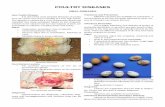
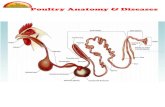
Indovax CD Poultry Diseases
-
Upload
surajsubedi -
Category
Documents
-
view
577 -
download
45
Transcript of Indovax CD Poultry Diseases

INDOVAX
Avian Encephalomyelitis
Chicken Anaemia
Poultry Diseases
Egg Drop Syndrome
Fowl Cholera
Infectious Coryza
Fowl Pox
Avian Infectious Bronchitis
Gumboro Disease (IBD)
Infectious Laryngotracheitis
Mareks Disease (MD)
Lymphoid Leucosis
Newcastle Disease (RD)
Avian Influenza (HPAI)
IBH – HHS (Leechi Disease)
Fowl Typhoid
CRD
Collibacillosis
Ascites
Avian Influenza (LPAI)
Gout (Non infectious)
Fatty Liver Syndrome
Viral Arthritis
(Click on tabs for details)

INDOVAX
Avian Encephalomyelitis
Avian encephalomyelitis is a disease of chickens marked by ataxia and tremor of the head, neck and limbs.
Aetiology - Picorna virus.
HostsAffects chicken, quail, turkeys.
TransmissionVertical transmission is a very important means of virus dissemination. Horizontal spread due to direct or indirect contact with ailing birds. Virus is shed in droppings.
Susceptibility to chemical & physical agentsFormalin fumigation is effective.
Viral strainsEnterotropic strains, embryo-adapted strains.
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
Incubation period1 to 7 days in embryo transmission11 days by oral administration.
SymptomsChicks in first week of their life show unsteadiness, sitting on hocks, paresis and even complete inability to move. The disease in adult birds is in apparent except for a transient drop in egg production.
Gross PathologyIn chicks – whitish areas on gizzard muscle .
DiagnosisBased on history, signs and isolation of virus from brain tissue.
Material for LaboratoryBrain tissue from affected chick stored in 50% glycerine saline to be sent on ice.
ControlControl of AE is achieved by vaccination of breeder flock during the growing period to ensure that they do not become infected after maturity.
Home Next Previous
Avian Encephalomyelitis

INDOVAX
Chicken infectious anaemia is a disease of young chicken characterized by aplastic anaemia and generalized lymphoid atrophy with concomittant immunosuppression.
AetiologyVirus classified as member of circoviridae – DNA virus.
HostThe chicken is the only known host for CIAV. All ages are susceptible but susceptibility to disease rapidly decreases in immunologically intact chicks during first 3 weeks of life.
TransmissionSpreads horizontally and vertically. Horizontal infection occurs by direct or indirect contact with ailing birds.
Resistance to chemical & physical agentsExtremely resistant to heat (56ºC to 70ºC for one hour). 1% glutarldehyde, 5% formalin, iodine, hypochlorites are effective.
Chicken Anaemia
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
Incubation periodUnder field conditions vertically infected chicks show increased mortality beginning at 10 – 12 days of age with peak at 17 – 24 days, second peak is at 30 – 34 days due to horizontal transmission.
Clinical symptomsPoor growth, pale birds, sudden rise in mortality (usually 13 – 16 days of age). No clinical signs or effect on egg production or fertility in parent flock during seroconversion.
Gross pathologyPale bone marrow, atrophy of thymus and bursa, discolored liver & kidney, gangrenous dermatitis.
DiagnosisOn basis of gross lesions, demonstration of ongoing seroconversion is parent flock. Virus may be isolated in specific cell line MDCC – MSB1.
Chicken Anaemia
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
Material for LaboratoryLiver or spleen tissue or rectal contents from diseased chickens in early phase of the disease to be sent on ice to the laboratory.
ControlIn addition to bio-security measures vaccination of parents is an important strategy of control.Current vaccine strategies are based on prevention of vertical transmission of virus by immunization of breeder flock and have been successful in reducing the incidence of anaemia in chicks.
Both live and inactivated vaccines are reported to be useful.
Chicken Anaemia
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
Viral arthritis is a contagious disease of domestic fowl – particularly broiler breeds – caused by REO virus.
Aetiology - REO virus.
HostsPrimarily disease of domestic fowl.
TransmissionVertical transmission through embryonated eggs. Horizontal spread occurs readily from bird to bird mainly by ingestion of contaminated faeces. Infection can occur through respiratory route also.
Resistance to chemical & physical agentsREO virus is heat resistant. It can withstand 60ºC for 8 to 10 hours. In poultry sheds at 22ºC or so, it can survive for a year.
Incubation periodDepends on virus pathotype. 9 to 13 days in contact exposure.
Viral Arthritis
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
SymptomsLameness, low morbidity, poor growth, inflammation of hock, swelling of tendon sheaths, rapture of gastrocnemius tendons.
Gross pathology Swelling of tendon sheaths, swelling of footpad, ulceration of articular cartilage, hemorrhage in tissues.
DiagnosisBased on history, lesions. Rising antibody titres, isolation of virus.
Material to be sent to laboratory Affected joint in 50% glycerine saline to be sent on ice.
ControlIn addition to bio-security measures, immunization of birds with live vaccine in growing stage followed by inactivated vaccine when the birds come in lay.
Viral Arthritis
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
Egg drop syndrome is a contagious disease of poultry characterized by sudden drop in production or a failure to achieve a normal peak in production.
Aetiology - Adenovirus subgroup III.
HostsChickens of all ages are susceptible to EDS.
TransmissionVertical transmission through eggs. Lateral spread of virus is slow and intermittent. In adult birds, presence of virus in feces probably arises from contamination by oviduct exudates. Droppings contain the virus in low titres and excretion of virus is intermittent.
Susceptibility to chemical & physical agentsGets inactivated by 0.5% formaldehyde or 0.5% glutaraldehyde.
Clinical symptomsEgg drop at peak or failure to peak. Egg drop may be 5 to 50% at least for 3 – 4 weeks. Rough, thin or soft shelled, shell less eggs, loss of shell pigment. Except for egg drop or laying misshapen – shell less eggs – there are no clinical symptoms.
Home Next Previous
Egg Drop Syndrome

INDOVAX
• Signs
- Loss of pigmentation
- Thin, soft shelled and misshapen eggs
Egg Drop Syndrome
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
Gross PathologyNo specific lesions.
DiagnosisAbnormalities of egg production – High HI titres in affected birds which were not vaccinated with EDS vaccine. Virus can be isolated in Duck embryo from the pouch shell gland of affected bird.
Material to be sent to laboratory Serum samples, abnormal egg samples.
ControlAn oil adjuvant inactivated vaccine is widely used and gives good protection against clinical EDS. Birds should be vaccinated between 14 and 16 weeks.
Indovax offers an effective EDS inactivated vaccine for control of the disease.
Indovax can assist in determining seroconversion in vaccinated birds.
Home Next Previous
Egg Drop Syndrome

INDOVAX
Fowl cholera is a serious, highly contagious disease caused by Pasteurella multocida.
AetiologyPasteurella multocida. Fowl cholera may be caused by any of 16 Heddlesson serotypes although certain serotypes appear to be more often associated with disease.
HostsAffects poultry, turkeys, ducks and geese. Death losses usually occur in laying flocks.
TransmissionChronically infected birds on the farm are major source of infection. Dissemination of Pasteurella multocida with in a flock is primarily by excretions from mouth, nose. Diseased birds contaminate their environment particularly feed & water. Disease could be mechanically transmitted by flies.
Incubation periodIncubation period is very short – 24 to 48 hrs.
Symptoms Depression, ruffled feathers, loss of appetite, diarrhoea, coughing, swollen and cyanotic wattles (in chronic cages), swollen joints (chronic cases), lameness, sudden death.
Fowl Cholera
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
• Signs
Chronic - Swollen wattles, sinuses, leg or wing joints - Tracheal rales and dyspnoea
Fowl Cholera
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
• Lesions
Liver - Swollen and usually contains multiple pin point foci
Fowl Cholera
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
• Lesions
Ovary - Petechial and eccymotic haemorhhages-General hyperemia is evident -with haemorrhages on heart
Fowl Cholera
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
• Lesions
Chronic cases - Oedematous lungs (Pneunomia)
Fowl Cholera
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
Gross PathologyHemorrhages on myocardium – hemorrhages on duodenum, pericardial effusions, yolk peritonitis.
DiagnosisExamine blood slides. Organisms can be isolated from heart blood.
Material to be sent to laboratory Femur bone kept in charcoal to be sent on ice to laboratory.
ControlBio-security measure, rodent control, control of flies and insects. Protect all the birds with fowl cholera vaccine. Every bird needs a primary dose and a booster dose set two weeks apart. The age of vaccination is decided on basis of the vulnerable age for this infection as seen on farm. The booster dose should be given at least 15 days before the vulnerable age – the age at which fowl cholera cases are seen on farm.
VaccinesINDOVAX offers very effective vaccine for fowl cholera. The vaccines are designed on basis of prevalent strain in locality and selection of strains is done on basis of cross protection tests in addition to somatic/capsular typing.
Fowl Cholera
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
Infectious coryza is an acute respiratory disease of chickens characterized by nasal discharge, sneezing, swelling of face under the eyes.
AetiologyHemophilus paragallinarum – Serovars A and C. TransmissionChronic or healthy carrier birds on the farm. On farms where multiple age groups are brooded and raised, spread of the diseases to successive age groups usually occurs with in 1 to 6 weeks after such birds are moved from the brooder house to growing cage near older birds. Susceptibility to chemical & physical agentsThese are delicate organisms and get rapidly inactivated outside the host.Incubation period 24 – 72 hours. Clinical symptomsFacial swelling, purulent ocular and nasal discharge,swollen wattles, sneezing, drop in egg production 10 – 40%, Inappetance.
Infectious Coryza
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
• Signs
Seromucoid nasal and ocular discharge Sometimes swollen wattles
Infectious Coryza
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
• Signs
Facial oedema and conjunctivitis
Infectious Coryza
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
Gross pathologyConjunctivitis, Tracheitis, Caseous material in sinuses.
Material for laboratory Chopped off head to be stored on ice and sent to laboratory by air. It is better to send a live bird for attempting isolation as the organism is very fragile and may get inactivated in transit.
ControlBio-security. All in all out management. Vaccination of entire flock with coryza bacterin. Two doses are necessary – primary and booster, set one fortnight apart. It is necessary to protect the birds at proper age so that they complete the primary & booster applications at least 15 days before the chicks are transferred in vicinity of older birds. It is also necessary to confirm that birds receiving primary vaccination or booster are not already suffering with coryza. It may be necessary to press near the infraorbital sinus to confirm absence of nasal exudate.
VaccinesINDOVAX offers H. paragallinarum vaccine containing local isolates belonging to group A and C. The vaccine is presented in either aluminium hydroxide gel form or stable water in oil emulsion.
Infectious Coryza
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
Fowl pox is a slow – spreading viral infection of chickens and turkeys characterized by proliferative lesions in the skin that progress to thick scabs and by lesions in the upper GI and respiratory tracts (diphtheritic form).
AetiologyLarge DNA virus – an avian poxvirus – family poxviridae.
HostsCan infect birds of both sexes and all ages and breeds.
Incubation period4 to 10 days.
Clinical signsWarty, spreading eruptions on un-feathered part of body- particularly visible and comb, wattles. In diphtheritic form caseous deposits are seen in buccal cavity, throat and some times in trachea. It is relatively slow spreading viral disease.
Post mortemThe cutaneous form can be easily seen in life. In diphtheritic form of the disease caseous plaques can be seen in mouth, pharynx, trachea and nasal cavities.
Fowl Pox
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
• Signs - Vary depending on host susceptibility & virulence of the virus
Cutaneous - Nodular lesions on comb, wattle, eyelids & other unfeathered parts
of the body
Fowl Pox
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
• Signs
Cutaneous - Nodular lesions on comb, wattle, eyelids & other unfeathered parts of
the body
Fowl Pox
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
• Signs
Diptheritic - Yellowish lesions on mucous membrane of mouth, oesophagus or
trachea -- leading to respiratory distress
Fowl Pox
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
Viral strainsA nucleoprotein precipitinogen is common to all poxviruses.
TransmissionBy direct or indirect contact. The disease may be transmitted by a number of species of mosquitoes.
ResistanceVirus can survive in dried scabs for months or even years. It is resistant to 1% phenol and 0.1% formalin. It gets inactivated by 1% caustic potash.
DiagnosisIt can be readily diagnosed on basis of flock history and presence of typical lesions.
Material for laboratory examinationDry scabs stored in sterile vials, Diphtheritic lesions from throat stored in 50% Glycerin saline to be sent on ice.
ControlRoutine immunization of birds with pox vaccine is practical method of control. Indovax Fowl Pox vaccine is available in 500 & 1000 dose vials along with a special diluent for the vaccine.
Fowl Pox
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
Infectious bronchitis is an extremely contagious respiratory disease of chickens characterized by coughing, sneezing, rales, egg drop and nephritis.
AetiologyIt is caused by a corona virus. Several sero types of corona virus have been recognized.
HostAll ages are susceptible but the disease is more severe in baby chicken. As age increases, chicken become more resistant to the nephrogenic effects, oviduct lesions and mortality due to infection.
Incubation period18 – 36 hours.
Clinical signsDrop in egg production 20 – 50%, soft shell eggs, rough shells, loss of internal egg quality, coughing and sneezing.
Gross pathologyFlaccid follicles, yolk in peritoneal cavity, caseous plugs found in trachea of young chick, swollen pale kidneys with tubules & ureter distended with urates.
Avian Infectious Bronchitis
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
• Clinical Signs (Layers / Adults)
- Decline in egg production in addition to respiratory signs
- Poor shell, shell less and mis-shapen eggs
- Severe decline in setting eggs and highly reduced hatchability
Avian Infectious Bronchitis
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
• Clinical Signs (Layers / Adults)
- Inferior quality of eggs with watery albumin
Avian Infectious Bronchitis
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
• Clinical Signs
- In broilers depression, ruffled feathers, wet droppings and nephrosis is seen
apart from respiratory signs
Avian Infectious Bronchitis
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
DiagnosisIsolation of virus in chick embryo. Several passages are necessary before the virus is isolated. Rising Elisa titre in birds together with egg drop and or respiratory symptoms is indicative of active infection.
TransmissionHighly contagious disease. When it occurs all susceptible birds on premises become infected. Air borne disease can jump considerable distances during an active outbreak. It can be spread mechanically by formites.
ResistanceInfectious bronchitis virus is considered to be sensitive to common disinfectants. The virus can survive for about one fortnight in summer months and 56 days in winter months.
Material for virus isolationTrachea, Kidneys, ileocaeccal tonsils duly preserved in 50% - glycerin saline should be sent on ice to the laboratory.
Avian Infectious Bronchitis
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
Control
Vaccination of birds with high passage Massachusetts strain of IB is a practical method of control. Vaccination has to be repeated from time to time to ensure adequate protection.
Indovax offers following products for control of infectious bronchitis:
• Infectious bronchitis vaccine (live) Mass strain - Bronkichick
• Infectious bronchitis vaccine (Inactivated) for breeders. This vaccine has the advantage that a prevalent strain of IB virus in a territory can be incorporated in inactivated vaccine.
• Newcastle disease + IB virus combined. Live vaccine available in the following combinations:
- Newcastle disease F. strain + IB virus for young chicks - Bronki-F- Newcastle disease LaSota strain + IB virus for older birds - Bronki-L
• Infectious bronchitis vaccine inactivated alone or in combination with ND, IBD, EDS is available for breeders.
Indovax can assist in sero monitoring of day old chicks, vaccinated birds.
Avian Infectious Bronchitis
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
Infectious bursal disease is an acute, highly contagious viral disease of young chickens. It is most often found in highly concentrated poultry producing areas. It causes marked morbidity and mortality in affected flocks. Although the disease causes severe losses, its affect on reducing the bird’s ability to develop immunity to other diseases in the most serious effect produced by this disease.
AetiologyInfectious bursal disease is caused by a birna virus. Serotype I variants of IBD virus have not been seen in India so far.
HostsChickens and turkeys are the natural hosts of the virus. The period of greatest susceptibility to clinical disease is between 3 and 6 weeks of age. Susceptible chicken younger than 3 weeks do not exhibit clinical signs but get sub clinical infection in which the bursa gets damaged resulting into immuno suppression.
TransmissionThe spread of the disease can occur by direct contact, contaminated litter & feces, care taker, contaminated air-equipment – feed, human traffic, insects and wild birds. It is extremely contagious.
Incubation period - 2 to 3 days.
Gumboro Disease (IBD)
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
• Lesions
Haemorrhages in thigh and pectoral muscles
Gumboro Disease (IBD)
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
• Lesions
Renal changes are prominent
Gumboro Disease (IBD)
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
• Lesions
Bursa is enlarged, gelatinous &
sometimes even bloody
Gumboro Disease (IBD)
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
• Lesions
Petechial or ecchymotic haemorrhages on mucosal surface, ocassionally
throughout the bursa
Gumboro Disease (IBD)
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
Clinical signsDepression, inappetance, unsteady gait, Huddling, Vent pecking, Diarrhoea with urates in mucus.
Post mortem lesionsOedamatous bursa, may be hemorrhagic to start with followed by regression of bursa, hemorrhages in skeletal muscles, swollen kidneys with urates.
DiagnosisA workable diagnosis can be made on basis of flock history and post mortem lesions. A laboratory procedure of isolation of virus can be used to substantiate the diagnosis.
Material to be sent to laboratory The affected bursa stored in 50% glycerin saline needs to be sent on ice to the laboratory.
ControlIt is universally accepted that the control of the disease depends on – (1) Bio-security (2) Proper vaccination.
Susceptibility to physical & clinical agentsIBD virus is very stable. The hardy nature of this virus is one reason for its persistent survival in poultry house. Formalin and iodophore are considered as effective disinfectants.
Gumboro Disease (IBD)
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
Vaccination strategies It is important to choose correct age for priming the birds. This can be done by knowing the maternal antibody pattern. In view of the variance in maternal antibody pattern of chick population, it may be necessary to do repeated vaccination. It is also necessary to review the vaccination strategies from time to time – particularly in commercial farms as the chick population originating from a breeder lot may have different levels of Mab – depending on immune status of the breeder flock.
VACCINES
INDOVAX offers very effective vaccines of proven worth for control of IBD.• Infectious Bursal Disease vaccine (live) Intermediate strain - GEORGIA – for layer and broiler chicks.• Infectious Bursal Disease vaccine (live) - IV95 strain for layer chicks carrying higher maternal antibodies and where the outbreaks are persistent. • Infectious Bursal Disease vaccine (live) – Bursa B2K strain for broiler chicks. A single application of the vaccine at 11 – 12 day age of the birds is usually effective.• Infectious Bursal Disease vaccine Inactivated alone or in combination with ND, IB is available for Breeders.
Indovax can assist in studying MAb profile and deciding vaccination schedules.
Gumboro Disease (IBD)
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
Infectious laryngo tracheitis is an acute, highly contagious herpes virus infection of chicken characterized by sever dyspnea, coughing and rales. It may manifest as subcute disease characterized by lacrimation, tracheitis, conjunctivitis and mild rales.
AetiologyHerpes virus strains appear to be homogenous antigenically.
HostsAll ages of fowl are susceptible. Young chicks are more vulnerable. Disease is usually seen in birds 3 to 9 months of age.
TransmissionVertical transmission not recorded. In the flock the disease spreads due to direct or indirect contact with ailing birds and fomites. Recovered birds or even vaccinated birds act as carrier.
Susceptibility to chemical & physical agents.It has been shown that the virus survives in trachea exudates & chicken carcasses for a period of 10 – 100 days at ambient temperature of 13 – 23ºC. However the virus gets inactivated at 38ºC within 48 hrs. 3% cresol or 1% lye will inactivate the virus in less than one minute.
Infectious Laryngotracheitis
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
Clinical signsDyspnoea, coughing of mucous or blood drop in egg prodution, ocular discharge, and sinusitis.
Gross PathologySever laryngo tracheitis often with blood in lumen, caseous plugs may be presence.
DiagnosisThe acute disease could be diagnosed on basis of spread, clinical syndrome and lesions in trachea. Mild forms cannot be diagnosed on clinical symptoms alone. Isolation of virus, intra nuclear inclusion bodies in trachea tissues and increase in titre between acute and convale scant sera are methods available.
Material to be sent to laboratory Affected trachea stored in 50% glycerin saline to be sent on ice to the laboratory.
ControlVaccination should only be done when there is a confirmed diagnosis of ILT. Live modified ILT vaccine is available and it can be used on chicks as well as adult birds as per immune response. Vaccinated birds can act as carries of the disease and hence vaccination should not be done where it is not indicated.
Infectious Laryngotracheitis
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
Marek’s disease is a lymphoproliferalive and neuropathic disease of domestic chicken caused by a highly contagious, cell associated oncogenic herpes virus.
AetiologyCell associated lymphotropic herpes virus.
HostsMDV infection in chickens is ubiquitous among poultry population through out the world. Clinical signs can be seen usually after 4 weeks of age. The age group 12 week to 24 week is very vulnerable.
TransmissionDirect and indirect contact. The epithelial cells in keratinising layer of feather follicle replicate fully infectious virus and serve as source of contamination to the neighboring environment.
Sero typesSero type I includes all oncogenic and pathogenic viruses, sero type II consists of naturally occurring avirulent strains of Marek’s virus (example SB1 strains) HVT is sero type III virus.
Mareks Disease (MD)
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
Incubation periodCytolytic changes occur in between 3 to 6 days, for classical disease with lameness 8 – 12 days.
Symptoms Paralysis of wings, legs and neck, loss of weight, grey iris, skin around feather follicle raised and roughened.
Mareks Disease (MD)
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
• Lesions
Peripheral nerves - Loss of striations and thickening
Mareks Disease (MD)
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
Gross PathologyGrey – white foci of neoplastic tissue in liver, spleen, kidney, gonads, heart & skeletal muscles thickening of nerve trunks and loss of striation.
Material to be sent to laboratory Enlarged liver, spleen, kidney, heart, gonads nerves for histopathology, skin with feather follicles for viral isolation.
DiagnosisHistory, clinical signs, distribution of lesions, age affected, histopathology. It is necessary to differentiate from lymphoid leucosis.
Mareks Disease (MD)
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
DisinfectionThe stability of cell associated MDV sero type I and II strain is completely dependent on the viability of the cells. Cell free virus found in feather follicle and cellular debris can remain viable for 4 – 8 months at room temperature. The virus gets inactivated by commonly used disinfectants.
VaccinationThe vaccination strategy depends on type of virulence of Marek’s infection. The infections caused by mild (mMDV) and virulent (vMDV) could be controlled by use of HVT cell free vaccine or HVT frozen vaccine. In case of very virulent (vvMDV) bivalent vaccines. HVT + SB1 would be necessary. In case of very virulent to (vv + MDV) infections use of sero type I vaccines is indicated.
VaccinesINDOVAX offers High PFU HVT vaccine cell free, freeze dried, HVT frozen vaccine and HVT + SB1 frozen vaccine.
It is necessary to keep the vaccinated chicks away from infected sheds at least for one month during which time the chicks would have acquired the required immune status.
Mareks Disease (MD)
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
Lymphoid leucosis is a disease of adult chicks characterized by lymphoid tumor response in most of the organs (except nerves) and lymphoid leucosis manifestation in bones, lymphatics and myeloid tissue.
AetiologyCaused by Exogenous lymphoid leucosis (LL) retro virus belonging to subgroups A, B, C, D, E and J.
TransmissionThe disease is transmitted in a variety of ways. The causative viral agent is passed out of the body of infected birds via eggs and feces. The virus may be transmitted mechanically from infected birds to susceptible birds by blood sucking parasites or by man in such procedures as fowl pox vaccination.
Incubation periodDepends on strain and dose of virus in field outbreaks, LL cases can occur anytime after 14 weeks of age, however incidence is usually highest at about sexual maturity.
Lymphoid Leucosis
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
Clinical signsVisceral tumors can be found in liver, spleen, kidneys and bursa of birds that are in general older than 25 weeks. The disease may manifest as osteopetrosis, erythroid and/or myeloid leukemia.The new J virus produces tumors in adult birds on surface of bones – junction of ribs, sternum and pelvis.
DiagnosisHistopathology of affected organs.
ControlNo vaccine is available. The only method available for control is laboratory detection of infected breeder and their elimination.
Breeding leucosis free offspring from Leucosis free breeders can eventually lead to eradication of this disease.
Lymphoid Leucosis
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
AetiologyParamyxovirus - 1 (PMV – 1) only one serotype of ND is known.
Pathology of the virusND – velognic – viscerotropic (vvND) it is also called as Asiatic or exotic ND. It is highly virulent for chickens. ND Neurotropic velogenic – causes neurological and respiratory signs.ND Mesogenic – these viruses are used as vaccines in previously immunized birds. ND Lentogenic – may cause sub clinical mild infections. Can affect any age. Most of the vaccine strains are Lentogenic strains.
HostsBirds of all age group are susceptible. The vulnerable age for the disease is first 6 weeks of the life or birds in late stage of their lay.
Newcastle disease is a contagious viral infection causing respiratory, nervous disorders in several species of fowl including chickens and turkeys.
Newcastle Disease
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
TransmissionDirect contact with secretions, specially feces from infected birds. Contaminated feed, water, implements, premises, human clothing etc. Disease spreads through Air to long distances.
Incubation period2 to 15 days (average 5 – 6 days).
Clinical signsGasping, coughing, drooping – wings, dragging legs, twisting of the head and neck, in appetance, partial or complete cessation of egg production, greenish diarrhoea.
Morbidity and mortality depend on virulence of virus, degrees of vaccinate immunity and condition of flock.
Gross PathologyHemorrhage in proventriculus Necrotic plaques in proventriculus, intestine, caecal tonsils, tracheitis.
Material to be sent to laboratory Lungs & Trachea, spleen in 50% glycerin saline to be sent on ice.
Newcastle Disease
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
• Gross Lesions
- Inflammation of trachea with haemorrhages
Newcastle Disease
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
• Gross Lesions
- Necrotic button ulcers in the intestines
Newcastle Disease
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
Necrotic button ulcers in the intestines
• Gross LesionsNewcastle Disease
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
- Airsacs are inflammed, cloudy and congested
• Gross Lesions
- Ovaries flaccid. Peritonitis & watery yolk material in abdominal cavity
Newcastle Disease
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
DiagnosisPresumptive diagnosis may be made on basis of clinical syndrome, P.M. lesions, rising titres in serology.Mere isolation of ND virus from the tissues is not enough to pronounce ND. The isolate has to be studied in tests known as minimum death time, intracerebral pathogenic index, intravenous pathogenic index in chickens.
ControlSystematic vaccination is the key of Newcastle disease control.Two types of vaccines are available: -
- Newcastle disease live vaccine. - Newcastle disease inactivated vaccine.
Live vaccine – The immune response to a vaccine increases as the pathogenicity of live vaccine increases. Therefore to obtain the desired level of protection without serious reaction, vaccination programmes are needed that involve sequential use of progressively more virulent viruses or live virus followed by inactivated vaccine.Newcastle disease live vaccine F.strain (ICPI 0.25) is used as primary dose in first few days (2 - 3 days) of the chick. It is a mild strain well tolerated by a young chick.
Newcastle Disease
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
The subsequent live vaccines consist of NDV LaSota strain which are administered 12 –15 days, 20 – 25 days, 35 –40 days ( if necessary). The repetition of LaSota vaccine will depend on Mab profile of the chick population.Newcastle disease mesogenic vaccine (R2B strain ) is administered when the birds are 8 to 10 weeks of age. Newcastle disease inactivated vaccine Encivax(Titre of bulk >109 EID50) is administered at point of lay.The HI titre of birds is routinely monitored. The layer birds should have HI titre of >26 HI in order to ensure sustained production. It may be necessary to boost the layer immunity by administration of LaSota (usually every 3 months) as per need.There are special circumstances when judicious use of ND killed vaccines is found beneficial in farms where there is persistent problem of ND and/or great variation in Mab titre of chicks, simultaneous vaccination of live and inactivated ND vaccine is found beneficial. Similarly in case of broiler birds having high maternal antibody – in many cases – simultaneous vaccination of live + inactivated ND vaccine is found beneficial.Indovax offers world class highly effective live vaccines prepared from CAV free SPF eggs – viz.Newcastle disease live vaccine F strain >106 EID50 with special diluent.Newcastle disease live vaccine LaSota strain >106 EID50 with special diluent.Newcastle disease live vaccine R2B strain >105 EID50 with special diluent.Newcastle disease inactivated vaccine Encivax(>109 EID50) stable water in oil emulsion – dose for adult birds 0.5 ml dose for chicks less than 1 month of age 0.2 ml.Indovax can assist in determining Mab titres for ND and assess sero conversion due to vaccination from time to time.
Newcastle Disease
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
Highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) is a highly contagious disease of poultry caused by influenza A virus subtypes H5 and H7 possessing a sequence at the hemagglutinating cleavage site that codes for multiple basic amino acids.
AetiologyVirus family orthromyxoviridae influenza A type virus subtype H5 and H7 possessing multiple basic amino acid at cleavage site.
HostsIt is primarily a disease of chicken. All age groups are affected.
TransmissionDirect contact with secretions from infected birds, especially faces. The virus concentration in droppings is highest. Contaminated feed, water, equipment and clothing. Clinically normal water birds – water fowl, sea birds may introduce the virus in flocks.
Resistance to Physical & Chemical actionInactivation at temperature 56ºC / 3 hours, 60ºC/ 30 min.PH Inactivated by acid pHDisinfectant – Inactivated by formalin and iodine compoundsSurvival - Remains viable for long periods in tissue faces and also in water.
Avian Influenza (HPAI)
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
Incubation period 3 – 5 days.
SymptomsSever depression, inappetance, drastic decline in egg production, facial oedema,cyanotic combs and wattles, petechial hemorrhages on internal mucous surfaces,sudden deaths (mortality can reach 100%).
Gross Pathology In case of sudden deaths – no lesions will be seen. Birds which survive the infection for a day or two may show sever congestion of musculature, oedema of head and neck area. Conjunctivitis, hemorrhagic tracheitis and mucous plugs in trachea, petechiae inside sternum and so, abdominal fat. Haemorrhages on all mucous surfaces.
DiagnosisThis is very important. It depends on isolation of the virus, typing of H and N antigens, intravenous pathogenic test in 6-week-old chicks, sequencing and presence of multiple basic amino acids at the hemagglution cleavage site. This is a highly specialized work and very few laboratories are equipped to do this work.We are fortunate to have high security disease laboratory of IVRI at Bhopal who are authorized to do this work.
Avian Influenza (HPAI)
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
Samples for viral isolation
Lung, Trachea, spleen pools of organs and faeces in glycerin saline to be sent on ice.
NOTE - The post motem and collection of samples should be left to experienced vets properly protected by sterile facemasks, gloves and apparel.
Zoonoses
World Health Organization, OIE and all the Governments of different countries of the world are apprehensive that the H5N1 outbreaks in poultry may infect human beings. If the virus mutates and gets capacity of human to human transfer – it may repeat the 1918 history of influenza pandemic that killed millions of human beings. H5N1 outbreaks are being recorded in the world since 2003 and in 2006 it affected almost entire ASIA, EUROPE and part of Africa.So far there is no evidence of human to human transfer.
Avian Influenza (HPAI)
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
ControlImportant steps in effective control are: -
• Quick diagnosis of indicator case.
• Culling of infected birds and their immediate vicinity of at least 3km. radius.
• Sanitary disposal of dead birds, animal products, cleaning disinfections of poultry houses.
• Restrictive measures on trade vaccination of birds for HPAI has been a debatable issue. Vaccinated birds may remain as healthy carrier of the disease. However, looking to the wide spread outbreaks, the quantum of culling operations and impeding all time danger several countries like Russia, China, France, Netherlands etc have opted for vaccination.
In India HSADL Bhopal has already developed an effective vaccine for H5N1. It is, however, necessary to monitor vaccinated population either through DIVA strategy or through sentinel birds or any such method which can detect a infected bird from vaccinated bird.
The OIE has already given a protocol for production & testing of avian influenza vaccines. Vaccination is now being considered an important tool of control by most of the international forums.
Avian Influenza (HPAI)
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
Low pathogenic avian influenza (LPAI) is a highly contagious disease of poultry caused by influenza virus type A other than H5 and H7.
AetiologyVirus family orthromyxoviridae genus influenza A subtypes other than H5 and H7. there are 15 recognized H subtypes and nine N subtypes.Influenza type A H9N2 has been causing serious losses to poultry industry, all the world over in recent past by way of mortality, egg drop, poor growth and performance.
HostsIt affects chickens, turkeys. All age groups are susceptible.
TransmissionDirect contact with secretions from infected birds, especially faece contaminated feed, water, equipment and clothing. Clinically normal waterfowl can transmit LPAI. The disease quickly spreads through airborne particles in a large geographical area.
Incubation periodDepends on the dose of virus, the route of exposure & ability to detect clinical signs.
Avian Influenza (LPAI)
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
SymptomsLPAI viruses when tested under laboratory conditions for IVPI test done on 6 week old bird, are not lethal.But when LPAI viruses infect the farm birds, they cause sizeable mortality. In uncomplicated infections of H9N2, the virus may cause serious drop in egg production, respiratory disease, anorexia and depression sinusitis low but elevated mortality. When other organisms such as pneumoviruses, Newcastle disease, E.coli, Pasteurella, Mycoplasma are present in population or birds under any stress are on the farm, the mortality may rise to high as 60 – 70%. There is considerable mortality in broiler chicks.Gross Pathology Facial swellings, egg peritonitis, mild preventricular haemorrhages, haemorrhatic tracheitis, pancreatic, nephritis. Material for laboratory investigationSerum, eggs for estimation of HI antibodies lung/trachea/spleen in glycerin saline to be sent on ice for virus isolation.DiagnosisDepends on isolation of virus and its subtyping in H and N antigens. ControlIn addition to bio-security measures systematic vaccination of the population with the inactivated oil adjuvant vaccine is beneficial for control of the disease. The immunized birds perform well and losses due to egg drop on incidental mortality excited by secondary pathogens is avoided.
Avian Influenza (LPAI)
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
Inclusion body hepatitis – hydro pericardium syndrome (Angara disease) is a contagious disease of poultry birds – particularly broiler birds characterized by high mortality due to hepatitis accompanied with hydro pericardium.
AetiologyFowl adeno virus sero type 4. F. adv. 4.
HostsThe layer chicks can be infected experimentally. But the disease in nature is usually seen only in broilers. Disease is seen in all age groups of commercial broilers.
TransmissionVertical transmission. Horizontal spread due to direct or indirect contact with ailing birds or its excretions.
Incubation period - Incubation period is short – 24 to 48 hrs.
SymptomsDepression, ruffled feather, respiratory distress inappetance. Death after a short sickness.
Inclusion body hepatitis – Hydropericardium syndrome (Leechi/Angara disease)
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
Inclusion body hepatitis – Hydropericardium syndrome (Leechi/Angara disease)
• Lesions
Liver - Enlarged and congested
Pericardium filled with fluid (Leechi appearance)
Heart - petechial haemorrhages
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
Gross Pathology Liver is congested to start with in advance stages the liver is pale yellow. There is spectacular hydropericardiiuum. The heart is completely immersed in yellowish pericardial fluid.
DiagnosisThe liver tissue gives a positive AGPT test against known positive serum. Virus can be isolated by yolk sac inoculation.
Material for diagnosisLiver in glycerin saline to be sent on ice.
ControlIn addition to bio-security measures vaccination of the commercial broilers is highly beneficial. Inclusion body hepatitis – hydro pericardium syndrome inactivated vaccine gives solid protection to vaccinates. Usually one vaccine dose is sufficient. In such flocks where the virus load is more, two doses may have to be given. Vaccination age is to be decided on basis of vulnerable age. If the disease appears in chicks less than 10 days of age, it is advisable to immunize broiler breeders so that the chicks have sufficient maternal antibody. Indovax offers a very effective vaccine for control of inclusion body hepatitis hydropericardium syndrome, both for commercial broilers as well as broiler breeders. The dose for commercial broiler is 0.2 ml. and dose for broiler breeders is 0.5 ml.
Inclusion body hepatitis – Hydropericardium syndrome (Leechi/Angara disease)
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
Fowl typhoid is an acute or chronic, septicaemic disease of poultry characterized by dullness, loss of appetite, fever and yellowish diarrhoea.
AetiologySalmonella gallinarum
HostsPrimarily affects chickens & turkeys. Guinea fowls, quails, pheasants and ducks are also susceptible. Broilers are more susceptible to disease.
TransmissionSpreads by both vertical and horizontal transmission. Horizontal transmission is through infected hen, egg, incubators and contaminated premises. Mechanical transmission also occurs. Infected and carrier birds shed the organisms in their droppings.
Susceptibility to chemical & physical agentsOrganism died within 10 min. at 60ºC and within a few minutes by direct exposure to sunlight. Gets inactivated by Phenol, dichloride of mercury, Potassium permagnate, formalin.
Incubation periodUsually 4 – 6 days.
Fowl Typhoid
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
SymptomsSigns include sudden or sporadic mortality, listlessness, loss of appetite, yellow diarrhoea accompanied with pasting of vent feathers. Respiratory distress with rapid breathing can also occur. Mortality may range from 10 to 90%. In chronic cases shrunken, pale combs and wattles are seen.
Gross PathologyEnlarged & mottled spleen, enlarged friable liver colored dark red or greenish brown and surface has a distinctive coppery bronze sheen after exposure to air for a short period is a consistent finding on post mortem. Catarrhal enteritis & dark brown bone marrow is also seen.Pericarditis with turbid yellow fluid pericardial sac & fibrin attached to surface of heart is a feature of chronic fowl typhoid. In laying birds, there may be retained yolks.
DiagnosisBased on gross lesions, isolation & identification of organism.
Material for laboratory examinationAffected internal organs to be sent on ice. Heart blood to be sent on ice.
ControlStrict hygiene measures. Chicks to be obtained from breeder flock known & tested to be free from disease. Routine disinfection of incubators and eggs.
Fowl Typhoid
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
It is a chronic respiratory disease of poultry characterized by respiratory rales, coughing, nasal discharge and conjunctivitis and frequently in turkeys, infraorbital sinusitis.
AetiologyMycoplasma gallisepticum
HostAffects 4 –10 weeks old birds especially the broilers & turkeys. Quail, duck, geese, pheasants are also susceptible.
TransmissionSpreads by both horizontal and vertical transmission. Horizontal transmission occurs readily by direct or indirect contact with infected birds or through droplet infection. Vertical transmission occurs through inovo transovarian route. Additional transmission may occur via fomites.
Susceptibility to physical & chemical agentsCommonly employed chemical disinfectants are effective. Gets inactivated by phenol, formalin, propiolactone and merthiolate. Organism is inactivated at 50ºC.
Incubation period 6 –10 days.
Chronic Respiratory Disease (CRD)
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
Clinical symptomsMost characteristic signs are tracheas rales, nasal discharge and coughing, loss of appetite and birds lose weight. Turkeys are more susceptible than chickens and develop more severe clinical signs including infra orbital Sinusitis. Ataxia, lameness may also be seen in affected cases. There may be reduction in egg production to as much as 50% in layer flock.
Gross pathologyMost important pathological lesion is cloudy appearance of air sacs and air sacculitis. There is catarrhal inflammation of trachea, nasal passages, sinuses and bronchi. Pericarditis and perihepatitis is seen in cases complicated with E.coli. Trachea and conjunctive may be congested. Occasionally arthritis and tenosynovitis is observed in chickens.
DiagnosisPost mortem examination. Blood testing by rapid serum agglutination test and Elisa. Isolation of organism from trachea or air sacs of affected birds.
Material for laboratory - Serum samples to be sent on ice.
ControlControl strategy is based on maintaining Mycoplasma free breeding stock. High level of bio-security is pivotal. All in all out production system and routine serological monitoring are helpful.
Chronic Respiratory Disease (CRD)
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
Collibacillosis is the commonest disease of poultry characterized by dullness, listlessness, ruffled feathers, diarrhoea, respiratory signs and septicemia.
Aetiology - Escherichia coli organisms.
HostsChickens, turkeys, ducks and pheasants all are affected but disease is most commonly seen in young chickens.
TransmissionE.coli is present in intestinal tract as normal inhabitant and shed in the faeces. Infection is transmitted by oral or inhalation route due to direct or indirect contact with ailing birds.
Susceptibility to chemical & physical agentsInactivated by most of disinfectants and temperature of 70 –80ºC.
Incubation period3 – 5 days.
Collibacillosis
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
SymptomsThe symptoms vary with the different types of infections. In acute septicemic form, mortality may begin rapidly and progress rapidly. However, in most cases, symptoms are listlessness with ruffled feathers, loss of appetite, dyspnoea, sneezing. Diarrhoea may be evident. Past like faeces soil the vent feathers. Omphalitis and naval infection is seen in young chickens.
Gross pathology Lesions vary from acute to chronic in the various forms of disease. Characteristic gross lesions are airsacculitis, peritonitis, perihepatitis and pericarditis. Fibrinous pericarditis and perihepatitis are most striking gross lesions. Liver, kidney and spleen are congested in septicemic cases. Omphalitis, salpingitis may be seen in young birds.
Collibacillosis
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
DiagnosisOn basis of gross lesions. Isolation and identification of organism from heart blood using growth media like EMB, MacConkey’s Agar.
Material to be sent to laboratory Heart blood with anticoagulant to be sent on ice, dead bird as such can be sent on ice.
ControlMaintain highest standards of flock management. Good hygiene in handling of hatching eggs. Control of predisposing factors and infections.
Collibacillosis
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
Ascites is a disease of broiler chickens characterized by accumulation of non-inflammatory transudate in abdominal cavity.
AETIOLOGYRight ventricular failure or hepatic fibrosis or lung damage. Also associated with inadequate supplies of oxygen, poor ventilation and physiology.
HostsAffects all species of poultry.
Clinical symptomsThere are sudden deaths in rapidly developing birds. Progressive weakness and abdominal distension, which is followed by recumbency. Clinically affected birds show signs of dyspnoea and cyanosis.
Ascites
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
Gross PathologyOn post mortem, enlarged heart, enlarged and thickened right ventricle, fluid in body cavities and heart sac is observed. Lungs and intestines are congested. Liver is enlarged, congested and have clotted protein adherent to its surface. There is general venous congestion.
DiagnosisGross lesions are characteristic.
Material to be sent to laboratory Dead bird as such can be sent to lab. on ice for diagnosis.
ControlAscites caused by pulmonary hypertension is controlled by reducing birds oxygen requirement, giving good ventilation and reducing ammonia in the shed. Ascites caused by lung damage or avoiding etiologic agents involved can control liver damage. Avoid predisposition of birds to other respiratory diseases.
Ascites
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
Gout is a metabolic disease of poultry characterized by depression, low feed intake and growth and swelling of joints.
AetiologyExcess protein or reduced water intake in diet, nephropathy, and deficiency of Vitamin A, high – calcium laying feed in layers.
Hosts - All poultry species are susceptible.
Symptoms Affected birds are dull, depressed and stunted. There is loss of appetite. There may be signs of lameness in cases of articular gout.
Gross PathologyChalky white deposits/urates are seen on pericardium, liver, air sacs and peritoneum. Kidney is swollen and greyish in colour. Ureter is dilated with white pasty material. Similar deposits may be seen in joints.
Diagnosis - Based on gross lesions.
Material to be sent to laboratory -Dead bird as such can be sent on ice.Control - Balanced diet with adequate supply of vitamin A should be given, ample supply of water.
Gout (Non-infectious)
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
Fatty liver syndrome is a non-infectious metabolic disease of layers characterized by enlarged fatty liver and excessive abdominal fat deposits.
AetiologyExcessive caloric intake/ faulty diet.
Hosts- Affects chickens primarily cage layers.
Clinical symptomsAffected birds appear overweight with heavy abdominal fat.
Egg production is decreased. Birds died due to liver rupture have pale combs & wattles.
Fatty Liver Syndrome
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
Gross pathologyPrimary gross lesion is an enlarged, yellowish, friable liver. Liver may show rupture with internal hemorrhage. Blood clots are found in abdominal cavity. Abdominal wall and subcutaneous tissues are generally full of fat.
Diagnosis - Based on gross lesions.
Material for laboratory - Dead hen as such can be sent on ice.
Control - Balanced ration containing adequate level of proteins and vitamins should be given. High energy diets should not be fed.
Fatty Liver Syndrome
Home Next Previous

INDOVAX
For more information, please contact :
INDOVAXCorporate Heights, SCO-24, Sector – 14
Gurgaon 122 001 – Haryana (INDIA)
Ph: 0091-124-231 5044 to 46, Fax: 0091-124-231 4680
E-mail: [email protected] Website : www.indovax.com