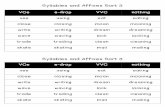
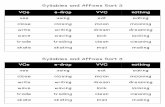
Derivational and Inflectional Affixes in @TheGoodQuote’s ...
KEY Writing Fiction Nonfiction SOL Not Tested · Aug. 24 ongoing 3.4 b Student will expand...
Transcript of KEY Writing Fiction Nonfiction SOL Not Tested · Aug. 24 ongoing 3.4 b Student will expand...

Greene County Public Schools
Language Arts Grade 3 Curriculum Guide 2015-2016 Quarters 1-4
KEY Writing Fiction Nonfiction SOL Not Tested
Bloom’s Taxonomy Abbreviations
R=Remember; U=Understand; An=Analyze; Ap=Apply; E=Evaluate; C=Create
Times/
Dates
SOL/
Strand
Objective/Content/ Essential Questions Vertical Alignment Vocabulary Cross-Curricular
Connections
First
Quarter
Aug. 18
ongoing
3.1 a-e
Introductory Activities, Introduction of
Daily Five, CAFÉ, and Initial Assessments.
Use effective communication skills in group
activities. ** Not Tested
a. Listen attentively by making eye contact,
facing the speaker, asking questions and
summarizing what is said. U
b. Ask and respond to questions from teachers
and other group members. U
c. Explain what has been learned. U
d. Use language appropriate for context. AP
e. Increase listening and speaking vocabularies
R
Essential Knowledge
To be successful with this standard, students are
expected to
participate in a range of collaborative discussions
building on others’ ideas and clearly expressing
their own (e.g., one-on-one, small-group, teacher
led).
engage in taking turns in conversations by:
making certain all group members have an
opportunity to contribute;
listening attentively by making eye contact
4.2b Listen and record
information
2.3d Retell
information shared by
others
4.1b Contribute to
group discussions
across content areas.
4.1e Use
grammatically correct
language and specific
vocabulary to
communicate ideas.
2.2a Increase listening
and speaking
vocabularies.
Comprehension
Extend
Vocabulary
Fluency
Understanding
Accuracy
Stamina
Listening
attentively
Summarizing
Eye contact
Explain
Language
Vocabulary
Units-Geography-
Create a map of a good
reader/writer, draw map of
classroom and label, Me on
the Map book
-Write own Me on the Map
book using complete sent
Reinforce spelling of map
terms
Math-Place Value.
Comparing numbers -
Reinforce word form in
sentences, reinforce spelling
of number words

while facing the speaker;
eliciting information or opinions from others;
supporting opinions with appropriate ideas,
examples, and details; and
indicating disagreement in a constructive
manner.
take initiative in moving a group discussion
forward by:
following rules for discussions and assigned
group roles;
contributing information that is on topic;
answering questions;
asking clarifying questions of the speaker;
summarizing the conclusions reached in the
discussion; and
explaining what has been learned.
ask and respond to questions to check for
understanding of information presented (e.g., stay
on topic, link remarks to those of others).
use language appropriate for the context of the
discussion.
increase their listening and speaking vocabularies
through group activities such as:
engaging in activities that require following
directions; and attempting to use new words in
meaningful sentences.
Aug. 24
ongoing
3.12 The student will use available technology for
reading and writing. AP
Essential Knowledge
To be successful with this standard, students are
expected to
use available technology for reading and writing.
read electronic media to gather specific
information, to gain knowledge, and for enjoyment.
use available technology to compose, edit and share
writing as well as to interact and collaborate with
others.
2.14 The student will
use available
technology for reading
and writing.
Computer
iPad
iPod
Website
Search engine
Internet
Key words
Search

ask and respond to questions about material
presented through various media formats.
Aug. 24
ongoing
3.3 a-b Apply word analysis skills when reading.
a. Use knowledge of regular and irregular
vowel patterns (based on student word study
level). AP
b. Decode regular multisyllabic words. AP
Essential Knowledge
To be successful with this standard, students are
expected to
apply knowledge of regular and irregular vowel
patterns to decode words.
apply knowledge of ambiguous vowel patterns
(e.g., ou/ow, oi/oy, oo, aw) to decode words.
apply knowledge of the change in tense (-ed),
number (-s), and degree (-er and -est) signified by
inflected endings to decode words.
decode regular multisyllabic words in order to read
fluently.
2.5a Use knowledge of
short, long, and r-
controlled vowel
patterns to decode and
spell words.
2.5c Decode regular
multisyllabic words.
Consonants
Vowel
Syllable
Compound words
Aug. 24
ongoing
3.4 b Student will expand vocabulary when
reading
b. use knowledge of roots and affixes AP
Essential Knowledge
apply knowledge of roots to decode unknown
words with the same root (e.g., company,
companion).
apply knowledge of affixes, (e.g., prefixes such as
ex-, dis-, un-, re-, mis-, non-, pre-; suffixes such as
-ly, -ful, -less, -able, -tion, -ness, and –ment) to
decode words.
determine the meaning of new words formed when
a known affix is added to the known word (e.g.,
care/careless, heat/reheat).
Review: un-, re-, dis-,
-er, -est, -s, -es, -ing, -
ed, -or
Prefix
un- in- tele- re-
im- dis- pre-
Suffix
-s -es -or -er
-ful -ly -ing -less
-ies -ed -est -y -
ied
Root (base) word
nonexamples

Aug. 24
ongoing
3.10 j The student will edit writing for correct
grammar, capitalization, punctuation, and
spelling. AP
j. Use correct spelling for frequently used sight
words,
Essential Knowledge
use correct spelling for frequently used words,
including irregular plurals (e.g., men, children).
use correct spelling for frequently used sight
words, including irregular plurals.
2.13h Use correct
spelling for commonly
used sight words,
including compound
words and regular
plurals.
Capitals
Punctuation
Period
Question mark
Exclamation point
9/1 –
10/16
3.6 a-l
Nonficti
on
(Text
Feature
s)
The student will continue to read and
demonstrate comprehension of nonfiction
texts.
a. Identify the author’s purpose. AN
b. Use prior and background knowledge as
context for new learning. AP, AN
c. Preview and use text features. AP
d. Ask and answer questions about what is
read. AN
e. Draw conclusions based on text. E
f. Summarize major points found in nonfiction
texts. AN
g. Identify the main idea. AN
h. Identify supporting details. R
j. Use reading strategies to monitor
comprehension throughout the reading process.
AP
k. Identify new information gained from
reading. R
l. Read with fluency and accuracy. AP
Essential Knowledge
monitor their comprehension throughout the
reading process by:
4.6c Explain the
author’s purpose
2.9c/4.6i Use prior and
background
knowledge as context
for new learning.
2.9a Preview the
selection using text
features.
4.6a Use text
structures, such as
type, headings, and
graphics, to predict
and categorize
information in both
print and digital.
2.9e Ask and answer
questions about what
is read
2.9f Locate
information to answer
questions.
4.6b Formulate
Author
Purpose
Prediction
Experience
Connection
Compare
Contrast
Draw conclusion
Plagiarism
Passage
directions
Fiction
Nonfiction
Problem
Solution
Questions
Paragraph
Flow chart
Decide
Important
Main reason
Read the flyer
Venn diagram
Units- Economics,
Scientific Method, Matter,
Water Cycle
Use nonfiction, content
related books to identify
text features and to read for
comprehension
Math- Rounding, Place
Value, Addition

becoming aware of when they do not
understand;
identifying exactly what is causing them
difficulty; and
generating their own questions to help
integrate units of meaning.
use text features to make meaning by:
applying phonetic strategies;
using punctuation indicators, such as commas,
periods, exclamation points, question marks,
and apostrophes showing contraction and
possession;
applying knowledge of simple and compound
sentence structures;
knowing when meaning breaks down and then
rereading to self-correct; and
using illustrations to gain information (e.g.,
maps, photographs).
identify new information gained from reading.
practice reading and rereading familiar
nonfiction texts with fluency and accuracy.
questions that might
be answered in the
selection.
4.6f Draw conclusions
and make simple
inferences using
textual information as
support
4.6e Summarize
supporting details
2.9g/4.6d ID the main
idea.
4.6k Use reading
strategies throughout
the reading process to
monitor
comprehension.4.6j ID
new information
gained from reading.
2.9h Read and reread
familiar passages with
fluency, accuracy, and
meaningful
expression.
4.6l Read with fluency
and accuracy
Web
Empty
Article
Opposite
Information
Website
Title
Story
9/1-9/18
3.10 a The student will edit writing for correct
grammar, capitalization, punctuation, and
spelling.
a. Use complete sentences. AP
Essential Knowledge
To be successful with this standard, students are
expected to
2.13 a Recognize and
use complete
sentences.
Complete
Sentence
(thought)
Subject
Predicate
Verb
Incorporate these skills into
the above stories

use complete sentences.
Noun
Adjective
9/21-9/25 3.10 c The student will edit writing for correct
grammar, capitalization, punctuation, and
spelling.
c. Use the word I in compound subjects. AP
Essential Knowledge
use the word I in compound subjects.
2.13c Capitalize all
proper nouns and the
word I
Complete
Sentence
(thought)
Subject
Predicate
Verb
Noun
Adjective
9/24-9/25 3.10 i i. Use the articles a, an, and the correctly. AP
Essential Knowledge
use articles a, an and the correctly.
Vowel
Consonant
article
Incorporate these skills into
the above stories
9/28-10/2 3.10 h The student will edit writing for correct
grammar, capitalization, punctuation and
spelling.
h. Use apostrophes with contractions AP
Essential Knowledge
punctuate correctly:
apostrophes in contractions with pronouns,
(e.g., I’d, we’ve);
2.13e Use apostrophes
in contractions and
possessives.
Apostrophe
Contraction
Possessive
pronoun
Incorporate these skills into
the above stories
10/5-
10/16
3.9 a-b The student will write for a variety of
purposes.
a. Identify the intended audience. AN
b. Use a variety of pre-writing strategies. AP
Essential Knowledge
use strategies for organization of information and
elaboration relevant to the type of writing.
4.7a Identify intended
audience
2.12a Generate ideas
before writing.
4.7c Use a variety of
pre-writing strategies
Graphic
Organizer
Pre-writing
Incorporate these skills into
the above stories

clarify writing when revising by including specific
vocabulary and information.
10/12 –
10/16
End of
First
Quarter
3.7 b The student will demonstrate
comprehension of information from a
variety of print and electronic resources.
b. Use table of contents, indices, and charts.
AP
Essential Knowledge
Use table of contents, indices, and charts.
2.10 a-b Use table of
contents, pictures,
charts, and captions
Table of contents
Index
Indices
Charts
Data
Units- Simple Machine
Use reference books to look
up content words and find
text features
Second
Quarter
10/19-
10/30
3.4 g The student will expand vocabulary when
reading.
g. Use word reference resources including the
glossary, dictionary and thesaurus. (introduce)
U, AN, AP
Essential Knowledge
using the glossary, dictionary, and thesaurus as
reference resources to learn word meanings.
Alphabetical Order
4.4c Use word-
reference materials,
including the glossary,
dictionary, and
thesaurus.
*Dictionary
*Glossary
Thesaurus
*Entry words
*Guide words
*Alphabetical
order
*Definition
(meaning)
Units- Energy
-Put vocab. in ABC order
-Use reference books to
look up vocabulary
Math-Multiplication Use
reference books to look up
vocab.
10/19 –
10/23
3.10 f f. Use commas in a simple series AP
Essential Knowledge
punctuate correctly:
commas in a simple series;
2.13j Use commas in
the salutation and
closing of a letter.
4.8e Use commas in
series, dates, and
addresses
Comma
Series
List
Units-Energy
Math-Multiplication
10/19 –
11/13
3.9 a-g
Letter
Writing
The student will write for a variety of
purposes. (letter, informative/explanatory,
narratives)
a. Identify the intended audience. AN
b. Use a variety of pre-writing strategies. C
2.12The student will
write stories, letters,
and simple
explanations:
a. generate ideas
Date
Heading
Greeting
Body
Closing
Units-Energy, Greece
Math-Multiplication,
Division

c. Write a clear topic sentence focusing on the
main idea. C
d. Write a paragraph on the same topic. C
e. Use strategies for organization of
information and elaboration according to the
type of writing. AP
f. Include details that elaborate the main idea.
C
g. Revise writing for clarity of content using
specific vocabulary and information. E
Essential Knowledge
To be successful with this standard, students are
expected to
use a variety of pre-writing strategies by:
identifying the intended audience;
using ideas from class brainstorming activities;
making lists of information;
talking to classmates about what to write;
reading texts by peer and professional authors;
using graphic organizers; and
selecting an appropriate writing form for
nonfiction writing (e.g., explanation,
directions, simple report), expressive writing
(e.g., narrative, reflection, and letter), and
creative writing (e.g., fiction and poetry).
write a clear topic sentence that focuses on the
main idea.
keep their written paragraphs on one topic.
follow the organization of particular forms of
writing for:
letters – date, greeting, body, and closing;
informative/explanatory purposes
introduce a topic and group related
information in paragraph form
use facts, definitions, opinions, quotations,
details, or other examples and information
to develop the topic
before writing
b. Organize writing to
include a beginning,
middle, and end
c. Expand writing to
include descriptive
detail
d. Revise writing for
clarity.
4.7 The student will
write cohesively for a
variety of purposes:
a. ID intended
audience
c. Use a variety of pre-
writing strategies
d. Organize writing to
convey a central idea.
e. Recognize different
modes of writing have
different patterns of
organization.
f. Write a clear topic
sentence focusing on
the main idea.
J. Revise writing for
clarity of content using
specific vocabulary
and information
Signature
Address
Audience
Graphic organizer
Main idea
Topic sentence
Supporting details
Transition words
elaborate

use specific vocabulary to inform and
explain the topic
provide a concluding statement or section
narratives
sequence events
use transition words and phrases for
sentence variety and to manage the
sequence of events
use specific vocabulary to convey
experiences and events
provide a conclusion
incorporate transitional words that clarify sequence
(e.g., first, next, and last).
use linking words (e.g., also, another, and, more)
and linking phrases (e.g., in order to, because of
this, for example) to connect ideas within
categories of information.
apply knowledge of the writing domains of
composing, written expression, and
usage/mechanics.
read their own writing orally to check for sentence
rhythm (sentence variety).
add specific details that further elaborate the main
idea.
use examples from their reading as models to
imitate in their writing.
use precise nouns, verbs, and adjectives.
use strategies for organization of information and
elaboration relevant to the type of writing.
clarify writing when revising by including specific
vocabulary and information.
10/26-
10/30
ongoing
3.4 b The student will expand vocabulary when
reading.
b. Use knowledge of roots, affixes, synonyms
and antonyms. AP
2.7c Use knowledge of
synonyms and
antonyms
2.7b Use knowledge
Synonym
Antonym
Opposite
Same
Units-Energy
Use vocabulary to reinforce
content words

Essential Knowledge
apply knowledge of roots to decode unknown
words with the same root (e.g., company,
companion).
apply knowledge of affixes, (e.g., prefixes such as
ex-, dis-, un-, re-, mis-, non-, pre-; suffixes such as
-ly, -ful, -less, -able, -tion, -ness, and –ment) to
decode words.
determine the meaning of new words formed when
a known affix is added to the known word (e.g.,
care/careless, heat/reheat).
use knowledge of synonyms (e.g., big/large,
mad/angry, ache/pain).
use knowledge of antonyms, (e.g., asleep/awake,
smile/frown, start/finish).
of prefixes and
suffixes
4.4b Use knowledge
of roots, affixes,
synonyms, antonyms,
and homophones.
**Thesaurus**
Math-Multiplication
10/26-
10/30
3.10 g g. Use simple abbreviations. AP
Essential Knowledge
use simple abbreviations.
2.13g Use knowledge
of simple
abbreviations.
Abbreviations
titles
11/6 –
11/13
3.4 c-f The student will expand vocabulary when
reading.
c. Apply meaning clues, language structure,
and phonetic strategies. AP
d. Use context to clarify meaning of unfamiliar
words. AP
e. Discuss meanings of words and develop
vocabulary by listening and reading a variety
of texts. U
f. Use vocabulary from other content areas. AP
Essential Knowledge
use context clues to verify meaning of unfamiliar
words and determine appropriate homophone
2.7 and 4.4 Students
will expand
vocabulary when
reading
Context Clues
Inference
Contractions
(3.4c)
Units-Greece
Math-Multiplication

usage.
using context clues, such as a restatement, a
synonym, an example, or a direct description or
definition included in the sentence or paragraph, to
clarify the meaning of unfamiliar words.
apply understanding of language structure to make
meaning from text by
using transition words of time sequence (e.g.,
first, second, next, later, after, and finally);
using transition words of compare-contrast
(e.g., like, unlike, different, and same); and
using transition words of cause-effect (e.g.,
because, if…then, when…then).
using vocabulary from history and social
science, mathematics, and science;
11/16 –
11/24
3.10 b The student will edit writing for correct
grammar, capitalization, punctuation, and
spelling.
b. Use transition words to vary sentence
structure. AP
Essential Knowledge
use transition words to vary sentence structure.
4.7 h Use transition
words for sentence
variety.
Transition words
(first, next, last,
then)
Units-Greece
Math – Multiplication,
Division
Write a paragraph about
how to solve a mult.
Problem using transition
words
11/16 –
12/18
3.5 a-m
Myths,
Legends
Fables
The student will read and demonstrate
comprehension of fictional text and poetry.
a. Set a purpose for reading. AP, E
b. Make connections between previous
experiences and reading selections. AN
c. Make, confirm, or revise predictions. C, E
d. Compare and contrast settings, characters,
and events. AN
e. Identify the author’s purpose. AN
2.8 and 4.5
2.8b Relate previous
experiences to the
main idea
4.5 f Describe the
relationship between
text and previously
read materials.
2.8a Make and
Myth
Legend
Fable
Moral
Hero
God/Goddess
Prediction
Experience
Connection
Units-Greece, Rome
Read Myths/Legends/Fables
and connect them to
Ancient Civ.
Math-Measurement

f. Ask and answer questions about what is read.
U, AN
g. Draw conclusions about text. E
h. Identify the problem and solution. AN
i. Identify the main idea. AN
j. Identify supporting details. R
k. Use reading strategies to monitor
comprehension throughout the reading process.
E
l. Differentiate between fiction and nonfiction.
AN
m. Read with fluency and accuracy. AP
Essential Knowledge
To be successful with this standard, students are
expected to
read for a specific purpose by:
locating specific information in a reading
selection;
identifying details that support a stated main
idea; and
expressing a stated main idea in their own
words.
make a variety of connections with the text, such
as:
connections between their own personal
experiences and what is happening in the text;
connections between the text they are reading
and other texts they have read, such as
identifying a similar plot or character; and
connections between what they already know
about the topic and what they find in the
reading that is new to them.
use specific details to make, justify, and modify
predictions by:
identifying details from their own experiences
and knowledge that supports their predictions;
identifying information from the text that
supports or contradicts a prediction; and
confirm predictions.
4.5i Make, confirm, or
revise predictions
2.8c Ask and answer
questions about what
is read.
2.8i Draw conclusions
based on the text
4.5h Draw
conclusions/make
inferences about text
2.8f/4.5e Identify the
problem and solution
2.8g/4.5c Identify the
main idea
4.5d Summarize
supporting details
4.5k Use reading
strategies to monitor
comprehension
throughout the reading
process
2.8j/4.5l read with
fluency and accuracy
Compare
Contrast
Draw conclusions
Passage
directions
Fiction
Nonfiction
Problem
Solution
Questions
Paragraph
Flow chart
Decide
Main reason
Read the flyer
Venn diagram
Web
Article
Information
Title
Story
Setting
Characters
Events
Main idea
Supporting details
Strategies
Fluency
Accuracy
Author’s purpose

revising predictions based on new
understandings.
Essential Knowledge cont.
gain meaning before, during, and after reading by:
asking and answering questions about what is
read to clarify meaning;
asking and answering questions to predict what
will happen next;
understanding that sometimes two or more
pieces of information need to be put together to
answer a question;
understanding that some questions are
answered directly in the text;
understanding that the answers to some
questions must be inferred from the reader’s
background experiences and knowledge; and
understanding the basic lessons or morals of
fairy tales, myths, folktales, legends, and fables
from diverse cultures.
apply knowledge of characterization by
describing a character’s attributes (traits,
motivations or feelings);
using evidence from the text to support
generalizations about the character;
comparing and contrasting characters within a
selection or between/among two or more
selections; and
explaining how the actions of characters
contribute to the sequence of events.
make generalizations about a character based on
that character’s response to a problem, the
character’s goal, and what the character says or
thinks.
apply knowledge of setting by:
identifying the time and place of a story, using
supporting details from the text; and
identifying the details that make two settings
similar or different.
compare and contrast settings, characters, and
events.

Essential Knowledge cont.
identify the author’s purpose (e.g., entertain,
inform, persuade).
ask and answer questions about the text to
demonstrate understanding.
draw conclusions about text to make meaning.
identify the problem (conflict) and solution, main
idea or theme, and supporting details.
use reading strategies to monitor comprehension
throughout the reading process by:
previewing and making predictions before
reading;
asking questions to confirm or refute
predictions during reading;
using context to confirm or self-correct word
recognition and
understanding, rereading as necessary;
becoming aware of when they do not
understand (e.g., by reflecting upon and
articulating what exactly is causing difficulty);
and
discussing the story or poem and/or writing a
summary after reading.
learn to differentiate between fiction and nonfiction
by distinguishing realism from fantasy, and fact
from opinion.
read with sufficient accuracy and fluency to
support comprehension.
practice reading and rereading familiar text that is
on their independent reading level to develop
fluency, accuracy, and prosody.
11/30 -
12/18
End of
Second
Quarter
3.9 a-g
Narrati
ve
Writing
The student will write for a variety of
purposes. (letter, informative/explanatory,
narratives)
a. Identify the intended audience. R
b. Use a variety of pre-writing strategies. AP
2.12The student will
write stories, letters,
and simple
explanations:
a. generate ideas
Audience
Graphic organizer
Main idea
Topic sentence
Supporting details
Units-Rome, Mali, Ancient
Civilizations
Math-Measurement

c. Write a clear topic sentence focusing on the
main idea. C
d. Write a paragraph on the same topic. C
e. Use strategies for organization of
information and elaboration according to the
type of writing. U, AP, R
f. Include details that elaborate the main idea.
C
g. Revise writing for clarity of content using
specific vocabulary and information. E
Essential Knowledge
To be successful with this standard, students are
expected to
use a variety of pre-writing strategies by:
identifying the intended audience;
using ideas from class brainstorming activities;
making lists of information;
talking to classmates about what to write;
reading texts by peer and professional authors;
using graphic organizers; and
selecting an appropriate writing form for
nonfiction writing (e.g., explanation,
directions, simple report), expressive writing
(e.g., narrative, reflection, and letter), and
creative writing (e.g., fiction and poetry).
write a clear topic sentence that focuses on the
main idea.
keep their written paragraphs on one topic.
follow the organization of particular forms of
writing for:
letters – date, greeting, body, and closing;
informative/explanatory purposes
introduce a topic and group related
information in paragraph form
use facts, definitions, opinions, quotations,
details, or other examples and information
to develop the topic
before writing
b. Organize writing to
include a beginning,
middle, and end
c. Expand writing to
include descriptive
detail
d. Revise writing for
clarity.
4.7 The student will
write cohesively for a
variety of purposes:
a. ID intended
audience
c. Use a variety of pre-
writing strategies
d. Organize writing to
convey a central idea.
e. Recognize different
modes of writing have
different patterns of
organization.
f. Write a clear topic
sentence focusing on
the main idea.
J. Revise writing for
clarity of content using
specific vocabulary
and information
Transition words
Elaborate
Paragraph
Sequence
Order
Organize
conclusion

use specific vocabulary to inform and
explain the topic
provide a concluding statement or section
narratives
sequence events
use transition words and phrases for
sentence variety and to manage the
sequence of events
use specific vocabulary to convey
experiences and events
provide a conclusion
incorporate transitional words that clarify sequence
(e.g., first, next, and last).
use linking words (e.g., also, another, and, more)
and linking phrases (e.g., in order to, because of
this, for example) to connect ideas within
categories of information.
apply knowledge of the writing domains of
composing, written expression, and
usage/mechanics.
read their own writing orally to check for sentence
rhythm (sentence variety).
add specific details that further elaborate the main
idea.
use examples from their reading as models to
imitate in their writing.
use precise nouns, verbs, and adjectives.
use strategies for organization of information and
elaboration relevant to the type of writing.
clarify writing when revising by including specific
vocabulary and information.
Third
Quarter
1/5 – 2/5
3.5 a-k
Fairy
Tales
Folk
The student will read and demonstrate
comprehension of fictional text and poetry.
a. Set a purpose for reading. AP, E
b. Make connections between previous
2.8 and 4.5
2.8b Relate previous
experiences to the
main idea
Fairy Tales
Folk Tales
Poetry
Stanza/verse
Units-Earth/Moon Cycles,
Famous Americans
Math- Time, Calendar,
Patterns, Graphing

Tales
Poetry
experiences and reading selections. AN
c. Make, confirm, or revise predictions. E
d. Compare and contrast settings, characters,
and events. E
e. Identify the author’s purpose. E
f. Ask and answer questions about what is read.
U, AN
g. Draw conclusions about text. E
h. Identify the problem and solution. AN
i. Identify the main idea. AN
j. Identify supporting details. R
k. Use reading strategies to monitor
comprehension throughout the reading process.
AP
l. Differentiate between fiction and nonfiction.
AN
m. Read with fluency and accuracy. AP
Essential Knowledge
To be successful with this standard, students are
expected to
read for a specific purpose by:
locating specific information in a reading
selection;
identifying details that support a stated main
idea; and
expressing a stated main idea in their own
words.
make a variety of connections with the text, such
as:
connections between their own personal
experiences and what is happening in the text;
connections between the text they are reading
and other texts they have read, such as
identifying a similar plot or character; and
connections between what they already know
about the topic and what they find in the
reading that is new to them.
4.5 f Describe the
relationship between
text and previously
read materials.
2.8a Make and
confirm predictions.
4.5i Make, confirm, or
revise predictions
2.8c Ask and answer
questions about what
is read.
2.8i Draw conclusions
based on the text
4.5h Draw
conclusions/make
inferences about text
2.8f/4.5e Identify the
problem and solution
2.8g/4.5c Identify the
main idea
4.5d Summarize
supporting details
4.5k Use reading
strategies to monitor
comprehension
throughout the reading
process
2.8j/4.5l read with
fluency and accuracy
rhyme
Prediction
Experience
Connection
Compare
Contrast
Draw conclusions
Passage
directions
Fiction
Nonfiction
Problem
Solution
Questions
Paragraph
Flow chart
Decide
Main reason
Read the flyer
Venn diagram
Web
Article
Information
Title
Story
Setting
Characters
Events
Main idea
Supporting details
Strategies
Fluency
Accuracy
Write word problems using
characters, skills listed
above.

use specific details to make, justify, and modify
predictions by:
identifying details from their own experiences
and knowledge that supports their predictions;
identifying information from the text that
supports or contradicts a prediction; and
revising predictions based on new
understandings.
gain meaning before, during, and after reading by:
asking and answering questions about what is
read to clarify meaning;
asking and answering questions to predict what
will happen next;
understanding that sometimes two or more
pieces of information need to be put together to
answer a question;
understanding that some questions are
answered directly in the text;
understanding that the answers to some
questions must be inferred from the reader’s
background experiences and knowledge; and
understanding the basic lessons or morals of
fairy tales, myths, folktales, legends, and fables
from diverse cultures.
apply knowledge of characterization by
describing a character’s attributes (traits,
motivations or feelings);
using evidence from the text to support
generalizations about the character;
comparing and contrasting characters within a
selection or between/among two or more
selections; and
explaining how the actions of characters
contribute to the sequence of events.
make generalizations about a character based on
that character’s response to a problem, the
character’s goal, and what the character says or
thinks.
apply knowledge of setting by:
identifying the time and place of a story, using
supporting details from the text; and
Author’s purpose

Essential Knowledge Cont.
identifying the details that make two settings
similar or different.
compare and contrast settings, characters, and
events.
identify the author’s purpose (e.g., entertain,
inform, persuade).
ask and answer questions about the text to
demonstrate understanding.
draw conclusions about text to make meaning.
identify the problem (conflict) and solution, main
idea or theme, and supporting details.
use reading strategies to monitor comprehension
throughout the reading process by:
previewing and making predictions before
reading;
asking questions to confirm or refute
predictions during reading;
using context to confirm or self-correct word
recognition and
understanding, rereading as necessary;
becoming aware of when they do not
understand (e.g., by reflecting upon and
articulating what exactly is causing difficulty);
and
discussing the story or poem and/or writing a
summary after reading.
1/5 – 1/15 3.10 j j. Use correct spelling for irregular plurals AP
Essential Knowledge
use correct spelling for frequently used words,
including irregular plurals (e.g., men, children).
use correct spelling for frequently used sight
words, including irregular plurals..
2.13h Use correct
spelling for commonly
used sight words,
including compound
words and regular
plurals.
4.8g Use correct
spelling for frequently
Plural
Singular
Irregular
Units-Earth/Moon Cycles,
Famous Americans
Use concepts from units in
plural examples

used words, including
common homophones.
1/20 –
1/29
3.10 e e. Use singular possessives. AP
Essential Knowledge
use singular possessives.
2.13 f Use
contractions and
possessives.
4.8h Use singular
possessives.
Possessive
Apostrophe
ownership
Units - Civics/ Famous
Americans
Math - Graphing
2/1 – 2/5 3.10 d d. Use past and present verbs. AP
Essential Knowledge
use past and present verbs
Verb
Past/present
Action
Linking(helper)
verb
Units - Civics/ Famous
Americans
Math - Graphing
2/8 – 2/27 3.6 i The student will continue to read and
demonstrate comprehension of nonfiction
texts.
i. Compare and contrast the characteristics of
biographies and autobiographies. AN
Essential Knowledge
compare and contrast the characteristics of
biographies and autobiographies.
Biography
Autobiography
Compare
Contrast
Time line
Units-Civics/Famous
Americans, Soil
Math- Graphing,
Fractions
Integrate with units by
reading Auto/Bio of Famous
Americans
2/9 – 3/11
3.9 a-g
Explana
tory/
Informa
tive
Writing
To be successful with this standard, students are
expected to
use a variety of pre-writing strategies by:
identifying the intended audience;
using ideas from class brainstorming activities;
making lists of information;
talking to classmates about what to write;
reading texts by peer and professional authors;
using graphic organizers; and
selecting an appropriate writing form for
nonfiction writing (e.g., explanation,
2.12The student will
write stories, letters,
and simple
explanations:
a. generate ideas
before writing
b. Organize writing to
include a beginning,
middle, and end
Audience
Graphic organizer
Main idea
Topic sentence
Supporting details
Transition words
Elaborate
Paragraph
Sequence
Units-Civics/Famous
Americans, Soil
Math-
Probability/Measurement
Write a bio of an explorer or
famous American
Determine probability of
survival for explorers given

directions, simple report), expressive writing
(e.g., narrative, reflection, and letter), and
creative writing (e.g., fiction and poetry).
write a clear topic sentence that focuses on the
main idea.
keep their written paragraphs on one topic.
follow the organization of particular forms of
writing for:
letters – date, greeting, body, and closing;
informative/explanatory purposes
introduce a topic and group related
information in paragraph form
use facts, definitions, opinions, quotations,
details, or other examples and information
to develop the topic
use specific vocabulary to inform and
explain the topic
provide a concluding statement or section
narratives
sequence events
use transition words and phrases for
sentence variety and to manage the
sequence of events
use specific vocabulary to convey
experiences and events
provide a conclusion
incorporate transitional words that clarify sequence
(e.g., first, next, and last).
use linking words (e.g., also, another, and, more)
and linking phrases (e.g., in order to, because of
this, for example) to connect ideas within
categories of information.
apply knowledge of the writing domains of
composing, written expression, and
usage/mechanics.
read their own writing orally to check for sentence
rhythm (sentence variety).
add specific details that further elaborate the main
c. Expand writing to
include descriptive
detail
d. Revise writing for
clarity.
4.7 The student will
write cohesively for a
variety of purposes:
a. ID intended
audience
c. Use a variety of pre-
writing strategies
d. Organize writing to
convey a central idea.
e. Recognize different
modes of writing have
different patterns of
organization.
f. Write a clear topic
sentence focusing on
the main idea.
J. Revise writing for
clarity of content using
specific vocabulary
and information
Order
Organize
conclusion
certain conditions

idea.
use examples from their reading as models to
imitate in their writing.
use precise nouns, verbs, and adjectives.
use strategies for organization of information and
elaboration relevant to the type of writing.
clarify writing when revising by including specific
vocabulary and information.
3/2 – 3/11
End of
Third
Quarter
3.4 a The student will expand vocabulary when
reading.
a. Use knowledge of homophones. AP
Essential Knowledge
use knowledge of homophones (e.g., be/bee,
hear/here, and sea/see) to understand unfamiliar
words.
2.7a/4.4a Use
knowledge of
homophones
homophone Units- Plants, Explorers
Math-Fractions
Fourth
Quarter
3/14 –
3/25
ongoing
3.7 a The student will demonstrate
comprehension of information from a
variety of print and electronic resources.
a. Use encyclopedias and other references
books, including online reference materials. U,
AN, AP
Essential Knowledge
make decisions about which resource is best for
locating a given type of information.
retrieve information from electronic sources.
use the Internet to find information on a given
topic.
2.10c Use dictionaries,
glossaries, and indices.
2.10d Use online
resources
4.9b Collect
information from
multiple resources
including online, print,
and media
Encyclopedia
Atlas
Topic
Reference
Website
Internet
Search
Search engine
Key words
Resource
Plagiarism
Units-Explorers, Animals
Math-Probability
3/14 –
4/15
3.11 a-d
Short
Report
The student will write a short report.
a. Construct questions about the topic. C
b. Identify appropriate resources. R
c. Collect and organize information about the
Review paragraph
writing
Review nonfiction/text
features
Plagiarism
Topic
Resources
Units-Animals
Math-Probability,
Division, Geometry

Writing topic into a short report. AN
d. Understand the difference between
plagiarism and using own words. AN
Essential Knowledge
focus on a central topic.
develop a list of questions pertaining to a specific
topic.
identify and use appropriate resources.
follow the organization of particular forms of
writing for short reports (e.g., opening, grouping of
like information into clear paragraphs, ordering of
paragraphs so that there is a logical flow of
information, and closing).
review their written drafts so that the language
and/or thoughts of another author are given proper
credit.
4.9 The student will
demonstrate
comprehension of
information resources
to research a topic
4/6 – 4/22 3.6 a-l
The student will continue to read and
demonstrate comprehension of nonfiction
texts.
a. Identify the author’s purpose. E
b. Use prior and background knowledge as
context for new learning. AN, AP
c. Preview and use text features. AP
d. Ask and answer questions about what is
read. U, AN
e. Draw conclusions based on text. E
f. Summarize major points found in nonfiction
texts. U
g. Identify the main idea. AN
h. Identify supporting details. R
j. Use reading strategies to monitor
comprehension throughout the reading process.
AP
k. Identify new information gained from
Review nonfiction Author
Purpose
Prediction
Experience
Connection
Compare
Contrast
Draw conclusion
Plagiarism
Passage
directions
Fiction
Nonfiction
Problem
Solution
Questions
Paragraph
Flow chart
Units-Animals
Math-Division, Geometry

reading. R
l. Read with fluency and accuracy. AP
Essential Knowledge
To be successful with this standard, students are
expected to
identify the author’s purpose (e.g., entertain,
inform, persuade).
use prior and background knowledge as context for
new learning by:
recognizing similarities between their own
personal experiences and the text;
recognizing similarities between the text they
are reading and other texts they have read; and
recognizing similarities between what they
already know about the topic and what they
find in the reading that is new to them.
use text formats such as the following to preview,
set a purpose for reading, and locate information
relevant to a given topic efficiently:
content text features, such as headings and
chapter layout by topic;
functional formats, such as advertisements,
flyers, and directions;
specialized type, such as bold face and italics;
and
visually and graphically represented
information, such as charts, graphs, graphic
organizers, pictures, and photographs.
apply understanding of text structure to guide
reading by:
making predictions based on knowledge of text
form types, such as narrative, informational,
graphic, and functional;
making predictions based on knowledge of
literary forms, such as biography and
autobiography; and
identifying sequence and cause-effect
relationships of information in functional texts,
such as recipes and other sets of directions.
Decide
Important
Main reason
Read the flyer
Venn diagram
Web
Empty
Article
Opposite
Information
Website
Title
Story

gain meaning before, during, and after reading by:
asking and answering questions to clarify
meaning;
understanding that sometimes two or more
pieces of information need to be put together to
answer a question; and
understanding that some questions are
answered directly in the text.
draw conclusions about what they have read.
summarize major points in a selection.
identify details that support the main idea of a
nonfiction selection.
state in their own words the main idea of a
nonfiction selection.
compare and contrast the characteristics of
biographies and autobiographies.
monitor their comprehension throughout the
reading process by:
becoming aware of when they do not
understand;
identifying exactly what is causing them
difficulty; and
generating their own questions to help
integrate units of meaning.
use text features to make meaning by:
applying phonetic strategies;
using punctuation indicators, such as commas,
periods, exclamation points, question marks,
and apostrophes showing contraction and
possession;
applying knowledge of simple and compound
sentence structures;
knowing when meaning breaks down and then
rereading to self-correct; and
using illustrations to gain information (e.g.,
maps, photographs).
identify new information gained from reading.
practice reading and rereading familiar nonfiction
texts with fluency and accuracy.

4/20 –
4/26
3.2 a-e The student will present brief oral reports
using visual media **Not Tested
a. Speak clearly. R
b. Use appropriate volume and pitch. R
c. Speak at an understandable rate. R
d. organize ideas sequentially or around major
points of information. AN, C
e. Use contextually appropriate language and
specific vocabulary to communicate ideas. AP
Essential Knowledge
To be successful with this standard, students are
expected to
deliver oral presentations in an engaging manner
that maintains audience interest by:
reporting on a topic, telling a story, or
recounting an experience with appropriate facts
and relevant details;
presenting information with expression and
confidence;
varying tone, pitch, and volume to convey
meaning;
speaking at an understandable rate;
selecting words and phrases for effect;
using visual media (e.g., images, posters, and
charts) to emphasize or enhance facts or
details;
using specific vocabulary appropriate for the
audience and the topic; and
using grammatically correct language.
stay on topic during presentations.
organize ideas sequentially or around major points
of information.
answer questions from the audience.
evaluate their own presentations, using class-
designed criteria.
Volume
Tone
Pitch
Expression
Rate
Visual media
Oral report
Specific
vocabulary
Communicate
Understandable
Units-Animals
Math-Geometry