Impacts of ocean acidification on mollusk fisheries and coral reefs
description
Transcript of Impacts of ocean acidification on mollusk fisheries and coral reefs

Impacts of ocean acidification on mollusk fisheries and coral reefs
Scott Doney & Sarah CooleyWoods Hole Oceanographic Institution
center for Climate and Energy Decision Making (CEDM) 2012

Ocean Acidification
Doney et al. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2009Dore et al. PNAS 2009
Observed trends-rising seawater CO2
-declining pH & carbonate saturation

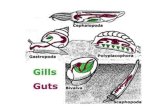
Marine Life Susceptible to Ocean Acidification
-Reduced shell formation -Habitat loss-Less available prey
New biological effects still being discovered

Social & Economic Impacts
Cooley, Kite-Powell, and Doney Oceanography (2009)Cooley & Doney, Environmental Research Letters (2009)
-Marine fisheries & aquaculture•food supply•jobs, livelihoods & trade
-Coral reefs•reef fisheries•tourism•shoreline protection
-Globally, largest impacts may be on developing island and coastal nations

U.S. ex-vessel revenue; NOAA NMFS; Cooley & Doney ERL 2009

Net importers
Net exporters
Cooley, Lucey, Kite-Powell, & Doney, Fish & Fisheries, 2012
Vulnerability to Ocean Acidification
Index Based on Mollusk Fisheries
Protein insufficientMollusks ≥ 1% of
proteinBoth
Least adaptable Most adaptable
-Exposure•chemistry change-Sensitivity•mollusk fisheries•seafood imports•protein supply-Adaptive capacity•per capita GNP

Modeling Coupled Natural-Human Systems
Atlantic Sea Scallop Integrated Assessment Model
Howarth figure
Collaboration with J. Hare & D. Hart, NOAA/NMFS

South Florida Coral Reef Modeling
Modeled Aragonite Saturation
Aragonite Saturation Trend

-Rising atmospheric carbon dioxide causes well-understood changes in seawater chemistry
-Acidification threatens coral reefs & shellfish
-Human impacts through impaired fisheries, tourism & coastal protection
-Adaptation strategies:•Ocean monitoring networks •Reduce other human stresses on ocean•Scientist-stakeholder partnerships•Coupled natural-human system models
Special Thanks To: Alan Barton, William Cheung, Charlie Colgan, Richard Feely, Hauke Kite-Powell & Noelle Lucey
Summary Points

In Gulf of Mexico
CESM 1.0 20th Century transient run with prescribed CO2 and fully coupled climate

South Florida Field Observations
Hofmann PLoS 2011
Coral Reefs
Days
Ongoing R/V Gordon Gunter DataWanninkhof et al. NOAA/AOMLhttp://www.aoml.noaa.gov/ocd/gcc/rvgunter_introduction.php

2−[CO3 ][CO2]
100−150% 50%
2100
8.2
8.1
8.0
7.9
7.81800 1900 2000 2100
50
40
30
20
10
0
300
240
180
120
60
0
pHμm
ol kg−1
Year
pH
CO2(aq)
CO32−
30% acidity16% [CO3 ]
2000
2−
Wolf-Gladrow et al. (1999)
Ocean Acidification
CO2 + H2O H2CO3 H+ + CO32- HCO3
-H+ + HCO3-CO2 + CO3 + H2O2- 2HCO3-−−<>−−