Integumentary System
description
Transcript of Integumentary System
-
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM OBJECTIVESAt the end of this session, Students will be able to: Define Integumentary System Know the parts of Integumentary System Describe 5 function of Skin. List 3 common disease/ disorder of integumentary system. Learn to prevent patients from bedsores.
-
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEYOBJECTIVESAt the end of this session, Students will be able to: Define Integumentary System Know the parts of Integumentary System Describe 5 function of Skin. List 3 common disease/ disorder of integumentary system. Learn to prevent patients from bedsores.
-
DEFINITION It is the system, which covers our entire body that is skin. Skin is the natural covering. It provides first line of defense against infection.
-
Parts of Integumentary System Skin Hair and Hair follicles. Nails Sebaceous glands is Sweat glands Nerve supply
-
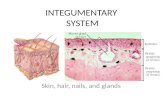
SKIN The skin covers and protect underlying structures from injury or bacteria invasion. Skin consists of 2 layers:
Epidermis Dermis
-
EpidermisDermis EpidermisDermis
-
Epidermis It is the most superficial or outer layer of the skin, which we can see. It is thickest on palms and soles. No blood vessels or nerves ending present on it. Hair, Secretions from sebaceous glands and sweat glands pass through epidermis. Dermis It is inner layer of the skin. It is tough and elastic. It consists of blood vessels, hair follicles, adipose (folds) tissue, sebaceous (oil) glands and sweat glands.
-
Hair and Hair Follicles They are found all over the body except on the palms and soles.Nails They form from same cells as epidermis and hair. It is hard, horey type of dead cells. They protect the tips of the finger and toes.
Sebaceous Gland It secrets thick oily substance through the ducts that leads to sebaceous gland. This oily secretion lubricates and keeps skin soft, pliable and also provides a protective film, which limits the absorption and evaporation of water from the surface.
-
Sweat Gland It secrets sweat or perspiration from tiny holes in the skin called poses. Function of sweat glands is maintaining body temperature and body rids itself of certain waste products through perspiration.Nerve Supply Due to presence of sensory nerve ending the body reacts by reflex action to unpleasant or painful stimuli and protects from further injuries.
-
Functions of SkinProtection Skin covers and protects underlying body structures from injury and microorganism invasion and acts as a mechanical barrier.Sense Organ The sensory nerve endings present in skin that allows sensory perception. The senses of touch, pain and change in temperature.
-
Temperature Regulation It regulates the body temperature by controlling the loss of heat from the body. The evaporation of sweat from the surface of the skin facilitates a loss of heat when environment becomes too warm.Minor Excretory Function The small amount of water, salt and waste product are eliminated by perspiration.Store Energy Skin can store energy in the form of fats and vitamins.
-
Hair Growth and Replacement
Sometimes hair loss may be temporary as a result of one or more of the following factors: exposure to drugs, dietary factors, radiation, high fever, or stress. Thinning of the hair, called alopecia can occur in both sexes, usually as a result of aging.
-
Burns
Major cause of accidental death, primarily as a result of their effects on the skin. Usually caused by heat, radiation, harmful chemicals, sunlight, or electrical shock.The immediate threat to life results primarily from fluid loss, infection, and the effects of burned, dead tissue. Burns are classified according to the depth of tissue involvement.
-
First- and second-degree burns are called partial- thickness burns.
Classification of BurnsSecond-degree burns involve the epidermis and part of the dermis. The skin appears red, tan, or white, and is blistered and painful.Third-degree burns involve the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous layer, which are often destroyed. Third-degree burns are called full thickness burns.
-
The most common type of cancer.
The greatest risk factor is exposure to UV rays of the sun.
The highest incidence is in people who have had severe sunburns, especially as children.Skin Cancer
-
Cyanosis : Sign of impaired circulation
Lesions : An abnormality of tissues of the body as a wound, sore, rash or boil.
Ulcer : Local destruction of the Epidermis
Common Problems of Integumentar System
-
Dermatitis : Inflammation of skin layer is reaction or irritating due to allergy
Cancer of : Tumor of the skin, which has high rate of death rate.
the Skin Burns : Excessive exposure of skin to heat or fire. Herpes Zoster : Inflammatory condition caused by virus that produce painful lesions
-
THANK YOU