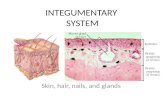
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM. COMPONENTS OF THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Figure 5-1.
Integumentary System
description
Transcript of Integumentary System

Integumentary System
CHAPTER 5

2
Integumentary System• Skin
– Integument or cutaneous membrane– Epidermis– Dermis– Subcutaneous layer
• Accessory structures– Hair– Nails – Glands

3
Layers and Structures of the Skin

4
Skin Lesions• Abrasion
– Scraping or rubbing away of skin or mucous membrane as a result of friction to the area• Example: carpet burn
• Abscess– Localized collection of pus in any body part
that results from invasion of pus-forming bacteria• Example: pustule = small abscess

5
Skin Lesions• Bedsore
– Ulcer in skin over a bony prominence– Also known as pressure ulcer
• Example: decubitus ulcer• Blister
– Small, thin-walled lesion containing clear fluid– Also known as a vesicle

6
• Bulla– Large blister
• Carbuncle– Circumscribed inflammation of skin and
deeper tissues; contains pus• Comedo
– Typical lesion of acne vulgaris• Example: whitehead = closed comedo• Example: blackhead = open comedo
Skin Lesions

7
Skin Lesions• Cyst
– Closed sac or pouch in or within the skin; contains fluid, semifluid, or solid material• Example: hydrocele = fluid-filled cyst• Example: sebaceous cyst = solid-filled cyst

8
Skin Lesions• Fissure
– Cracklike sore or groove in the skin or mucous membrane• Example: anal fissure
• Fistula– Abnormal passageway between two tubular
organs; or from an organ to the body surface• Example: recto-vaginal fistula

9
Skin Lesions• Hives
– Circumscribed, slightly elevated lesions on skin; paler in center than surrounding edges
– Also called wheals• Example: mosquito bite
• Laceration– Tear in skin; torn, jagged wound

10
Skin Lesions• Macule
– Small flat, discoloration of the skin; neither raised nor depressed• Example: bruises, freckles
• Nodule– Small, circumscribed swelling protruding
above the skin

11
Skin Lesions• Papule
– Small, solid, circumscribed elevation on the skin
– Example: pimple, wart, elevated mole• Polyp
– Small, stalklike growth, protruding upward or outward from membrane surface
– Example: nasal polyp

12
• Pustule– Small elevation of skin filled with pus
• Example: small abscess on the skin• Scales
– Thin flakes of hardened epithelium that are shed from the epidermis
• Ulcer– Circumscribed, open sore or lesion of skin,
accompanied by inflammation• Example: decubitus ulcer
Skin Lesions

13
Skin Lesions • Vesicle
– Small, thin-walled, lesion containing clear fluid• Example: blister
• Wheal– Circumscribed, slightly elevated lesion of the
skin – Paler in center than surrounding edges
• Example: hives

PATHOLOGICAL CONDITIONS
Integumentary System

15
Acne Vulgaris• Pronounced
– (ACK-nee-vul-GAY-ris)• Defined
– Common inflammatory disorder seen on face, chest, back, and neck
– Appears as papules, pustules, and comedos

16
Albinism• Pronounced
– (AL-bin-izm)• Defined
– Condition characterized by absence of pigment in the skin, hair, and eyes

17
Burns• Defined
– Tissue injury produced by flame, heat, chemicals, radiation, electricity, or gases
– Extent of damage determined by: • Mode and duration of exposure• Thermal intensity or temperature• Anatomic site of the burn

18
• First-degree or superficial burns– Example: sunburn
• Second-degree or partial-thickness burns– Example: flash contact with hot objects
• Third-degree or full-thickness burns– Example: deep burns from a fire
Burns

19
Callus• Pronounced
– (CAL-us)• Defined
– Common, usually painless thickening of the epidermis at sites of external pressure or friction, such as weight-bearing areas of the feet and on the palmar surface of the hands• Also known as a callosity

20
Carcinoma, Basal Cell
• Pronounced– (car-sih-NOH-mah BAY-sal sell)
• Defined– Most common malignant tumor of epithelial
tissue, occurring most often on areas of skin that are exposed to the sun• Presents as a slightly elevated nodule with a
depression or ulceration in the center that becomes more obvious as the tumor grows

21
• Pronounced– (car-sih-NOH-mah SKWAY-mus sell )
• Defined– Malignancy of the squamous, or scalelike,
cells of the epithelial tissue– Much faster growing than basal cell
carcinoma – Greater potential for metastasis if not treated
Carcinoma, Squamous Cell

22
Carcinoma, Squamous Cell
• Frequent sites on sun-exposed areas– Top of nose– Forehead– Margin of external ear– Back of hands– Lower lip

23
Dermatitis• Pronounced
– (der-mah-TYE-tis)• Defined
– Inflammation of skin, seen in several different forms
– Acute or chronic– Contact or seborrheic

24
Eczema• Pronounced
– (EK-zeh-mah)• Defined
– Acute or chronic inflammatory skin condition characterized by erythema, papules, vesicles, pustules, scales, crusts, scabs, and itching

25
Exanthematous Viral Diseases
• Pronounced– (eks-an-THEM-ah-tus viral diseases)
• Defined– Skin eruption or rash accompanied by
inflammation, having specific diagnostic features of an infectious viral disease

26
Exanthematous Viral Diseases• Examples:
– Rubella = German Measles = 3 day measles– Roseola Infantum– Rubeola = Red Measles = 7-10 day measles– Erythema Infectiosum = Fifth disease

27
Gangrene• Pronounced
– (GANG-green)• Defined
– Tissue death due to loss of adequate blood supply, invasion of bacteria, subsequent decay with foul odor

28
Herpes Zoster• Pronounced
– (HER-peez ZOS-ter)• Defined
– Acute viral infection, characterized by painful, vesicular eruptions on the skin that follow along nerve pathways of underlying spinal or cranial nerves
– Highest incidence in adults over 50

29
Herpes Zoster
Image courtesy of Robert A. Silverman,M.D., Pediatric Dermatology,Georgetown University

30
Impetigo• Pronounced
– (Im-peh-TYE-goh)• Defined
– Contagious superficial skin infection characterized by serous vesicles and pustules filled with millions of staphylococcus or streptococcus bacteria • Usually forming on the face