Integumentary System
-
Upload
cynthia-mathis -
Category
Documents
-
view
33 -
download
0
description
Transcript of Integumentary System

Integumentary SystemIntegumentary System
Chapter 5Chapter 5

Objectives:Objectives:
1- Describe the functions of the 1- Describe the functions of the integumentary system.integumentary system.
2- Identify the major structures found 2- Identify the major structures found in the three layers of the skin.in the three layers of the skin.
3. Describe the anatomy and 3. Describe the anatomy and physiology of hair and nailsphysiology of hair and nails
4. Define some common 4. Define some common dermatopathological disorders.dermatopathological disorders.

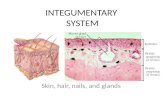
This system is divided into:This system is divided into:1- skin1- skin2- hair2- hair3- glands3- glands4- nails4- nails5- nerve endings5- nerve endingsI) I) Skin Skin Skin is an organ because it consists of Skin is an organ because it consists of
different tissues that are joined to different tissues that are joined to perform a perform a specific function.specific function.Largest organ of the body in surface area Largest organ of the body in surface area and weight.and weight.DermatologyDermatology is the medical specialty is the medical specialty concerning the diagnosing and treatment concerning the diagnosing and treatment of of skin disorders.skin disorders.


Anatomy (structure)Anatomy (structure)EpidermisEpidermis (thinner outer layer of skin) (thinner outer layer of skin)Dermis Dermis (thicker connective tissue layer)(thicker connective tissue layer)HypodermisHypodermis (subcutaneous layer or Sub-Q) (subcutaneous layer or Sub-Q)Muscle and boneMuscle and bone
Physiology (function)Physiology (function)1- Protection1- Protection
- physical barrier that protects - physical barrier that protects underlying tissues from injury, UV light underlying tissues from injury, UV light and bacterial invasion.and bacterial invasion.
- mechanical barrier is part - mechanical barrier is part non non specific immunity specific immunity (skin, tears and (skin, tears and saliva).saliva).

2- Regulation of body temperature2- Regulation of body temperature- high temperature or strenuous - high temperature or strenuous
exercise; sweat is evaporated from exercise; sweat is evaporated from the skin surface to cool it down.the skin surface to cool it down.
- - vasodilationvasodilation (increases blood (increases blood flow) andflow) and vasoconstriction vasoconstriction (decrease in blood flow) regulates (decrease in blood flow) regulates body temp.body temp.
3-Sensation3-Sensation - nerve endings and receptor - nerve endings and receptor
cells that detect stimuli to temp., cells that detect stimuli to temp., pain, pressure and touch.pain, pressure and touch.

4- Excretion4- Excretion - sweat removes water and small - sweat removes water and small
amounts of salt, uric acid and ammonia amounts of salt, uric acid and ammonia from the body surfacefrom the body surface
5- Blood reservoir 5- Blood reservoir - dermis houses an extensive network - dermis houses an extensive network
of blood vessels carrying 8-10% of total of blood vessels carrying 8-10% of total blood flow in a resting adult. blood flow in a resting adult.
6- Synthesis of Vitamin D (cholecalciferol)6- Synthesis of Vitamin D (cholecalciferol) -UV rays in sunlight stimulate the -UV rays in sunlight stimulate the
production of Vit. D. Enzymes in the production of Vit. D. Enzymes in the kidney and liver modify and convert to kidney and liver modify and convert to final form; final form; calcitriolcalcitriol (most active form of (most active form of Vit. D.) Calcitriol aids in absorption of Vit. D.) Calcitriol aids in absorption of calcium from foods and is considered a calcium from foods and is considered a hormone.hormone.

Epidermis: keratinized stratified Epidermis: keratinized stratified squamous epithelium with four distinct squamous epithelium with four distinct cell types and five distinct layers. cell types and five distinct layers.


Cells in the epidermis:Cells in the epidermis:- keratinoytes- keratinoytes- melanocytes- melanocytes- Merkel cells- Merkel cells- Langerhans’ cells- Langerhans’ cells
1- Keratinocytes: most abundant 1- Keratinocytes: most abundant - produce keratin (fibrous protein)- produce keratin (fibrous protein)- protective; waterproofing the skin - protective; waterproofing the skin - continuous mitosis- continuous mitosis- form in the deepest layer called the - form in the deepest layer called the stratum basale stratum basale- cells push their way up to the - cells push their way up to the
surface surface where they are dead cells where they are dead cells filled with filled with keratin; will slough keratin; will slough off. Regenerates every off. Regenerates every 25-45 days. 25-45 days.


2- Melanocytes: 2- Melanocytes: - cells produce brownish/black pigment- cells produce brownish/black pigmentcalled melanin. (8% of epidermal cells)called melanin. (8% of epidermal cells)- stratum basale- stratum basale- branching processes (dendrites)- branching processes (dendrites)- melanin accumulates in melanosomes- melanin accumulates in melanosomes and transported along dendrites of and transported along dendrites of the melanocytes to keratinocytes. the melanocytes to keratinocytes.- melanin accumulates on the superficial - melanin accumulates on the superficial aspect of the keratinocyte shielding its aspect of the keratinocyte shielding its nucleus from harmful UV light. nucleus from harmful UV light.- lack of melanin: albino- lack of melanin: albino


3- Merkel cells:3- Merkel cells:- stratum basale- stratum basale- epidermis of hairless skin- epidermis of hairless skin- attach to keratinocytes by desmosomes- attach to keratinocytes by desmosomes- make contact with a sensory neuron - make contact with a sensory neuron ending ending called a Merkel disc (touch).called a Merkel disc (touch).
4- Langerhans’ cells:4- Langerhans’ cells:- star-shaped cells arising from bone - star-shaped cells arising from bone marrow marrow that migrate to epidermis.that migrate to epidermis.- epidermal dendritic cells (macrophages)- epidermal dendritic cells (macrophages)- interact with a WBC called a T- helper cell- interact with a WBC called a T- helper cell- easily damaged by UV light.- easily damaged by UV light.



Stratum corneum
Stratum lucidum
Stratum spinosum
Stratum granulosum
Stratum basale

5 layers of the epidermis:5 layers of the epidermis:1- 1- Stratum corneum (horny layer)Stratum corneum (horny layer)
- - layer has many rows of dead cells filled layer has many rows of dead cells filled with with keratinkeratin
-- continuously shed and replaced continuously shed and replaced (desquamation)(desquamation) -- effective barrier against light, heat and effective barrier against light, heat and
bacteriabacteria- 20-30 cell layers thick- 20-30 cell layers thick- dandruff and flakes- dandruff and flakes- 40 lbs. of skin flakes in a lifetime (dust - 40 lbs. of skin flakes in a lifetime (dust mites!)mites!)

2- 2- Stratum lucidumStratum lucidum -- seen in thick skin of the palms and soles seen in thick skin of the palms and soles
of of feet.feet. - 3-5 rows of - 3-5 rows of clearclear flat dead cells flat dead cells - keratohyalin (precursor) to keratin- keratohyalin (precursor) to keratin
3- 3- Stratum granulosumStratum granulosum- 3-5 rows of flattened cells- 3-5 rows of flattened cells- nuclei of cells flatten out- nuclei of cells flatten out- organelles disintegrate cells eventually - organelles disintegrate cells eventually diedie- keratohyalin granules (darkly stained) - keratohyalin granules (darkly stained)
accumulate accumulate - lamellated granules secrete glycolipids - lamellated granules secrete glycolipids into into extracellular spaces to slow water extracellular spaces to slow water loss in the loss in the epidermisepidermis

4- 4- Stratum spinosumStratum spinosum: “spiny layer”: “spiny layer”
- 8-10 rows of polyhedral (many - 8-10 rows of polyhedral (many sided) cellssided) cells
- appearance of prickly spines- appearance of prickly spines
- shrink when prepared for - shrink when prepared for slideslide
- melanin granules and Langerhans’ - melanin granules and Langerhans’ cell predominatecell predominate


5- 5- Stratum basale: Stratum basale: deepest epidermal deepest epidermal layerlayer
- attached to dermis- attached to dermis
- single row of cells- single row of cells
- mostly columnar keratinocytes- mostly columnar keratinocytes
- with rapid mitotic division - with rapid mitotic division
- stratum germinativum- stratum germinativum
- contain merkel cells and melanocytes - contain merkel cells and melanocytes
- 10-25%- 10-25%



Dermis:Dermis:
- flexible and strong connective tissue- flexible and strong connective tissue
- elastic, reticular and collagen fibers- elastic, reticular and collagen fibers
- cells: fibroblasts, macrophages (WBC),- cells: fibroblasts, macrophages (WBC),
mast cells (histamine).mast cells (histamine).
- nerves, blood and lymphatic vessels- nerves, blood and lymphatic vessels
- oil and sweat glands originate- oil and sweat glands originate
- two layers: papillary and reticular- two layers: papillary and reticular

1- Papillary layer: 1- Papillary layer:
- loose connective tissue with nipple - loose connective tissue with nipple like like surface projection called dermal surface projection called dermal
papilla.papilla.
- capillaries- capillaries
- contain pain receptors - contain pain receptors
- contain touch receptors (Meissner’s - contain touch receptors (Meissner’s corpusclescorpuscles
- dermal ridges- epidermal ridges- - dermal ridges- epidermal ridges- pattern called fingerprintspattern called fingerprints

2- Reticular layer:2- Reticular layer:- dense irregular c.t.- dense irregular c.t.- collagen fibers offer strength- collagen fibers offer strength- holds water- holds water- dermal tearing causes stretch - dermal tearing causes stretch
marks.marks.- striae- striae
Skin color: attributed to melanin, Skin color: attributed to melanin, hemoglobin and carotene. hemoglobin and carotene.
Race is determined by amount of Race is determined by amount of melanin not # of melanocytes.melanin not # of melanocytes.

Local accumulation of melanin will result inLocal accumulation of melanin will result infreckles and pigmented moles.freckles and pigmented moles.
Melanin is made through interaction with Melanin is made through interaction with tyrosinase present in melanocytestyrosinase present in melanocytes
UV light stimulates melanin production. UV light stimulates melanin production. Excessive UV light can damage DNA and Excessive UV light can damage DNA and cause solar elastosis (elastin fibers clump)cause solar elastosis (elastin fibers clump)
Carotene is formed from Vit. A and deposits Carotene is formed from Vit. A and deposits in stratum corneum and imparts an orange in stratum corneum and imparts an orange tone to skintone to skin

FrecklesFreckles

Hemoglobin (blood) will impart pinkish Hemoglobin (blood) will impart pinkish tones to skin. Blushingtones to skin. Blushing
1- Redness (erythema) - reddened skin, 1- Redness (erythema) - reddened skin, embarrassment, fever, hypertension, embarrassment, fever, hypertension, inflammation, or allergy inflammation, or allergy
2- Pallor/blanching - pale skin, emotional 2- Pallor/blanching - pale skin, emotional distress or anemia, low blood distress or anemia, low blood pressure pressure
3- Jaundice - liver disease, bile deposited 3- Jaundice - liver disease, bile deposited in tissue in tissue
4- Bronzing - bronze coloration 4- Bronzing - bronze coloration (Addison's disease) hypofunction of (Addison's disease) hypofunction of adrenal cortex adrenal cortex
5- Black & blue - bruises, escaped blood 5- Black & blue - bruises, escaped blood clots in tissue spaces (clotted blood clots in tissue spaces (clotted blood masses = hematomas) masses = hematomas)

Hair color:Hair color:
Dark hair: mostly melaninDark hair: mostly melanin
Blond and red hair: melanin with Fe Blond and red hair: melanin with Fe and S.and S.
Gray hair: loss of pigment (decr. Gray hair: loss of pigment (decr. tyrosinase)tyrosinase)
White hair: air bubbles in the White hair: air bubbles in the medullary hair medullary hair shaft. shaft.

Hair (pili)Hair (pili)
- main function is - main function is protectionprotection
- hair root nerve - hair root nerve plexus for touchplexus for touch
- normal hair loss - normal hair loss in adult 70-100 in adult 70-100 hairs/dayhairs/day



Hair anatomy:Hair anatomy:- composed of dead columns of - composed of dead columns of keratinized cells.keratinized cells.- shaft: is the superficial portion of hair- shaft: is the superficial portion of hair- root: below the surface in the dermis- root: below the surface in the dermisShaft and root are composed of three Shaft and root are composed of three layers: inner medulla, middle cortex layers: inner medulla, middle cortex and outer cuticle.and outer cuticle.
Inner medulla has 2-3 rows of polyhedral Inner medulla has 2-3 rows of polyhedral cells where pigment is locatedcells where pigment is located
Cortex is major portion of shaftCortex is major portion of shaftCuticle is scaly and heavily keratinized Cuticle is scaly and heavily keratinized
(shingles)(shingles)

Vellus hair: fine hair Vellus hair: fine hair Terminal hair : coarser hair; axillary and Terminal hair : coarser hair; axillary and pubic region. Grow in response to sex pubic region. Grow in response to sex hormoneshormonesHirsutism: excessive hairiness: incr. Hirsutism: excessive hairiness: incr. androgensandrogens

Hair follicle surrounds the root.Hair follicle surrounds the root.
Bulb is the enlargement at the end of the Bulb is the enlargement at the end of the follicle.follicle.
- Also houses the germinal layer- Also houses the germinal layer
Papilla (nipple like) is located in the bulb Papilla (nipple like) is located in the bulb and is where the blood supply nourishes and is where the blood supply nourishes the hair.the hair.

Arrector pili (pl. pilorum) is smooth muscle Arrector pili (pl. pilorum) is smooth muscle located in the dermis and is attached to located in the dermis and is attached to the side of the hair shaft.the side of the hair shaft.
- fright, cold and emotions will contract - fright, cold and emotions will contract muscle and pull hair in vertical position. muscle and pull hair in vertical position. “Goose bumps”.“Goose bumps”.


Glands:Glands:Two types of glands exist in the integument.Two types of glands exist in the integument.
- Sebaceous glands (oil glands)- Sebaceous glands (oil glands)- Sudoriferous glands (sweat glands)- Sudoriferous glands (sweat glands)
Sebaceous glands: (holocrine glands)Sebaceous glands: (holocrine glands)- connected to hair follicle- connected to hair follicle- not found on palms and soles of feet- not found on palms and soles of feet- secretes sebum (fats, cholesterol - secretes sebum (fats, cholesterol
and and proteins proteins- keep hair from drying out, keeps - keep hair from drying out, keeps
skin moistskin moist- whiteheads, blackheads and acne- whiteheads, blackheads and acne



Whitehead: Whitehead: When the trapped sebum When the trapped sebum and bacteria stay below the skin surface, and bacteria stay below the skin surface,
a a whiteheadwhitehead is formed. is formed.

Blackhead: Blackhead: A A blackheadblackhead occurs when the occurs when the trapped sebum and bacteria partially open trapped sebum and bacteria partially open
to the surface and turn black due to to the surface and turn black due to melanin, the skin's pigment. Blackheads melanin, the skin's pigment. Blackheads
can last for a long time because the can last for a long time because the contents very slowly drain to the surface.contents very slowly drain to the surface.

Sudoriferous glands: exocrine glandsSudoriferous glands: exocrine glands
- millions located throughout the skin- millions located throughout the skin
- two types:- two types:
- eccrine: more common (merocrine) - eccrine: more common (merocrine)
- originate in subQ layer- originate in subQ layer
- duct empties on skin surface- duct empties on skin surface
- palms and soles of feet- palms and soles of feet
- sweat is watery (99% H- sweat is watery (99% H220)0)
- sweating regulated by - sweating regulated by sympathetic nervous sympathetic nervous
systemsystem


- apocrine: axillary and pubic region- apocrine: axillary and pubic region
- duct empties onto hair follicle- duct empties onto hair follicle
- viscous fluid- viscous fluid
- causes body odor (“b-o “) when - causes body odor (“b-o “) when bacteria break it down bacteria break it down

Ceruminous glands: located in ear onlyCeruminous glands: located in ear only
- modified apocrine glands- modified apocrine glands
- originate in Sub Q layer- originate in Sub Q layer
- ducts open onto EAM.- ducts open onto EAM.
- produces cerumen (ear wax) : - produces cerumen (ear wax) : brown brown sticky substance that sticky substance that prevents foreign prevents foreign material from material from entering.entering.


Nails:Nails:
- Produced by cells in the epidermis- Produced by cells in the epidermis
- Nail plate (body): visible portion- Nail plate (body): visible portion
- Nail root: located under cuticle- Nail root: located under cuticle
- Lunula: half moon crescent shaped- Lunula: half moon crescent shaped
white portion under cuticlewhite portion under cuticle
- Nail bed: located under nail plate- Nail bed: located under nail plate
- Hypoxia: decr. oxygen in blood, - Hypoxia: decr. oxygen in blood, nail bed will turn blue- nail bed will turn blue- cyanosiscyanosis


Nerve endings:Nerve endings:- Exteroceptors (stimulus outside of body) - Exteroceptors (stimulus outside of body)
- Pacinian (lamellated) corpuscles: - Pacinian (lamellated) corpuscles: deep deep pressure and stretchpressure and stretch
- Meissner’s (tactile) corpuscles: light - Meissner’s (tactile) corpuscles: light touch, vibration and touch, vibration and
discriminative discriminative touch.touch.- hair root plexus- hair root plexus- free (naked) nerve endings: - free (naked) nerve endings:
nociceptors nociceptors (pain) and (pain) and thermoreceptors ( hot –thermoreceptors ( hot – deep deep and cold- surface)and cold- surface)
- Ruffini’s corpuscles: deep pressure- Ruffini’s corpuscles: deep pressure

Pacinian corpusclePacinian corpuscle

HypodermisHypodermis
- called subcutaneous, Sub-Q or - called subcutaneous, Sub-Q or superficial superficial fasciafascia
- anchors skin to underlying - anchors skin to underlying structuresstructures
- contains adipose tissue and blood - contains adipose tissue and blood vesselsvessels
- common site for injection- common site for injection

Dermatopathological termsDermatopathological terms Macule – flat spot on skin with color Macule – flat spot on skin with color
(freckle) (freckle) Wheal – round and temp. elevation of skin Wheal – round and temp. elevation of skin
(hives) (hives) Papule - solid elevated area, epidermal and Papule - solid elevated area, epidermal and
papillary (insect bite) papillary (insect bite) Nodule - large papules extending into Nodule - large papules extending into
subcutaneous layer (cyst) subcutaneous layer (cyst) Vesicle - papule with fluid core (varicella Vesicle - papule with fluid core (varicella
zoster virus) zoster virus) Pustule - papule with pus core (acne) Pustule - papule with pus core (acne) Erosion - ruptured vesicle (ulcer) Erosion - ruptured vesicle (ulcer) Xeroderma - "dry skin" Xeroderma - "dry skin" Hemangiomas - benign tumor in the dermis Hemangiomas - benign tumor in the dermis
(capillary and cavernous) (capillary and cavernous)

Sebaceous hyperplasia - enlargement of the Sebaceous hyperplasia - enlargement of the sebaceous gland sebaceous gland
Pruritis - irritating itching sensation of the skin Pruritis - irritating itching sensation of the skin Seborrheic dermatitis - inflammation around Seborrheic dermatitis - inflammation around
abnormally active sebaceous glands abnormally active sebaceous glands Basal cell carcinoma - malignant cancer Basal cell carcinoma - malignant cancer
originating in the germinative layer originating in the germinative layer Squamous cell carcinoma - malignant cancer Squamous cell carcinoma - malignant cancer
originating in the top layer of the skin originating in the top layer of the skin Malignant melanomas - metastasizing Malignant melanomas - metastasizing
melanocytes melanocytes