Indian airways (1)
-
Upload
shubhi-jain -
Category
Recruiting & HR
-
view
157 -
download
1
description
Transcript of Indian airways (1)

Indian Airlines(Air India and other players)
Submitted by: Shubhi Jain (12114064) Shyam Sundar Choudhary (12114065)
Submitted to:

● Name of India’s National Carrier● Fastest Growing Aviation Industry● Established in 1953 under ACA● Two Entities :
○ Air India■ provide international air services
○ Indian Airlines■ focuses on domestic routes■ provides routes to some important countries within asia
● Passengers carried by india’s airlines○ 61.42 million in 2013,58.81 million in 2012(according to DGCA)
Directorate General of Civil Aviation, Government of India
○ 4.43 % groth in 2013
Introduction

Introduction...● Continue loses over the years, Human Resources ,ATF
prices ,regional connectivity and pilot strikes are the major problems
● IA’s network○ Air India currently operates a fleet of 113 aircrafts (with 18 more on
orders),making it one of the largest airlines (by fleet size) in asia and the world (as of feb 2014)
○ Around 500 airports and 1100 registered aircrafts in india

Introduction...● Destinations :
○ International network

Introduction...● Destinations :
○ Domestic network

Introduction...● Destinations :
○ West Asia network

Background● Air India
○ founded in july 1930 as TATA Airlines by JRD Tata ,headquartered in mumbai
○ commenced operations from 15 october 1932○ after world war 2 (in 1946)Tata Airlines renamed as Air India and 49%
of airline was acquired by Govt. of India○ In 1953 Air India International Limited was born as a fruit of ACA and
Tata Airlines fully acquired by Govt. of India○ Entered the jet age in 1960 when it’s first boeing 707-420 named
Gauri Shankar,was delivered
Tata Air Services Air India during 1940’s to 2007 Air India(current logo)

Background...● Indian Airlines
○ Founded in 1953 as Indian Airlines Limited based in delhi and focused primarily on domestic and several nearby country’s routes
○ Administrated by Ministry of Civil Aviation and Headquartered in Delhi○ In 1990 Vayudoot(a low capacity and short haul domestic airline with
huge long term liabilities) merged into IA ○ Indian Airlines Corporation Inherited a fleet of 99 aircrafts from seven
airlines that made it up○ On Dec. 7 2005 rebranded as Indian○ In 2007 Govt. of India announced that Indian would be merged into Air
India and Air India acquired around 51% of share capital○ Indian had codeshare agreements with Air India Regional,GMG
Airlines,Gulf Air and Uzbekistan Airways○ On 27 feb. 2011 indian merged into Air India○ Jet age for IAC began in 1964 with intro of Sud Aviation Caravelle

Background...● After 1990 : Entry of private players● In 1991 Air Sahara was established● In 1993 Jet Airways,second largest player in terms of both market share
and passengers carried,commenced their operations● Air Sahara sold to Jet Airways in 2007 as marketing name of JetKonnect● In 1996 Alliance Air was founded and renamed Air India Regional● As of 2005 IA was the second largest airline in India after Jet Airways while
Air Sahara was third in this list● In 1993 ModiLuft was established and renamed as SpiceJet in 1996● Kingfisher Airlines Founded in 2003 and commenced operations from 2005● Kingfisher flights were suspended in oct. 2012 and licence revoked in feb.
2013 by Govt. of India● In 2006 IndiGo established headquartered in Gurgaon

Major Players

Major Players● Public Sector
○ Air India○ Air India Regional
● Private Sector○ IndiGo○ Jet Airways○ JetKonnect○ SpiceJet○ GoAir
● Startup players○ these are planning to enter the market○ Omega Air,Magic Air,Premier Star etc.

Major Players...● As of 2013, Air India have showed signs of recovery with its domestic
market share increasing to 19.1% as of May 2013 but still lags behind other major carriers IndiGo, Jet Airways and SpiceJet
● IndiGo is low cost carrier and largest airline in india with the market share of 28.6% as of dec 2013
● IndiGo offers 485 daily flights connecting 36 destinations with fleet of 76 new airbus A320 aircraft and also ordered 100 new aircrafts by 2015-16
● To keep average fleet age low IndiGo returns it’s old aircrafts to the leasing companies
● Jet Airways operates over 3000 daily flights to 76 worldwide destinations● GoAir operates domestic passenger services to 21 cities with over 100
daily and approximately 750 weekly flights● SpiceJet is third largest airline in terms of market share
○ fleet of 58 aircrafts○ ordered for 70 new aircrafts

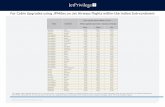
Budget & Revenue of Indian Aviation Industry● Revenue of $14.2 billion in 2011 ● Revenue of Air India
○ Total Revenue of Air India increased from Rs.140,620.1 million in 2010-11 to Rs.147,138.1 million during 2011-12
○ Operating Revenue was (in 2011-12)Rs.146,753.0 million as against previous year(2010-11) revenue of Rs 139,760.3 million
○ Passenger Revenue increased from Rs.104,438.2 million in 2010-11 to Rs.114,236.9 million
○ In 2013-14 National carrier's passenger revenue was up 22 per cent -- at Rs 3,332 crore in July-September as against Rs 2,732 crore in the same period last year,

Budget & Revenue...
source:www.airindia.com

Budget & Revenue...
● Expenditure of Air India○ The total expenditure incurred during the year 2011-12 was Rs.
234,594.8 million as compared figure of year 2010-11 Rs 213,215.9 million
○ Operating Expenses increased from Rs.180,808.0 miillon to Rs 198.139.9 million due to ■ Increase in fuel price by Rs.23,996.1 million ie. 39.3% ■ Increase in interest on working capital loans by Rs.4533.1 million

Budget & Revenue...
source:www.airindia.com

Challenges Faced After a period of drastic growth, Indian Airlines is now gripped with challenges that are also impacting the industry across the globe.● high Aviation Turbine Fuel (ATF) prices
○ ATF prices have almost doubled during last years○ Due to this depreciating rupee coupled with global recession has
directly impacted the Indian Airline Industry.The industry reported a $10.4 billion loss in the 2009.
● Human resources○ rising labor costs○ shortage of skilled labor

● Pilots strikes○ 1993- 46 days strike○ 1994- Nov. faced an evident agitation○ 1996- demand for high wages○ 1997- strike for foreign allowance,fixed flying hours,free meal
and wage parity○ 8th May,2012 100 pilots went on medical leave as a mark of
protest ○ Due to this strike AI suffered a loss of 500 crores(US$90.5
million) in 45 days
Challenges Faced...

● excess capacity○ Driven by drastically increasing passenger traffic 3-4 years back○ This resulted in excess capacity of around 15% to 20%○ Even though the industry grew above 40%, almost half of the growth
was primarily stimulated due to low fares. ● Regional Connectivity
○ due to the lack of connectivity of rural areas
● Inability of the Indian airlines to achieve cost parity with their global peers
Challenges Faced...

ACTIONS TAKEN● In 2007, the government had merged Air India (AI) and Indian Airlines (IA)
to make one of the largest airlines.But 5 years later , it has come not to be.● Air India has been provided an additional ₹1,000 crore in the revised
Budget Estimates for 2013-14 taking the total equity infusion from the Government during the year to ₹6,000 crore.
● In addition, Finance Minister P Chidambaram also provided Air India a budgetary allocation of ₹5,500 crore as equity infusion while ₹22 crore has been earmarked for the Pakyong airport, which is being developed in Sikkim by the Airports Authority of India in the interim Budget 2014-15.

After the introduction of Apex scheme in air industries

No. of employees decreases by 51%Productivity increases 44%Staff cost decreases by 13%

Steps government should take1. INFRASTRUCTURE● Airports
construction of new airports, expansion and modernization of existing airports
● Connectivity to Airports improvement in connecting infrastructure (road, metro, sea link, etc.) and better airspace management

2. Central planning & control system(cpcs)3. Planning & sheduling4. Hub control centre(HCC)5. Crew Management system6. Infusion of Additional Equity

7. HR & TRAINING● Licensing of Pilots, Engineers and other personnel● Availability of skilled , trained personnel● Training Infrastructure
8. PASSENGER/USER RELATED● Stakeholders Grievance Redressal mechanisms● Facilities for persons with reduced mobility

6. ECONOMIC REGULATION
Fares:a) Appropriate and adequate fares to coveroperational costsb) Issues related to excessive, predatory anddiscriminatory pricingc) Issues related to unbundling of services andtheir pricing behaviour

References
● wikipedia.com● airindia.com● thehindubusinessline.com

THANK YOU