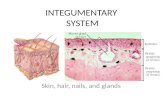
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
description
Transcript of INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM

INTEGUMENTARY INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEMSYSTEM
CHAPTER CHAPTER 16: SKIN16: SKIN

FUNCTIONS OF THE SKINFUNCTIONS OF THE SKIN1.1. ProtectsProtects the body –prevents loss of the body –prevents loss of
water, salt, heat & against invasion of water, salt, heat & against invasion of pathogens & toxinspathogens & toxins
2.2. LubricatesLubricates skin surface (with sebum, skin surface (with sebum, secreted from sebaceous glands)secreted from sebaceous glands)
3.3. Maintains temperatureMaintains temperature • Cools body by evaporation (with sweat Cools body by evaporation (with sweat
secreted from sweat glands)secreted from sweat glands)• Has blood vessels that dilate & constrictHas blood vessels that dilate & constrict
4.4. Has nerve fibers under the skin that Has nerve fibers under the skin that aid in aid in sensationssensations of pain, pressure, of pain, pressure, touch, and temperaturetouch, and temperature

• EpidermisEpidermis – outermost layer – outermost layer• Basal layer - deepest layer of epidermisBasal layer - deepest layer of epidermis• Stratum Corneum – cells are called “horny cells” or Stratum Corneum – cells are called “horny cells” or
keratinized cells, outermost layer of epidermiskeratinized cells, outermost layer of epidermis• Lacks blood & lymph vessels & connective tissueLacks blood & lymph vessels & connective tissue
• CoriumCorium (Dermis) (Dermis) – middle layer between epidermis – middle layer between epidermis and subcutaneous layerand subcutaneous layer• Contains blood & lymph vessels, hair follicles, glands, Contains blood & lymph vessels, hair follicles, glands,
and nerve fibersand nerve fibers• Has connective tissue cells & elastic collagen fibersHas connective tissue cells & elastic collagen fibers
• SubcutaneousSubcutaneous – innermost layer – innermost layer• Lipocytes (fat cells) mostly present; help to act as a Lipocytes (fat cells) mostly present; help to act as a
heat insulator and for energy storageheat insulator and for energy storage
LAYERS OF SKINLAYERS OF SKIN

Epidermis
Dermis
Subcutaneous tissue
Stratum corneum
Basal layermelanocytes
You will need to be able to locate and/or identify individual layers of skin

• Hair – tight network of horny cells filled with Hair – tight network of horny cells filled with keratin & melanocytes; keratin production keratin & melanocytes; keratin production determines hair colordetermines hair color
• Nails – hard keratin plates composed of horny Nails – hard keratin plates composed of horny cellscells
• GlandsGlands• Sebaceous – located all over the body except Sebaceous – located all over the body except
palms of hands and soles of feet, produce sebum palms of hands and soles of feet, produce sebum to lubricate skin to lubricate skin
• Sweat – coiled gland most numerous on palms of Sweat – coiled gland most numerous on palms of hands & soles of feet, sweat is a mixture of water hands & soles of feet, sweat is a mixture of water and salt, functions to cool the bodyand salt, functions to cool the body
ACCESSORY ORGANS OF SKINACCESSORY ORGANS OF SKIN

Figure 16-2. (A) Anatomical structure of a nail. (B) Onycholysis. Infection or trauma to the nail may be the cause of the detachment of the nail from its plate. (B from Seidel HM: Mosby's Guide to Physical Examination, 5th ed. St. Louis, Mosby, 2003, p. 214.)

diaphor / o = diaphor / o = sweatsweat diaphor / esis = diaphor / esis = profuse sweating conditionprofuse sweating condition
hidr / o = hidr / o = sweatsweat an / hidr / osis = an / hidr / osis = condition of not sweatingcondition of not sweating
ichthy / o = ichthy / o = dry, scalydry, scaly ichthy / osis = ichthy / osis = dry, scaly skindry, scaly skin
myc / o = myc / o = fungusfungus dermat / o / myc / osis = dermat / o / myc / osis = fungal skin inffungal skin inf
onych / o = onych / o = nailnail onych / o / myc / osis =onych / o / myc / osis = fungus in nailfungus in nail
trich / o = trich / o = hairhair trich / o / myc / osis = trich / o / myc / osis = fungus in hairfungus in hair
xer / o = xer / o = drydry xer / o / derma = xer / o / derma = dry skindry skin
ungu / o = ungu / o = nailnail sub / ungu / al = sub / ungu / al = under the nailunder the nail
adip / = adip / = fatfat adip / ose = adip / ose = pertaining to fatpertaining to fat
albin / o = albin / o = whitewhite albin / ism = albin / ism = condition of white (skin)condition of white (skin)
kerat / o = kerat / o = hard, horny tissue hard, horny tissue kerat / osis = kerat / osis = abnormal condition of ……abnormal condition of ……
xanth / o = xanth / o = yellowyellow xanth / oma = xanth / oma = yellow mass (tumor)yellow mass (tumor) melan / o = melan / o = blackblack melan / oma = melan / oma = black tumorblack tumor
seb / o = seb / o = oily (sebum)oily (sebum) seb/ o / rrhea = seb/ o / rrhea = oily dischargeoily discharge
COMBINING FORMS RELATED TO SKINCOMBINING FORMS RELATED TO SKIN

• CystCyst – thick walled, closed sac or pouch – thick walled, closed sac or pouch containing fluid or semi-solid materialcontaining fluid or semi-solid material
• FissureFissure – groove or crack-like sore – groove or crack-like sore• MaculeMacule – discolored (often red) flat lesion – discolored (often red) flat lesion
TYPES OF SKIN LESIONSTYPES OF SKIN LESIONS

• PapulePapule – small solid elevation of the skin – small solid elevation of the skin• PolypPolyp – mushroom like growth extending on stalk from – mushroom like growth extending on stalk from
surface of mucous membranesurface of mucous membrane• PustulePustule – small elevation in skin containing pus – small elevation in skin containing pus• UlcerUlcer – open sore on skin or mucous membrane – open sore on skin or mucous membrane• Decubitus ulcerDecubitus ulcer – bedsore, from staying in one position – bedsore, from staying in one position• VesicleVesicle – small collection of clear fluid, blister – small collection of clear fluid, blister• WhealWheal – smooth, slightly – smooth, slightly
elevated swollen area elevated swollen area that is more red or pale that is more red or pale than surrounding skin than surrounding skin (also called hive) (also called hive)
TYPES OF SKIN LESIONSTYPES OF SKIN LESIONS

Figure 16-4. Bullae (large blisters) in bullous pemphigoid (a chronic skin disorder in older individuals). The pemphigoid (pemphix means bubble) bullae occur as the entire thickness of the epidermis detaches from its foundation. (From Kumar V, Cotran RS, Robbins SL: Basic Pathology, 7th ed. Philadelphia, WB Saunders, 2003, p. 797.)
BULLAEBULLAE

• AlopeciaAlopecia – absence of hair – absence of hair from areas where hair from areas where hair normally growsnormally grows
• PruritisPruritis – itching associated – itching associated with many skin conditionswith many skin conditions
• UrticariaUrticaria – hives; acute – hives; acute allergic reaction where red, allergic reaction where red, round wheals develop on skinround wheals develop on skin
ABNORMAL SKIN SYMPTOMSABNORMAL SKIN SYMPTOMS
Figure 16-5. Dermatologic signs. (A) Alopecia areata. (B) Ecchymoses, right hand. (C) Petechiae. (D) Senile purpura. Fragile blood vessels
rupture with minimal trauma.
(E) Urticaria

• ImpetigoImpetigo – characterized by – characterized by vesicles, pustules, and crusted vesicles, pustules, and crusted over lesions; Rx – antibiotics over lesions; Rx – antibiotics and proper handwashingand proper handwashing
• ScabiesScabies – accompanied by – accompanied by severe itching; Rx – topical severe itching; Rx – topical medications to medications to destroy mites destroy mites
ABNORMAL SKIN CONDITIONSABNORMAL SKIN CONDITIONS

• TineaTinea – named by location, – named by location, Rx Rx for all: antifungals for all: antifungals • corpuscorpus – body, commonly – body, commonly
called ringwormcalled ringworm• tinea pedistinea pedis – feet, commonly – feet, commonly
called athletes footcalled athletes foot• tinea barbaetinea barbae – under a beard – under a beard• tinea capitistinea capitis – on the scalp – on the scalp
ABNORMAL SKIN CONDITIONSABNORMAL SKIN CONDITIONS
Figure 16-9. (A) Tinea corporis (ringworm). (B) Tinea unguium. Fungal infection of the nail causes the distal nail plate to turn yellow or white. Hyperkeratotic debris accumulates, causing the nail to separate from the nail bed (onycholysis).

WartWart – verruca is medical term for wart – verruca is medical term for wart
ABNORMAL SKIN CONDITIONSABNORMAL SKIN CONDITIONS
Figure 16-12. Verruca vulgaris. Warts are multiple papules with rough, pebble-like surfaces.

Figure 16-6. (A) Formation of a blackhead (comedo) in a dilated pore filled with sebum, bacteria, and pigment. (B) Acne vulgaris on the face.
ACNEACNE• AcneAcne – papular and – papular and
pustular lesions of the pustular lesions of the skinskin

• EczemaEczema – inflammatory skin disease with red, – inflammatory skin disease with red, pepulovesicular lesionspepulovesicular lesions
• PsoriasisPsoriasis – chronic condition; itchy, scaly, red – chronic condition; itchy, scaly, red plaques on the skin covered by silvery grey scalesplaques on the skin covered by silvery grey scales
ABNORMAL SKIN CONDITIONSABNORMAL SKIN CONDITIONS
Figure 16-8. Psoriasis. Scaly erythematous plaque, with silvery scales on top.

Figure 16-10. Vitiligo on the hand (Latin: vitium meaning a 'blemish'). Epidermal melanocytes are completely lost in depigmented areas through an autoimmune process.
ABNORMAL SKIN CONDITONSABNORMAL SKIN CONDITONS

Figure 16-11. (A) Callus on the sole of the foot. (B) Keloid. (A from Mosby's Medical, Nursing, and Allied Health Dictionary, 6th ed., St. Louis, Mosby, 2002, p. 265; B from Ignatavicius DD, Workman ML: Medical-Surgical Nursing: Critical Thinking for Collaborative Care, 4th ed. Philadelphia, WB Saunders, 2002, p. 1544.)

• CellulitisCellulitis – acute infection of skin marked by heat, – acute infection of skin marked by heat, redness, pain, and swelling; Rx: antibioticsredness, pain, and swelling; Rx: antibiotics
• GangreneGangrene – death of tissue from loss of blood – death of tissue from loss of blood supplysupply
ABNORMAL SKIN CONDITIONSABNORMAL SKIN CONDITIONS

Figure 16-7. Burns. (A) Second-degree injury. Wound sensation is painful and very sensitive to touch and air currents. (B) Third-degree burn showing viable color (deep-red, white, black and brown). The wound itself is insensate (does not respond to pinprick sensation).
BURNSBURNS• First degree – superficial burn, First degree – superficial burn,
affecting epidermal layer of skin, affecting epidermal layer of skin, skin is red and dry; Ex – sunburnskin is red and dry; Ex – sunburn
• Second degree – affecting Second degree – affecting epidermal and dermal layers; skin is epidermal and dermal layers; skin is red and has blisters; Ex - burn from red and has blisters; Ex - burn from cookingcooking
• Third degree – epidermal and Third degree – epidermal and dermal layers destroyed, dermal layers destroyed, subcutaneous tissue damaged, subcutaneous tissue damaged, charred white, grey and/or black charred white, grey and/or black tissuetissue

Figure 16-15. (A) Actinic (solar) keratosis. (B) Squamous cell carcinoma. Lesions are often nodular and ulcerated.
ABNORMAL SKIN CONDITIONSABNORMAL SKIN CONDITIONS
• Actinic Keratosis Actinic Keratosis – – precancerous skin lesion precancerous skin lesion (usually caused by sun (usually caused by sun exposure)exposure)
• Squamous Cell CarcinomaSquamous Cell Carcinoma - -malignant tumor of squamous malignant tumor of squamous epithelial cell of epidermis, epithelial cell of epidermis, remember epithelial cells also remember epithelial cells also line internal organs so you line internal organs so you can have squamous cell can have squamous cell carcinoma in the mouth, carcinoma in the mouth, larynx, lung, etc…larynx, lung, etc…

Figure 16-13. (A) Basal cell carcinoma. (B) Kaposi sarcoma.
ABNORMAL SKIN ABNORMAL SKIN CONDTIONSCONDTIONS
Basal Cell CarcinomaBasal Cell Carcinoma – – malignant tumor of malignant tumor of basal cell layer of basal cell layer of epidermisepidermis
Karposi’s SarcomaKarposi’s Sarcoma - - tumors develop in the tumors develop in the tissues below the skin tissues below the skin surface, or in the surface, or in the mucous membranes. mucous membranes. Common in HIV+ Common in HIV+ patients patients

The ABCDs of melanoma. (A)Asymmetry: one half
unlike the other half. (B) Border: irregular or
poorly circumscribed border.
(C)Color: varied from one area to another; shades of tan & brown; black; sometimes white, red or blue.
(D)Diameter: usually larger than 6mm (diameter of a pencil eraser).
ABNORMAL SKIN CONDITIONSABNORMAL SKIN CONDITIONS