Instructional Leadership Math Cadre 6 th – 12 th Grade SHIFT 2: COHERENCE THE PROE CENTER.
-
Upload
alexandra-reynolds -
Category
Documents
-
view
216 -
download
2
Transcript of Instructional Leadership Math Cadre 6 th – 12 th Grade SHIFT 2: COHERENCE THE PROE CENTER.

Instructional Leadership Math Cadre6th – 12th GradeSHIFT 2: COHERENCE
THE PROE CENTER

Multi-Tiered System of Support (MTSS/RtI)
Statewide System of Support
Priority
Focus
Foundational
Focus Areas:- Continuous
Improvement Process (Rising Star)
- Common Core ELA- Common Core Math- Teacher Evaluation- Balanced Assessment

Commitments

Today’s Outcomes
Use the Standards for Mathematical Practice while problem solving
Define coherence in the Common Core Identify coherence within the standards Utilize coherent problem solving structures that build conceptual
understanding Describe instructional strategies for computation Explore resources that build coherence Plan for implementation

Today’s Agenda
Review Shift 1: Focus Digging Deeper with the Standards for Mathematical
Practice Shift 2: Coherence Supporting Diverse Learners: Modes of Representation Problem Solving Structures Coherent instructional resources Common Core Math in the Media

Shift 1: Focus
REVIEW

Focusing on Solving Problems
USING THE STANDARDS FOR MATHEMATICAL PRACTICE

Solving Problems
Standards for Mathematical Practice
1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them.
2. Reason abstractly and quantitatively.
3. Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others.
4. Model with mathematics
5. Use appropriate tools strategically.
6. Attend to precision.
7. Look for and make use of structure.
8. Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning.

Debriefing the Activity
Discuss:
1) The content
2) The math practices

Shift 2: Coherence

Coherence
Math should make sense.

Mike McCallum
The Importance of Coherence in Math

Coherence
Math should make sense
A progression of learning
Coherence supports focus
Use supporting material to teach major content
Math should make sense• Within a grade level• Across many grade levels

Coherence WITHIN a grade level
The standards within a grade level strategically allow: Instruction that reinforces major content and
utilizes supporting standards
Important to remember: Meaningful introduction to topics so that skills
complement one another

Coherence WITHIN a grade level
Use addition and subtraction within 100 to solve word problems involving lengths that are given in the same units, e.g., by using drawings (such as drawings of rulers) and equations with a symbol for the unknown number to represent the problem. 2.MD.5
Draw a scaled picture graph and a scaled bar graph to represent a data set with several categories. Solve one- and two- step “how many more” and “how many less” problems using information presented in scaled bar graphs.
3.MD.3
Geometric measurement: understand concepts of area and relate area to multiplication and addition. 3.MD.3rd cluster
Make a line plot to display a data set of measurements in fractions of a unit ( ½, ¼, 1/8). Solve problems involving addition and subtraction of fractions by using information presented in line plots. 4.MD.4

Coherence ACROSS grade levels
Students apply skills from previous grade levels to learn new topics in their current grade level
Meaningful math progressions reflect this, building knowledge across the grade levels

Coherence ACROSS grade levels
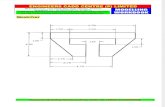
One of several staircases to algebra designed in the OA domain.

Coherence ACROSS grade levels
4.NF.4. Apply and extend previous understandings of multiplication to multiply a fraction by a whole number.
5.NF.4. Apply and extend previous understandings of multiplication to multiply a fraction or whole number by a fraction.
5.NF.7. Apply and extend previous understandings of division to divide unit fractions by whole numbers and whole numbers by unit fractions.
6.NS. Apply and extend previous understandings of multiplication and division to divide fractions by fractions.
6.NS.1. Interpret and compute quotients of fractions, and solve word problems involving division of fractions by fractions, e.g., by using visual fraction models and equations to represent the problem.
Grade 4
Grade 5
Grade 6
CCSS

Coherence Activity

Learning Progression:
A pathway or stream students travel as they progress toward mastery of the skills.
These streams contain carefully sequenced building blocks (content standards) that
support students’ progression towards mastery.

Benefits of Progressions/Streams
Enables teachers to build instructional sequences
Provide a framework to systematically implement effective formative assessment

Common Core Progression Streams
1. Counting and Cardinality (K)
2. Algebraic Thinking (K-HS)
3. Number and Quantity
4. Geometry
5. Functions
6. Statistics and Probability
7. High School Modeling
Visual Map


Activity:Progression Jigsaw
1) Read the intro for your designated Progression
2) Read your grade level in the designated Progression, highlighting key skills for your grade level
3) Create a flow-chart of skills, visually depicting how the skills in each grade level build on one another in developing conceptual understanding within the Progression (domain)
4) Creatively share your learning progression with the rest of the group

Modes of Representation

Modes of Representation
Manipulativesor Tools
Pictures/ Graphs
Written Symbols
Oral/Written
Language
Real-Life Situations

Building Conceptual Understanding
Adding Modes of Representation
45 45 x 24 x 24

Problem Solving Structures
WRITE A SIMPLE MULTIPLICATION/DIVISION WORD PROBLEM.

Addition & Subtraction Result Unknown Change Unknown Start Unknown
Add to
Two bunnies sat on the grass. Three more bunnies hopped there. How many bunnies
are on the grass now?2 + 3 = ?
Two bunnies were sitting on the grass. Some more bunnies hopped there. Then there were five bunnies. How many bunnies hopped over
to the first two?2 + ? = 5
Some bunnies were sitting on the grass. Three more bunnies hopped there. Then
there were five bunnies. How many bunnies were on the grass before?
? + 3 = 5
Take From
Five apples were on the table. I ate two apples. How many apples are on the table
now?5 – 2 = ?
Five apples were on the table. I ate some apples.
Then there were three apples. How many apples did I eat?
5 – ? = 3
Some apples were on the table. I ate two apples. Then there were three apples. How
many apples were on the table before?? – 2 = 3
Total Unknown Addend Unknown Both Addends Unknown
Put Together/ Take Apart
Three red apples and twogreen apples are on the table. How many
apples areon the table?
3 + 2 = ?
Five apples are on the table.Three are red and the rest are green. How
many applesare green?
3 + ? = 5, 5 – 3 = ?
Grandma has five lowers.How many can she put in her
red vase and how many in her blue vase?5 = 0 + 5, 5 = 5 + 05 = 1 + 4, 5 = 4 + 15 = 2 + 3, 5 = 3 + 2
Difference Unknown Bigger Unknown Smaller Unknown
Compare
(“How many more?” version):Lucy has two apples. Julie has five apples.
How manymore apples does Julie have than Lucy?
(“How many fewer?” version):Lucy has two apples. Julie has five apples.
How many fewer apples does Lucy have than Julie?
2 + ? = 5, 5 – 2 = ?
(Version with “more”):Julie has three more apples than Lucy. Lucy has two apples. How many apples does Julie
have?(Version with “fewer”):
Lucy has 3 fewer apples thanJulie. Lucy has two apples.
How many apples does Julie have?2 + 3 = ?, 3 + 2 = ?
(Version with “more”):Julie has three more apples than Lucy. Julie
has five apples. How many apples does Lucy have?
(Version with “fewer”):Lucy has 3 fewer apples than
Julie. Julie has five apples.How many apples does Lucy have?
5 – 3 = ?, ? + 3 = 5

Multiplication & Division
Unknown Product Group Size UnknownNumber of Groups
Unknown3 x 6 = ? 3 x ? = 18, and 18 ÷ 3 = ? ? x 6 = 18, and 18 ÷ 6 = ?
Equal Groups
There are 3 bags with 6 plums in each bag. How many plums are there in all?
Measurement example. You need 3 lengths
of string, each 6 inches long. How much string will you need altogether?
If 18 plums are shared equally into 3 bags, then how many plums will be in each bag?
Measurement example. You have 18 inches
of string, which you will cut into 3 equal pieces. How long will each piece of string
be?
If 18 plums are to be packed 6 to a bag, then how many bags are needed?
Measurement example. You have 18 inches of string, which you will cut into pieces that
are 6 inches long. How many pieces of string will you have?
Arrays, Area
There are 3 rows of apples with 6 apples in each row. How many apples are there?
Area example. What is the area of a 3 cm by
6 cm rectangle?
If 18 apples are arranged into 3equal rows, how many apples will be in each
row?
Area example. A rectangle has area 18 square centimeters. If one side is 3 cm long,
how long is a side next to it?
If 18 apples are arranged into equal rows of 6 apples, how many rows will there be?
Area example. A rectangle has area 18
square centimeters. If one side is 6 cm long, how long is a side next to it?
Compare
A blue hat costs $6. A red hat costs 3 times as much as the blue hat. How much does the
red hat cost?
Measurement example. A rubber band is 6 cm long. How long will the rubber band be when it is stretched to be 3 times as long?
A red hat costs $18 and that is3 times as much as a blue hat costs. How
much does a blue hat cost?
Measurement example. Arubber band is stretched to be
18 cm long and that is 3 times as long as it was at first. How long was the rubber band
at first?
A red hat costs $18 and a blue hat costs $6. How many times as much does the red hat
cost as the blue hat?
Measurement example. A rubber band was 6 cm long at first. Now it is stretched to be 18
cm long. How many times as long is the rubber band now as it was at first?
General a x b = ? a x ? = p, ad p ÷ a = ? ? x b = o, and p ÷ b = ?

Problem Solving Structures
WHICH PROBLEM SOLVING STRUCTURE DID YOU USE?

Instructional Strategies
FOR MULTIPLICATION

Additive Properties
Repeated Addition
Skip Counting

Distributive Property
Area/AreaPartial ProductBox methodDecomposing

Advanced Strategies
Double and Halve
(Standard Algorithm)

Coherence in Action
VIEWS YOU CAN USE

Dan Meyer
Math Class
Needs a
Make-over

Dan Meyer Resources
Dan Meyer createsCoherence forteachers, too.
Three-Act Math Tasks
on Livebinders

Math Common Core in the Media

Planning for Next Steps
TAKING IT BACK TO MY CLASSROOM
SHARING WITH MY COLLEAGUES

Comments…
Questions…
Concerns…