JEOPARDY!
-
Upload
mckenzie-alvarado -
Category
Documents
-
view
17 -
download
2
description
Transcript of JEOPARDY!

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
Click Once to BeginJEOPARDY!Chemistry Final Review

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
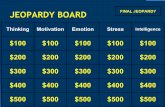
JEOPARDY!
100 100 100 100 100 100
200 200 200 200 200 200
300 300 300 300 300 300
400 400 400 400 400 400
500 500 500 500 500 500
Dissolving Concentration Solubility/ Precipitation
Parts of Solutions Acids and Bases Real Life Applications

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
What does dissolve in water mean?

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
Dissolve in water means that the ions of the compound break up when put in water

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
What is an electrolyte?

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
An electrolyte is a compound that dissolves in water

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
What are unsaturated, saturated, and supersaturated solutions?

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
Unsaturated means that more solute can be added, saturated
means that a solution has dissolved all the solute it can hold, supersaturated means
that due to an increase in heat a solution has more solute
dissolved than it can normally hold.

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
Break up (NH4)3PO4 into ions

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
3NH4+ + PO4
3-

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
What is the formula for vinegar and what kind of electrolyte is it?
Why?

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
The formula is HCH3COO and it is a weak electrolyte because the not many H+ ions
dissociate.

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
If you 2.5 moles of Na+ is dissolved in 5 L of water, what
is the molarity?

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
.5 M Na+

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
What is the molarity of Cl- in 1.2 M CaCl2?

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
2.4 M Cl-

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
Find the %(W/V) for 60 g of solute in .6 L of a solution

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
10%(W/V) Don’t forget to convert to milliliters for %
(W/V)

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
Find the molarity of 5.6 g of lead nitrate in 400 mL water

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
5.6 g x (l mol/331.2 g/mol) = .0169 mol.
.0169 mol/.4 L = .0423 M

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
Daily Double!!!What is the total ion molarity for 6.7 g of
Ammonium Sulfide in 5 L of water?

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
6.7 g x (1 mol Ammonium Sulfide/68.154 g/mol) = .0983 mol
.0983 mol x 3 ions = .295 mol

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
What is a solute?

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
A solute is the chemical that is dissolved

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
If 11 moles of NaCl are dissolved in 330 kg of water,
what is its molality?

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
.033 m

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
When magnesium chloride is placed into water, it seems to disappear. Does it disappear? If not, why does it seem this
way?

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
Magnesium chloride does not disappear when put in water, the particles are just surrounded by water and
too tiny to see.

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
What is hydration and ionization?

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
Hydration is what occurs when an ionic compound
dissolves in water, ionization is the process
of breaking up the compound into separate
ions.

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
What kind of electrolytes conduct electricity well? Why?

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
Strong electrolytes conducted electricity better because they make free-
floating ions in water.

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
What is a precipitate?

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
A precipitate is an insoluble compound that does not
dissolve in water

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
If silver nitrate was mixed with sodium chloride, would a
precipitate form?

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
Yes, AgCl would precipitate

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
Indicate what precipitates forms, if any:
NaNO3 + Li2CO3

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
No precipitate forms

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
Indicate what precipitates forms, if any:Ca(CH3COO)2 + Na3PO4

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
Ca3(PO4)2 would form

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
Indicate what precipitates forms, if any:
Magnesium iodide and mercury (I) flouride

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
Hg2I2 and MgF2 would form

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
What is the difference between pH and pOH?

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
pH is a measure of the H+ concentration
and pOH is a measure of the OH-
concentration

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
If there are .006 mol of H+ in 2 L of water, what is the H+
concentration?

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
.006 mol/2 L = .003 M H+

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
If the pH increase by 2, what happens to the H+
concentration?

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
It decreases by 100

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
What is the H+ concentration if the pOH is 8.6?

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
14 – 8.6 = 5.4pH = 5.4
10-5.4 = 3.98 x 10-6

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
If .05 moles of HCl are put in 60 L of water, what is the pH?
Daily Double!!!

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
.05 moles / 60 L = -8.33 x 10-4 M
10(-8.33 x 10-4) = 3.08

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
What are real life uses for an acid and a base?

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
Acid: Batteries, fertilizers, soaps,
shampoo, detergents
Base: Drain cleaner, laxatives, antacids

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
How could the sweetness of lemonade be maximized in
accordance with saturation?

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
Super saturation of the lemonade with sugar

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
What effects from acid rain suggest that it is acidic?

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
Corrosion of metal/stone, lower the pH of water bodies, damage to nature via resource ruination

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
Name one important food and the electrolyte in it

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
Banana (K+), Salty foods (Na+/Cl-), Milk (Ca2+), Leafy
Greens (Mg2+)

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
If you frequently have heartburn , would putting ketchup on your French fries increase or
decrease the odds of you getting heartburn? Why?

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
It would increase your odds of getting
heartburn because ketchup has vinegar (acetic acid), which is
acidic.

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
Final Jeopardy
If .5 mol H2SO4 dissolved in 30 L of water is added to 2 mol HCl dissolved in 10 L of water, what is the pOH?

Template byBill Arcuri, WCSD
Click Once to Begin
.5 mol / 40 L = .0125 M x 2 H+
= .025 M H+ in H2SO4
2 mol / 40 L = .5 M H+ in HCl.
.025 M H+ in H2SO4 + .05 M H+ in HCl = .075 M H+ total.
-log(.075 M) = 1.1214 – 1.12 = 12.87
pOH = 12.87