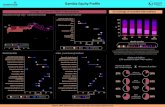
Kenya Equity Profile - Countdown 2030
Transcript of Kenya Equity Profile - Countdown 2030
Kenya Equity Profile
3.8% received less than 3 interven�onsMothers & Children
Wealth and area of residence Composite coverage index ‐ subna�onal coverage
Wealth Quin�les Urban | rural areas of residence
Wealth quin�les
Number of interven�ons
1 2 3 4 5 6 870
67%belong to
poorest quintile 23%
64%
29%
12%
87% live inrural areas
44%Rift Valley
region
havemothers with no education
43%
Mothers & childrenwith <3 interven�ons X All mothers & children
Source: DHS 2014 (Analyses based on the most recent publicly available survey)
%
0
20
40
60
80
100
Q1Poorest
Q2 Q3 Q4 Q5Richest
Demand for family planningsa�sfied with modern methods
rural
urban
Skilled a�endant at delivery
rural
urban
Immuniza�on ‐ DPT3
rural
urbanImproved sourceof drinking water
rural
urban
Q1 Poorest Q2 Q3 Q4 Q5 Richest
Coverage (%)0 20 40 60 80 100
0 20 40 60 80 100
0 20 40 60 80 100 0 20 40 60 80 100
Demand for family planningsa�sfied with modern methods
Antenatal care (4 or more visits)
Neonatal tetanus protec�on
Skilled a�endant at delivery
Postnatal care for mothers
Postnatal care for babies
Immuniza�on ‐ Rota
Immuniza�on ‐ DPT3
Immuniza�on ‐ Measles
Diarrhoea treatment: ORS
Early ini�a�on of breas�eeding
Exclusive breas�eeding
Con�nued breas�eeding (1 year)
Vitamin A supplementa�on
Careseeking for symptomsof pneumonia
• antenatal care (4+ visits) • tetanus toxoid during pregnancy• skilled a�endant at delivery • child received vitamin A supplementa�on • BCG (tuberculosis) vaccina�on • DPT3 (diphtheria–tetanus–pertussis)
vaccina�on • measles vaccina�on • improved drinking water source
Q1 Poorest Q2 Q3 Q4 Q5 Richest
Urban Rural
Coverage (%)
Q1 Poorest Q2 Q3 Q4 Q5 Richest
Coverage (%) Coverage (%)
Coverage of essen�al RMNCH interven�ons Co‐coverage of essen�al interven�ons
Demand for family planningsa�sfied with modern methods
Antenatal care (4 or more visits)
Neonatal tetanus protec�on
Skilled a�endant at delivery
Postnatal care for mothers
Postnatal care for babies
Immuniza�on ‐ Rota
Immuniza�on ‐ DPT3
Immuniza�on ‐ Measles
Careseeking for symptomsof pneumonia
Diarrhoea treatment: ORS
Early ini�a�on of breas�eeding
Exclusive breas�eeding
Con�nued breas�eeding (1 year)
Vitamin A supplementa�on
Kenya Equity Profile
Indicators Na�onal
Wealth quin�lesWealth‐related
equity indicatorsWoman's educa�on Child's sex
Area ofresidence
Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Q5Ra�o
Q5/Q1Difference
Q5‐Q1CIX SII None Primary Secondary+ Male Female Rural Urban
Demand for family planningsa�sfied with modern methods
70.7 45.6 66.4 72.8 78.2 78.8 1.7 33.3 7.9 32.0 35.8 70.1 76.7 ‐ ‐ 66.7 76.7
Antenatal care (4 or more visits) 55.8 43.6 48.9 54.3 60.2 73.2 1.7 29.6 11.0 35.0 42.5 51.3 66.9 55.7 55.8 49.8 66.2
Neonatal tetanus protec�on 51.1 42.8 45.3 50.6 52.2 62.8 1.5 19.9 8.1 23.5 41.6 47.9 58.5 51.9 50.2 47.6 56.5
Skilled a�endant at delivery 64.5 34.0 54.0 66.6 84.1 92.9 2.7 58.9 20.1 69.5 28.8 58.8 86.2 66.0 63.0 53.8 83.9
Postnatal care for mothers 53.6 32.2 48.9 53.0 65.5 74.9 2.3 42.7 17.1 49.8 21.9 49.7 70.5 54.7 52.4 45.7 67.9
Postnatal care for babies 35.7 23.6 28.2 38.3 42.4 50.1 2.1 26.4 16.2 33.1 19.1 33.0 45.6 34.5 37.0 30.5 45.2
Immuniza�on ‐ Rota ‐ ‐ ‐ ‐ ‐ ‐ ‐ ‐ ‐ ‐ ‐ ‐ ‐ ‐ ‐ ‐ ‐
Immuniza�on ‐ DPT3 90.1 83.7 90.4 92.0 93.9 92.8 1.1 9.2 2.2 12.0 77.7 90.7 93.4 89.7 90.6 89.4 91.4
Immuniza�on ‐ Measles 87.1 76.4 86.9 88.3 94.5 93.1 1.2 16.7 4.2 22.4 70.8 86.2 94.1 87.9 86.2 84.6 91.7
Careseeking forsymptoms of pneumonia
65.7 62.6 66.7 64.9 63.4 73.5 1.2 10.9 2.0 7.7 57.1 65.7 68.5 67.7 63.7 66.7 63.6
Diarrhoea treatment: ORS 53.8 52.1 53.3 55.3 55.0 54.5 1.0 2.4 1.3 3.8 51.6 52.4 57.5 56.3 51.0 51.9 57.5
Early ini�a�on of breas�eeding 62.2 66.7 61.0 58.8 64.4 58.8 0.9 ‐7.9 ‐2.4 ‐7.1 76.0 61.4 58.8 62.3 62.1 63.1 60.5
Exclusive breas�eeding 61.4 55.8 57.9 53.6 74.8 69.8 1.2 13.9 5.2 20.7 54.8 59.8 66.6 62.2 60.5 57.0 70.9
Con�nued breas�eeding (1 year) 90.4 90.2 91.0 88.7 88.0 95.3 1.1 5.1 0.3 1.9 87.4 92.8 87.4 88.4 92.2 91.2 88.9
Vitamin A supplementa�on 71.7 64.3 71.3 72.5 76.2 76.4 1.2 12.2 3.8 15.1 60.0 72.0 75.8 71.6 71.9 69.7 75.4
Source: DHS 2014 (Analyses based on the most recent publicly available survey)
Kenya Equity Profile
Indicators Coast North Eastern Eastern Central Ri� Valley Western Nyanza Nairobi
Demand for family planningsa�sfied with modern methods
58.4 10.2 77.2 83.9 62.3 71.8 67.4 81.5
Antenatal care (4 or more visits) 61.1 38.1 52.8 61.9 49.9 50.7 59.1 70.9
Neonatal tetanus protec�on 64.5 33.5 54.7 58.0 45.3 45.3 44.5 60.3
Skilled a�endant at delivery 61.1 35.3 66.0 90.2 53.5 54.6 68.3 91.1
Postnatal care for mothers 49.6 14.9 61.6 71.9 46.7 34.9 63.8 71.6
Postnatal care for babies 39.0 5.1 36.3 62.8 23.0 28.3 41.2 55.5
Immuniza�on ‐ Rota ‐ ‐ ‐ ‐ ‐ ‐ ‐ ‐
Immuniza�on ‐ DPT3 92.2 77.8 93.7 95.5 88.4 90.3 89.8 88.0
Immuniza�on ‐ Measles 86.6 69.8 92.1 97.2 83.1 85.7 85.3 92.5
Careseeking forsymptoms of pneumonia
66.0 35.4 67.6 70.3 68.1 56.5 71.0 65.2
Diarrhoea treatment: ORS 63.1 55.3 47.2 50.6 53.0 45.6 55.3 63.4
Early ini�a�on of breas�eeding 62.1 80.8 64.9 48.1 69.4 52.8 58.4 60.8
Exclusive breas�eeding 70.1 43.1 52.4 73.2 58.2 59.5 59.4 ‐
Con�nued breas�eeding (1 year) 95.1 71.6 96.3 90.6 94.3 89.5 80.7 ‐
Vitamin A supplementa�on 69.6 55.3 73.9 79.2 67.5 77.8 69.9 77.8
Source: DHS 2014 (Analyses based on the most recent publicly available survey)
Indicator coverage by country region
Kenya Equity Profile
Source: DHS 2014 (Analyses based on the most recent publicly available survey)
• Demand for family planning sa�sfied with modern methods: percentage of women in union using modern contracep�ves among those who are fer�le and do not want a child in the next two years, at least.
• Antenatal care, 4 or more visits: percentage of women who had at least 4 visits of antenatal care during pregnancy.
• Neonatal tetanus protec�on: percentage of women who received tetanus injec�ons during pregnancy.
• Skilled a�endant at delivery: percentage of women who had delivery a�ended by a doctor, a nurse, or an auxiliary nurse or trained midwife. The specific �tles and cadres can vary between countries.
• Postnatal care for mothers and for babies: percentage of mothers and babies who went through a health check within 48 hours a�er the delivery.
• Immuniza�on for rotavirus, DPT3 and measles:percentage of children aged 12 to 23 months who received these vaccines.
Interven�ons and inequality measures Combined coverage indicators
Interpre�ng the graphs
To monitor progress towards the Sustainable Development Goals, it is essen�al to monitor the coverage of health interven�ons in subgroups of the popula�on because na�onal averages can hide important inequali�es. Here, we selected 15 interven�ons represen�ng the con�nuum of care of reproduc�ve, maternal, neonatal and child health (RMNCH) to show how countries are faring in terms of coverage by regions of the country, wealth quin�les (5 equal sized groups), urban or rural area of residence and both wealth and area. In the table presented in page 2, we also present results by woman's educa�on and child's sex.
We also present simple measures of wealth inequality (difference and ra�o) and complex measures. These are the slope index of inequality (SII), for absolute inequality, and the concentra�on index (CIX), for rela�ve inequality. The SII can be interpreted as the difference in coverage between the two extremes of the wealth distribu�on. The CIX is similar to the Gini index and gives an idea of how concentrated the coverage of each indicator is, towards the rich (posi�ve value) or the poor (nega�ve value). The CIX can vary from zero (no inequality) to 100 (maximum concentra�on), but in prac�ce values above 30 already represent a fairly high level of inequality.
A short descrip�on of the interven�ons is presented below. The full defini�on of the interven�ons tracked by Countdown can be found in the annexes of the main report.
• Careseeking for pneumonia: percentage of children who presented symptoms of pneumonia and were taken to a health facility.
• Treatment for diarrhea with ORS: percentage of children with diarrhea who received oral rehydra�on salts.
• Early ini�a�on of breas�eeding: percentage of children who were put to the breast in the first hour of life.
• Exclusive breas�eeding: percentage of children less than six months of age who are being exclusively breas�ed (receiving only breastmilk, not even water or tea).
• Con�nued breas�eeding at one year: percentage of children aged 12 to 15 months of age who are s�ll being breas�ed.
• Vitamin A supplementa�on: percentage of children who received vitamin A in the six months preceding the interview (in countries where there is a supplementa�on program).
Composite coverage index – CCIWe present a map of each country with the CCI by region. The CCI is a neat way to summarize coverage by health interven�ons using a single number, in place of several of them. It is calculated as the weighted mean of eight selected interven�ons – demand for family planning sa�sfied, antenatal care (4+ visits), skilled a�endant at delivery, BCG, DPT3 and measles vaccines, and finally careseeking for pneumonia and ORS for diarrhea.
Co‐coverageCo‐coverage is a count of how many, out of 7 or 8 interven�ons offered in the country, the pair of mother and child received. Ideally, they will receive all interven�ons available, but in prac�ce we observe very different situa�ons. The interven�ons considered here are antenatal care (4+ visits), tetanus toxoid during pregnancy, skilled a�endant at delivery, BCG, DPT3 and measles vaccines, vitamin A supplementa�on and improved source of drinking water. The count goes from zero, to the maximum of 7 or 8 interven�ons, depending on the country.
In the equiplots, the graphs with aligned dots, each dot represents the coverage of a given interven�on for a subgroup. It can be area or residence, or wealth quin�les (the first quin�le includes the poorest 20% of the sample, and so on). The quin�les are labelled Q1 to Q5. The distance between the dots is the difference in coverage between the relevant groups. The larger the difference, the bigger the absolute inequali�es in the country. Ideally, in this type of graph, we would like to see all the dots close together on the right side, where coverage approaches 100%.
The map shows the regions of each country, and CCI coverage using colors to highlight differences across the regions. The darker the color, the higher the coverage. The actual values (%) are presented below the names of the regions. At the bo�om, we also present an equiplot of the CCI by wealth quin�les. Not to be confused with a map scale!
Co‐coverage is presented in two ways. The top graph displays how many mothers and children in each of the five wealth quin�les receive zero, one, two, up to eight of the interven�ons included in the co‐coverage measure. We typically see that the high‐count sec�ons increase and are much bigger towards the richer quin�les. The bo�om sec�on shows differences in key characteris�cs of mothers and children that received less than 3 of these interven�ons in comparison to all mothers and children living in the country. Comparisons presented include likelihood to belong to the poorest quin�le, to live in rural areas or specific geographical regions, and for the mother to have received no educa�on. For instance, compared to the 20% of the mothers and children in the poorest quin�le, we o�en see that a much higher propor�on (30‐40%) of those receiving less than three interven�ons belong to that quin�le.








![Developing a country RMNCH scorecard - ALMA 2030 · evidence-based, country-led RMNCH strategy/planning dialogue INTRODUCTION Objectives of Country countdown “[Bring] old and new](https://static.fdocuments.us/doc/165x107/5e1c399a5bd17741ee6a423b/developing-a-country-rmnch-scorecard-alma-evidence-based-country-led-rmnch-strategyplanning.jpg)