Integumentary system
-
Upload
m-carol-carlisle -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
693 -
download
0
Transcript of Integumentary system

Integumentary System
Tissues in combinationTissues in combination

Functions of Integument
Protection of underlying tissuesProtection of underlying tissues Excretion of salts, water, organic wasteExcretion of salts, water, organic waste Maintenance of normal body tempMaintenance of normal body temp Synthesis of vitamin DSynthesis of vitamin D Storage of nutrientsStorage of nutrients Sensitivity to touch, pressure, pain, tempSensitivity to touch, pressure, pain, temp

Skin is the largest organ of your body – 16% by weight 2 Functional components2 Functional components
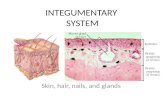
Cutaneous membrane – layers of tissuesCutaneous membrane – layers of tissues Accessory structures – hair, nails, glandsAccessory structures – hair, nails, glands
Cutaneous membrane has 3 regionsCutaneous membrane has 3 regions Epidermis – epithelial layerEpidermis – epithelial layer Dermis – CT layersDermis – CT layers Hypodermis – fat layer (deep)Hypodermis – fat layer (deep)

Epidermis
Stratified squamous epithelium in 4 (or 5) Stratified squamous epithelium in 4 (or 5) layerslayers 1. Stratum Germinativum (basale)1. Stratum Germinativum (basale)
Deepest layer – basement membraneDeepest layer – basement membraneStem cells – replace shed cellsStem cells – replace shed cells

2. Stratum spinosum2. Stratum spinosum
Bound together by desmosomesBound together by desmosomes Several cells thickSeveral cells thick Spiky looking under microscopeSpiky looking under microscope
3. Stratum granulosum3. Stratum granulosum Grainy layerGrainy layer Make keratohyalinMake keratohyalin

4. Stratum lucidum *4. Stratum lucidum * *only found on palms and soles*only found on palms and soles Clear layerClear layer Makes eleidinMakes eleidin
5. Stratum corneum5. Stratum corneum True keratin develops from keratohyalin True keratin develops from keratohyalin
and eleidinand eleidinKeratin is tough, flexible, water Keratin is tough, flexible, water
resistant, fibrous proteinresistant, fibrous protein

S. Corneum cont.
Cells become thin and flatCells become thin and flat Become packed with keratinBecome packed with keratin Organelles break down and cells dieOrganelles break down and cells die Eventually sloughed offEventually sloughed off From mitosis; 6 weeks to new epidermisFrom mitosis; 6 weeks to new epidermis Relatively dry – unattractive to microorganismsRelatively dry – unattractive to microorganisms Lipids are secreted by glands to maintain barrierLipids are secreted by glands to maintain barrier Xerosis – dry skinXerosis – dry skin

Cornification
Accumulation of keratin – keratinized Accumulation of keratin – keratinized Occurs everywhere except the surface of Occurs everywhere except the surface of
the eyesthe eyes Thin skin – 1.5 to 4mm; epidermis Thin skin – 1.5 to 4mm; epidermis
is .08mm, about 20 cell layers thickis .08mm, about 20 cell layers thick Palms and soles have 30+ layersPalms and soles have 30+ layers

Epidermal Ridges
Deeper layers of epidermis form ridgesDeeper layers of epidermis form ridges Increased contact with dermis – diffusion of Increased contact with dermis – diffusion of
nutrientsnutrients Base for fingerprints (genetically Base for fingerprints (genetically
determined)determined) Fingerprints provide gripFingerprints provide grip
Monitored by nerves for touch, pressure, Monitored by nerves for touch, pressure, pain, temp. info.pain, temp. info.

UV Radiation
Vitamin D synthesis – sterol altered by UVVitamin D synthesis – sterol altered by UV Stresses skinStresses skin
Breaks down underlying CTBreaks down underlying CTWrinklesWrinkles
Skin cancerSkin cancer Destroys folate – folate helps protect against Destroys folate – folate helps protect against
spina bifidaspina bifida Tanning beds are as risky as the sunTanning beds are as risky as the sun

Color of epidermis
1. Underlying blood vessels – reddish1. Underlying blood vessels – reddish In dermisIn dermis
2. Carotene – orange yellow pigment2. Carotene – orange yellow pigment In epitheliaIn epithelia
3. Melanin – yellow brown to black3. Melanin – yellow brown to black In between stem cellsIn between stem cells

Melanin
Secreted by melanocytes, passed to adjacent cellsSecreted by melanocytes, passed to adjacent cells Everyone has approximately the same number Everyone has approximately the same number
of melanocytes; but activity, and color and size of melanocytes; but activity, and color and size of granules of melanin differsof granules of melanin differs
Absorbs UV radiation, protects deeper layersAbsorbs UV radiation, protects deeper layers Activity increases with exposure to UVActivity increases with exposure to UV
Accelerates slowly – maxes about 10 days after Accelerates slowly – maxes about 10 days after initial exposureinitial exposure

Dermis
1. Papillary (superficial) layer1. Papillary (superficial) layer 2. Reticular (deep) layer2. Reticular (deep) layer Both contain fibers, blood vessels, Both contain fibers, blood vessels,
lymphatic vessels, fat cells, muscle cells, lymphatic vessels, fat cells, muscle cells, nerve endings, and accessory structuresnerve endings, and accessory structures

Papillary layer
Loose CTLoose CT Capillaries and nerves that supply epidermisCapillaries and nerves that supply epidermis Named for Named for dermal papillaedermal papillae (bumps) that (bumps) that
project between epidermal ridgesproject between epidermal ridges

Reticular layer
Dense irregular CTDense irregular CT Collagen fibers extend into papillary layerCollagen fibers extend into papillary layer Elastin fibersElastin fibers

Lines of Cleavage
Bundles of collagen tend to run parallelBundles of collagen tend to run parallel Different areas of body are oriented differentlyDifferent areas of body are oriented differently Surgeons use these lines to minimize scarring, Surgeons use these lines to minimize scarring,
heal fasterheal faster Stretch marks – bundles that have been pulled Stretch marks – bundles that have been pulled
apart by rapid weight gain or pregnancy apart by rapid weight gain or pregnancy (perpendicular to lines of cleavage)(perpendicular to lines of cleavage)

Hypodermis
Subcutaneous layerSubcutaneous layer Adipose tissueAdipose tissue Insulates against heat lossInsulates against heat loss Energy reserveEnergy reserve Cushioning for kidneys and babiesCushioning for kidneys and babies Collagen fibers extend into here from dermisCollagen fibers extend into here from dermis Hypodermic needle introduces drugs into fat layer, Hypodermic needle introduces drugs into fat layer,
slowly enters circulationslowly enters circulation

Skin cancers
Basal cell carcinoma – S. germinativum Basal cell carcinoma – S. germinativum cells are affected, most common typecells are affected, most common type
Squamous cell carcinoma – also epithelial, Squamous cell carcinoma – also epithelial, more deadly than basal cellmore deadly than basal cell
Melanoma – cancer of melanocytes, most Melanoma – cancer of melanocytes, most deadly form, more likely from severe burnsdeadly form, more likely from severe burns Size, shape, colorSize, shape, color
Moles – benign tumors of melanocytesMoles – benign tumors of melanocytes

Accessory Structures
HairHair Found everywhere except: sides and Found everywhere except: sides and
soles of feet, palms of hands, sides of soles of feet, palms of hands, sides of fingers and toes, lips, portions of external fingers and toes, lips, portions of external genitaliagenitalia
Color – variations in melaninColor – variations in melaninGray – pigment lessensGray – pigment lessensWhite – air bubble in shaftWhite – air bubble in shaft

Hair Follicle
Tube hair occupies Tube hair occupies Deep into dermis Deep into dermis StructureStructure
Papilla – bump containing nerves and Papilla – bump containing nerves and blood vesselsblood vessels
Matrix – epithelium at base of follicle Matrix – epithelium at base of follicle that forms hair, basal cells divide, that forms hair, basal cells divide, cornification of outer layerscornification of outer layers

Hair Structure
Medulla – soft core closest to center of papilla; Medulla – soft core closest to center of papilla; soft keratinsoft keratin
Cortex – farther out – hard keratin, stiffnessCortex – farther out – hard keratin, stiffness Cuticle – superficial – hard keratin coats hairCuticle – superficial – hard keratin coats hair Root – enclosed by matrix, bulb of follicleRoot – enclosed by matrix, bulb of follicle Shaft – the hair itselfShaft – the hair itself
Straight hair – round in cross sectionStraight hair – round in cross section Curly hair – flat or oval in cross sectionCurly hair – flat or oval in cross section

Hair types
1. Vellus hair – peach fuzz1. Vellus hair – peach fuzz 2. Terminal hair – heavy, dark, hair on 2. Terminal hair – heavy, dark, hair on
head, eyebrows, eyelashes, etc.head, eyebrows, eyelashes, etc. 3. Intermediate hair – hair on arms and legs3. Intermediate hair – hair on arms and legs Hormones change hair from one form to Hormones change hair from one form to
another another PubertyPuberty Male pattern baldnessMale pattern baldness

Hair loss may also be caused by
Drugs (chemo)Drugs (chemo) Dietary factorsDietary factors RadiationRadiation High feverHigh fever StressStress Pregnancy hormonesPregnancy hormones
Hair grows 1/3mm per dayHair grows 1/3mm per day Stays in scalp for 2 – 5 yearsStays in scalp for 2 – 5 years 50 hairs lost per day is normal50 hairs lost per day is normal

Hair Functions
Control heat lossControl heat loss Arrector pili – small smooth muscle that Arrector pili – small smooth muscle that
pulls on follicle to make hair stand uppulls on follicle to make hair stand upIncreases trapped air insulationIncreases trapped air insulationCauses goosebumps in humansCauses goosebumps in humans
Reduces frictionReduces friction

Nails
Made of keratin at the nail root (not visible)Made of keratin at the nail root (not visible) Lunula – pale crescent at base of nailLunula – pale crescent at base of nail
Blood vessels are obscuredBlood vessels are obscured Protection of finger and toe tips (claws in Protection of finger and toe tips (claws in
some animals)some animals)

Glands
Sebaceous glandsSebaceous glands Holocrine glands found along hair folliclesHolocrine glands found along hair follicles Secrete Secrete sebumsebum
Inhibits bacterial growthInhibits bacterial growthLubricates and protects hair shaft and skin Lubricates and protects hair shaft and skin
Contraction of arrector pili helps squeeze Contraction of arrector pili helps squeeze sebum onto skin surfacesebum onto skin surface
Sebaceous follicles discharge directly onto skinSebaceous follicles discharge directly onto skin

Sweat glands
1. Apocrine sweat glands – stinky sweat 1. Apocrine sweat glands – stinky sweat (bacteria that eat this sweat contribute to the (bacteria that eat this sweat contribute to the smell)smell) Found in armpits, around nipples, groinFound in armpits, around nipples, groin Associated with hair folliclesAssociated with hair follicles Send social chemical messages in Send social chemical messages in
mammals about sexmammals about sex

2. Merocrine sweat glands – watery sweat 2. Merocrine sweat glands – watery sweat (99% water, some salt, waste)(99% water, some salt, waste) Cools the body “sensible perspiration”Cools the body “sensible perspiration” Discharge onto skin surfaceDischarge onto skin surface Palms and soles – 3000 per sq. in.Palms and soles – 3000 per sq. in. Flushes out microorganismsFlushes out microorganisms Smaller than apocrine glandsSmaller than apocrine glands

Control of sweat glands
Sebaceous and apocrine are hormonally Sebaceous and apocrine are hormonally controlled; all on or all offcontrolled; all on or all off
Merocrine are nerve controlled, can be Merocrine are nerve controlled, can be regional regional Sweaty palmsSweaty palms

Ceruminous glands
Modified sweat glands in ear canalModified sweat glands in ear canal Secretions mix with sebum to make Secretions mix with sebum to make
cerumencerumen – ear wax – ear wax ProtectionProtection Bug repellentBug repellent

Nerve endings
Pain – free nerve endings in epidermisPain – free nerve endings in epidermis TouchTouch
Merkel’s discs – in epidermisMerkel’s discs – in epidermis Meissner’s corpuscles – in papillaeMeissner’s corpuscles – in papillae Root hair plexus – around hair at base of Root hair plexus – around hair at base of
folliclefollicle Pressure – Pacinian corpuscle – in hypodermisPressure – Pacinian corpuscle – in hypodermis Cold – Krause corpuscle – in dermis, roundCold – Krause corpuscle – in dermis, round Heat – Ruffini corpuscle – in dermis, flattenedHeat – Ruffini corpuscle – in dermis, flattened