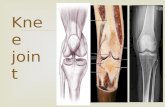
Knee Joint Knee Joint Articular surfaces : It is a large and complicated joint which includes 3...
-
Upload
joella-wilcox -
Category
Documents
-
view
224 -
download
1
Transcript of Knee Joint Knee Joint Articular surfaces : It is a large and complicated joint which includes 3...

Knee JointKnee Joint
Articular surfaces : It is a large and complicated joint which includes 3 articulations : 1- between 2 condyles of femur / and upper surfaces of 2 tibial condyles. 2- between the patella / and patellar surface of femur.
Type : 1-between the condyles of femur & tibia: is synovial hinge joint. 2-between the patella & femur : is synovial joint of plane gliding type.

Capsule of Knee JointCapsule of Knee JointAnteriorly : it is absent, replaced by pouching of synovial membrane upward beneath the quadriceps tendon, forming the suprapatellar bursa.
On each side of patella : It is strengthened by expansions from tendons of vastus lateralis & medialis.
Posteriorly : 1- the capsule is strengthened by expansion of semimembranosus ms. called oblique popliteal ligament. 2- the capsule is pierced by popliteus tendon opposite the back of lateral condyle of tibia.
Lateral view

Ligaments of knee JointLigaments of knee JointExtracapsular Ligaments : 1- Ligamentum patellae : -above, it is attached to lower border of patella./and below to tibial tuberosity. -it is a continuation of common tendon of quadriceps femoris ms. 2- lateral collateral ligament : -it is cordlike, attached above to lateral condyle of femur./and below to the head of fibula. -this ligament is not firmly adherent to the capsule. -It is separated from lateral meniscus by the tendon of popliteus ms.

3-Medial collateral ligament : -it is a flat band, attached above to medial condyle of femur./and below to medial surface of shaft of tibia. -it is firmly attached to medial lemniscus. 4- Oblique popliteal ligament -is a tendinous expansion of semimembranosus ms. -it strengthens the posterior aspect of the capsule.

Ligaments of Knee JointLigaments of Knee JointIntracapsular ligaments : 1-anterior cruciate ligament : -inferiorly : it is attached to the anterior part of intercondylar area of tibia. -superiorly : attached to posterior part of medial surface of lateral condyle of femur. -it prevents posterior displacement of femur on tibia. With knee joint flexed, it prevents tibia from
being pulled anteriorly. 2-posterior cruciate ligament : -inferiorly : it is attached to posterior part of intercondylar area of tibia. -superiorly : attached to anterior part of
lateral surface of medial condyle of femur. -it prevents anterior displacement of femur on tibia. With knee joint flexed, it
prevents tibia from being pulled posterioly.
Anterior veiw
Posterior veiw

3- Two menesci : --are c-shaped sheets of fibrocartilage, placed between condyles of femur & tibia.
--the peripheral border is thick and attached to the capsule, while the inner border is thin and concave and forms a free
edge.
--each meniscus is attached to upper surface of tibia by anterior & posterior horns. --because the medial meniscus is also attached to medial collateral ligament, it is relatively immobile.
--Their function : 1- is to deepen the upper articular surfaces of tibial condyles to receive the convex femoral condyles. 2- they serve as cushions between
the two condyles.
Upper end of tibia
Posterior aspect

Synovial MembraneSynovial Membrane It lines the capsule and attached to the articular margins.
On front and above the joint : it forms a pouch extending up beneath quadriceps femoris ms. for about 3 fingerbreadth above the patella, forming suprapatellar bursa., which helds in position by the attachement of a small portion of vastus intermedius, called articularis genu ms.
At the anterior part of the joint : it is reflected from the back of ligamentum patellae to form infrapatellar fold ,/ the free borders of the fold is called, alar folds. /It encloses infrapatellar pad of fat.

Synovial MembraneSynovial Membrane At the back of the lateral meniscus : it forms a pouch medial to popliteus tendon and separates the tendon from lateral meniscus & lateral femoral condyle.
At the back of medial meniscus : -it forms the semimembranosus bursa -it may communicate with synovial cavity of the joint.
At the back of the capsule : -It is reflected forward from the posterior part of the capsule around the front of cruciate ligaments, so cruciate ligaments lie behind the synovial membrane and not communicate with the synovial cavity (extrasynovial).

Bursae of Knee JointBursae of Knee JointThey are found wherever skin, ms. Or tendon rubs against bone.
4 are located in front of joint (anterior) / and 6 behind the joint (posterior).
Suprapatellar bursa + popliteal bursa always communicate with the joint. / semimembranosus bursa may communicate with joint.

Bursae of Knee JointBursae of Knee JointAnterior bursae : 1-suprapatellar bursa : lies beneath quadriceps ms. And communicates with joint cavity.
2-prepatellar bursa : lies in subcutaneous tissue between skin & front of lower part of patella + upper part of ligamentum patellae.
3-superficial infrapatellar bursa : lies in subcutaneous tissue between skin and front of lower part of ligamentum patellae.
4-deep infrapatellar bursa : lies between back of ligamentum patellae and tibia.

Bursae of Knee JointBursae of Knee JointPosterior bursae : 1-popliteal bursa : lies
in association with the tendon of popliteus and communicates with
the joint cavity. 2-semimembranosus bursa : is found related to insertion of semimembranosus ms. And may
communicate with joint cavity. 3- the remaining 4 bursae : are found related to : tendon of insertion of biceps + related to tendons of insertion of sartorius, gracilis, and semitendinosus muscles, lying beneath lateral & medial heads of
gastrocnemius.

RelationsRelations and and Nerve Supply Nerve Supply of Knee Jointof Knee Joint Anteriorly : prepatellar bursa.
Posteriorly : -popliteal vessels + L.Ns. -tibial N. + common peroneal N. -boundaries of popliteal fossa : upward & medially : semimembranosus & semitendinosus. Upward & laterally : biceps femoris. Downward & medially : medial head of gastrocnemius. Downward & laterally : lateral head of gastrocnemius.
Medially : sartorius, gracilis, and semitendinosus.
Laterally : biceps + common peroneal N.
N.supply : 1-femoral N. 2-Obturator N. 3-Common peroneal N. 4-Tibial N.

Movements of Knee jointMovements of Knee joint1- Extension :
-It is produced by : quadriceps femoris. -It is accompanied by slight lateral rotation of tibia (or medial rotation of femur), because the medial condyle of femur is curved from before backwards, while the lateral condyle is straight.
2- Flexion :
-by hamstring ms. : biceps, semitendinosus, and semimembranosus. -Assisted by : sartorius, gracilis, and popliteus.
3- Medial rotation : by sartorius, gracilis, and semitendinosus.
4- Lateral rotation : by biceps femoris.


Meniscal injury of knee Meniscal injury of knee jointjoint Injury of medial meniscusInjury of medial meniscus is is
moremore commoncommon than the lateral than the lateral oneone, because of its , because of its strong strong attachment to the medial attachment to the medial collateral ligament,collateral ligament, which which restricts the mobility of medial restricts the mobility of medial meniscus.meniscus.
The injury occursThe injury occurs when when femur femur is suddenly rotated medially is suddenly rotated medially on tibia,on tibia, with with semiflexed knee semiflexed knee joint specially in foot-ball joint specially in foot-ball players.players.
The tibia is usually abducted The tibia is usually abducted on femuron femur and and medial meniscusmedial meniscus is is pulled into abnormal pulled into abnormal positionposition between femoral & between femoral & tibial condyles.tibial condyles.
injury of medial meniscus on playing football.
Tearing of medial meniscus of knee joint
Tearing of peripheral part
Tearing of anterior partTearing of posterior part
Complete bucket handle tear

Strength of Knee joint /and Strength of Knee joint /and injury of its ligaments :injury of its ligaments :
The strength and stability of the joint depends The strength and stability of the joint depends largely on the strength oflargely on the strength of quadriceps femoris ms.quadriceps femoris ms. + + integrity of theintegrity of the ligamentsligaments that bind femur to tibia. that bind femur to tibia.
Medial collateral ligament injury :Medial collateral ligament injury : -It is -It is more commonmore common than the lateral one. than the lateral one. -Partial tearing of the ligament -Partial tearing of the ligament can can result result from from forced abduction forced abduction of tibia on femur. of tibia on femur. -Sprains of medial -Sprains of medial collateral lig. result in collateral lig. result in tenderness overtenderness over femoral or femoral or tibial attachments of ligament.tibial attachments of ligament.
Lateral collateral ligament injury :Lateral collateral ligament injury : -it is -it is less commonless common than medial collateral lig. than medial collateral lig. -it can -it can resultresult from from forced adductionforced adduction of tibia on femur.of tibia on femur.

Strength of Knee joint /and Strength of Knee joint /and injury of its ligaments :injury of its ligaments :
Cruciate ligaments injury :Cruciate ligaments injury : --Tears of anterior Tears of anterior cruciate ligamentcruciate ligament are common thanare common than the posterior cruciate ligament. the posterior cruciate ligament. --it is accompanied byit is accompanied by damage to damage to other structures : other structures : collateral collateral ligaments are commonly torn./ligaments are commonly torn./ or or the joint cavity fills with blood the joint cavity fills with blood (hemarthrosis)(hemarthrosis) and is swollen. and is swollen. -In -In ruptured anterior cruciate lig.,ruptured anterior cruciate lig., tibiatibia can be can be pulled excessivelypulled excessively forward forward on the femur.on the femur. ––In ruptured posterior cruciate lig.,In ruptured posterior cruciate lig., tibia tibia can be can be moved excessivelymoved excessively backward on the femur.backward on the femur.
B, test for integrity of anterior cruciate ligament.
C, test for integrity of posterior cruciate ligament.


Joints of Foot : Joints of Foot : Subtalar (Talo-calcanean) Joint Subtalar (Talo-calcanean) Joint :: Articulation :
1-inferior surface of body of talus. 2-facet on middle of upper surface of calcaneum.
Type : plane synovial joint.
Ligaments : medial, lateral talo-calcaneal ligaments + interosseous strong (talo-calcaneal) ligament between sulcus tali & sulcus calcanei.
Movements : Gliding and rotatory.

Talo-calcaneonavicular Joint Talo-calcaneonavicular Joint Articulation : 1-rounded head of talus. 2-upper surface of sustentaculum tali. 3-concave surface of navicular bone.
Type : ball and socket synovial.
Ligaments : plantar calcaneo-navicular ligament (Spring ligament) : -strong, between sustentaculum tali posteriorly & tuberosity of navicular bone anteriorly.

Calcaneo-cuboid jointCalcaneo-cuboid jointArticulation : 1-anterior end of calcaneum. 2-posterior surface of cuboid.
Type : plane synovial.
Ligaments : 1-bifurcated ligament : -strong y-shaped, lying on upper surface of joint. -stem : is attached to upper surface of anterior part of calcaneum. -lateral limb : attached to upper surface of cuboid bone. -medial limb : attached to upper surface of navicular bone.
Lateral view

Calcaneo-cuboid jointCalcaneo-cuboid joint2-Long plantar ligament : -strong ligament lying on the lower surface of joint. -between : undersurface of calcaneum & undersurface of cuboid + bases of 2nd , 3rd and 4th metatarsal bones. -it bridges over the groove for peroneus longus tendon, coverting it into a tunnel. 3-short plantar ligament : - strong ligament between undersurface of calcaneum and cuboid bones.

Movements in Subtalar, Movements in Subtalar, Talo-calcaneonavicular, Talo-calcaneonavicular, and Calcaneo-cuboid Joints :and Calcaneo-cuboid Joints :
Talo-calcaneonavicular + calcaneo-cuboidTalo-calcaneonavicular + calcaneo-cuboid joints joints are referred to as midtarsal or are referred to as midtarsal or transverse tarsal transverse tarsal joints.joints.
Inversion + eversion of footInversion + eversion of foot take place in take place in subtalar subtalar + + transverse tarsal joints.transverse tarsal joints.
Inversion is performed by :Inversion is performed by : tibialis anterior, tibialis tibialis anterior, tibialis posterior, extensor H.L + medial tendons of posterior, extensor H.L + medial tendons of extensor D.L.extensor D.L.
Eversion is performed by :Eversion is performed by : peroneus longus, peroneus longus, peroneus brevis, and peroneus tertius. Lateral peroneus brevis, and peroneus tertius. Lateral tendons of extensor digitorum longus assist.tendons of extensor digitorum longus assist.


Femoral nerve injury Femoral nerve injury (L2,3,4)(L2,3,4)
Causes : By stab or gunshot wounds, but a complete division is rare.
Motor changes : 1-quadriceps femoris muscle is paralyzed and knee cannot be extended. In walking, This is compansated for to some extend by the action of adductor ms.
Sensory changes : 1- loss of skin sensation over anterior & medial sides of thigh. ( intermediate + medial cutaneous N. of the thigh injury). 2-loss of sensation over medial side of leg + medial border of foot as far as the ball of big toe. (saphenous N. injury)

Sciatic nerve injury Sciatic nerve injury (L4,5/S1,2,3)(L4,5/S1,2,3) Causes :
1-penetrating wounds. 2-fractures of pelvis or dislocation of hip joint. 3-wrong injections into gluteus maximus or medius ( upper outer quadrant of the buttock is the best site).
In 90% of cases, common peroneal part of the sciatic N. is the most affected because its fibres lie most superficial in sciatic N.
Motor changes : 1-paralysis of hamstring ms., but weak flexion of knee is possible by the action of sartorius (Femoral N.) + gracilis (obturator N.). 2-paralysis of extensors of the leg, leading to foot drop.

Sciatic nerve injury Sciatic nerve injury (L4,5/S1,2,3)(L4,5/S1,2,3) Sensory changes :