Knee Joint A
-
Upload
kartikeya-kumar -
Category
Documents
-
view
221 -
download
0
Transcript of Knee Joint A
-
8/8/2019 Knee Joint A
1/20
Presented byShubham Rao
Knee Joint
-
8/8/2019 Knee Joint A
2/20
The Knee:
The largest and most complex joint structure Transmit Loads Participate in motion
Aids conservation of momentum Provides a force couple for body activities
-
8/8/2019 Knee Joint A
3/20
Definitions:
Kinematics is the study of movement withoutreference to forces
Kinetics is the study of movement withreference to forces
-
8/8/2019 Knee Joint A
4/20
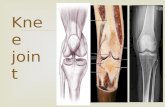
Anatomy of the knee
3 Bones
Tibia, Femur, Patella 3 Compartments Medial, Lateral, Patellofemoral
4 Ligaments MCL, LCL, ACL, PCL 2 Menisci
Articular Cartilage
-
8/8/2019 Knee Joint A
5/20
The Knee Joint
-
8/8/2019 Knee Joint A
6/20
-
8/8/2019 Knee Joint A
7/20
-
8/8/2019 Knee Joint A
8/20
Menisci Functions
Deepen the articulation
Increase area of contact Shock absorption a skier lands from a jump
Increase stability Cups the femoral condyle Nutrition of cartilage
Sweeping synovial fluid across joint
-
8/8/2019 Knee Joint A
9/20
Range of Motion
Three different planes inwhich movements of theknee takes place
1. Sagittal plane2. Frontal plane3. Transverse plane
-
8/8/2019 Knee Joint A
10/20
-
8/8/2019 Knee Joint A
11/20
Tibia-femoral motion in theTransverse plane Influenced by knee position in Sagittal plane
Ex. If knee is in full extension rotation isrestricted by interlocking of condyles withtibia
Rotation increases as the knee is flexed maximum 90 degree flexion Beyond 90 degree decreases, due to soft tissue restriction
-
8/8/2019 Knee Joint A
12/20
Tibia-femoral motion in the frontalplane Abduction and Adduction is also affected by the
amount of knee flexion Ex. Full extension precludes motion
Vulgus /Varus
-
8/8/2019 Knee Joint A
13/20
Types of motion at knee joint
Rolling Motion
Initiates flexion
Gliding Motion
Occurs at end of flexion
-
8/8/2019 Knee Joint A
14/20
Gliding Motion
-
8/8/2019 Knee Joint A
15/20
Rolling Motion
-
8/8/2019 Knee Joint A
16/20
Instantaneous Center of RotationICR "If one rigid body rotates
about another rigid body,
its motion at any instantcan be described by apoint or axis of rotationcalled the instantaneouscenter of rotation.
For normal knees Pathway of ICR is
semicircular Located on the femoral
condyles
-
8/8/2019 Knee Joint A
17/20
Joint Contact Forces
We would haveequal distributionof forces w/o any
varus or valgusstresses
-
8/8/2019 Knee Joint A
18/20
Patellar Kinematics
Patella or the knee cap is directly in contact with the femoral
condyles in flexion It is said to be lateral side dominant dominant Greater surface area of contact on the lateralside as opposed to the medial
-
8/8/2019 Knee Joint A
19/20
-
8/8/2019 Knee Joint A
20/20