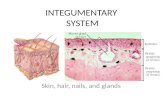
Integumentary System
description
Transcript of Integumentary System

By
Jittipan Chavadej , Ph.D.
Anatomy Dept.,Fac. of Scienceyr.,2
000

Structural development • begin as a single layer of ectode
rmal cells
• formation of a thin outer layer periderm at the end of the first month• - third month three layers - basal layer, intermediate layer&supl layer of peridermal cells

Diagram showing the formation of the skin at various stages of development

•6th - month epidermis beneath periderm
differentiation into the definitive layers• Sloughs of peridermal cells int
o the amniotic fluid• Immigrant cells in the epidermis-2nd -month melanoblast- late in 1st - trimester Langerhans cells- Merkel cells

Melanoblast -( cyte) :
- derived from neural crest
- - midpregnancy begin producin g pigment granules = melanos
omes -Dark skin more pigment granules/cellAlbinism - genetic trait, lack of enz
-yme tyrosinase: tyrosine melanin

Epidermal differentiation - Movement of epidermal cells lo
ss of adhesiveness e.g. fibronect in, laminin&collagen types I&IV
Keratohyalin granules (histidine&sulph
- ur rich), (closely associated with keratin filamen
t)- stratum granulosum (keratinocyte)
Keratin filaments- stratum corneu m

Unspecialized cells- mitotic activity
Produce keratin filamen t (desmosome)
-Flattened cell breakin g up nuclear membra
ne
- Lost nuclei bag of de nsely packed with ker
atin filaments• - 1 5 2 0 layers of
dead cells

One of the prominent features of thick skin=presence of epidermal
- ridges and creases >loops & whorlsDermatoglyphics- basic patterns(
epi. ridge) for genetic analysis or c riminal investigation (unique to i
ndividual)

Dermis• Mesodermal cells from dermat
ome / beneath ectoderm
•3rd - month transition from highl y cellular embryonic form
fibroblast + fibrous intercellular matrix
• Becomes highly vascularized + sensory nerve

- Future dermis loosely aggregated mesenchymal
cells

Epidermal appendagesHair - induction from dermis
-12th week :down growth of hair bud
- hair papillae hair shaft epithelial hair sheath - arrector pili muscle : dermal root sheath & dermal papilla
- sebaceous gl. - fat like substance hair follicle

Diagram showing development of a hair and a sebaceous gland

5th -mo. hair shaft keratinizatio n forming granules of trichohyali
n (hardness of the hair)
- Late stage of hair formation hair-- --bulb > melanocytes >color

Mammary Gland
• Mammary line or ridge (6 wk.) :bas e of forearm
region of hind limb Small solid outbudding
lactiferous duct formation+alve oli of the gland
- epithelial pit (nipple after birth)

Stages in the embryonic developme nt of the humanmammary gland
Diagram showing posit
ion of mammary line

Abnormalities of Skin Development
•Ichthyosis- genetically transmitted disorders of keratinization
Harlequin - autosomal recessivedisorder
•Hypertrichosis- formation of hai r follicle
•Atrichia - congenital absence of hair

A: - milk line mammary glands form along this line
B: common sites of formation of supernumerary nipples/m ammary gland

•Polythelia - accessory nipples( axillary region)
•Polymastia - supernumerary brests