Introduction to Color Theory. Color is the reflection or absorption of white light from any given...
-
Upload
abel-fleming -
Category
Documents
-
view
221 -
download
0
Transcript of Introduction to Color Theory. Color is the reflection or absorption of white light from any given...

Introduction to Color Theory
Color

Color is the reflection or absorption of white light from any given surface.White Light: is all the colors combined
Hue is identified as any color
What is Color?

Wavelengths of light

Color when refracted


1672
Sir Isaac Newton

Sir Isaac NewtonPassed a beam of white light into a prism and
found that it created a spectrum.
The Experiment


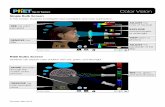
RGB LightAdditive color process for
producing lightCreates variations of light
because black is the absence of light
Lower light intensity produces darker color
Higher light intensity produces lighter color
Computers, Plasma and LCD TVs, Projectors, or any other device that uses light to create color

Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, Black
Subtractive color process because it subtracts from the color whiteWhite is the combination of
all colorCMYK is used in all printing
devices. The inks overlap to form the various colors
CMYK

Color Half is the use of small CMYK dots to create the illusion of solid color
Saves money by not using as much ink
Color Halftone

Color HarmoniesColors schemes in Art

RedYellowBlue
Primary Colors

Piet Mondrian
Composition II in Red, Blue, and Yellow
1930
Primary Colors

GreenOrangeViolet
Secondary Colors

Henri Matisse
Boy With Butterfly Net
1907

Paul Cezanne
Still Life with Onions
1895
Complimentary

Colors found adjacent on the color wheel“Family resemblance”Changes in value can enhance the contrast of
the hues
Analogous

Claude MonetWater Lily Pond
c. 1899
Analogous

Red, yellow, orangeColors are intended to excite the viewer
Warm Colors

Vincent van Gogh
Still Life: Vase with 12 Sunflowers
1888
Warm Colors

Violet, Green, BlueUse to express unhappiness, depression or
sadness
Cool Colors

Pablo Picasso
The Tragedy
1903
Monochromatic

“Mono” meaning one“Chroma” meaning color
Monochromatic

Hues that are across from each other on the color wheel
Complimentary Colors

Adding white to a hue
Tint

Adding gray to a hue
Tone

Adding black to a hue
Shade

Basic use of Color