomatous) Simple atypical hyperplasia ... Progression of Hyperplasia](https://static.fdocuments.us/doc/165x107/5b8a421e7f8b9a50388bc13d/endometrium-presentation-dr-wright1-endometrial-hyperplasia-simple-hyperplasia.jpg)



