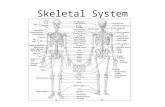
I. General Information about the Skeletal System A. ______________________- study of movement of the...
-
Upload
remington-fuller -
Category
Documents
-
view
217 -
download
1
Transcript of I. General Information about the Skeletal System A. ______________________- study of movement of the...
I. General Information about the Skeletal System
A. ______________________- study of movement of the human body.
Kinesiology
Human Skeleton(206 bones TOTAL)
•Skull (22 bones)•Hyoid (1 bone)•Auditory ossicles (6 bones)•Vertebral column (26 bones)•Thorax (25 bones)
= 80 bones total
AXIAL Skeleton
B. Division of the Skeletal System
Human Skeleton(206 bones TOTAL)
•Clavicle (2 bones)•Scapula (2 bones)•Upper limbs (60 bones)•Pelvic Girdle (2 bones)•Lower limbs (60 bones)
= 126 bones
Appendicular Skeleton
C. Bone and Surface Markings1. Depressions & Openings:
a. ___________________- opening for blood vessels, nerves and/or ligaments. example –
b. _____________________- shallow depression in or on the bone. example -
Foramen
Opening in pelvis bone
Fossa
Coronoid fossa of the humerus
2. Processes that form jointsa. _________________- large rounded prominence that forms joints.example –
b. _________________- rounded project that is supported on a thinner “neck” and forms a joint.example -
condyle
Knobs on lower femur at knee
head
Top of the femur (“ball”)
3. Processes that tendons, ligaments & other tissue connect to:
a. _____________________ - large, blunt projection only on the femur (not the “ball” part)
b. _____________________ - prominent border or ridge Example -
Trochanter
Crest
Illiac crest at top of hip bone
c. ____________________- large, rounded projection, usually with a rough surface.Example –
d. __________________________________- a sharp, slender project.Example -
Turbocity
Deltoid turbocity of the humerus
Spine or Spinous process
The part of the vertebrae that you can palpate on someone’s back
4. ______________________- to make contact with. (ex- me humerus articulates with the radius)
articulate
D. General differences between male & female skeletons
1. Male bones are _______________ and_____________________ than female bones.
2. Male points of _____________________
are larger.
largerheavier
Muscle attachment
II. Upper Appendage A. Definition of Upper Appendage:
_______
__________________________________
B. Pectoral Girdle – the _______________ &
________________ that anchors the limb
to the axial skeleton.
Pectoral Girdle + Upper Limb
claviclescapula
1. ___________________ (collar bone)a. it is the ___________________ fractured bone due to one
outstretching their arms when s/he falls.
ClavicleMost commonly
Scapular spine
Infraspinous process
2. ________________________ (shoulder blade)scapula
_________________Used for attachment to shoulder muscles.
_________________attaches to rotator cuff muscles.
____________-Articulates with the __________. (This is where a “separated shoulder” occurs.)
ACROMION
CLAVICLE
__________________ Articulates with the head of the _________________ to form a ball & socket joint.
Glenoid Fossa
humerus
______________________________Used for attachment to chest and arm muscles.
Coracoid process
____________________- faces towards the ribs.Subscapular fossa
3. ____________________________- an injury where the joint between the lateral end of the clavicle and the acromion of the shoulder is affected (often happens with forceful trauma).
Separated shoulder
HEAD Anatomical neck
C. ____________________- (upper arm bone)Humerus
_____________articulates with the glenoid fossa of the scapula.
__________________________Where the humerus narrows.
_________________________-Attachment point for deltoid muscle.
Deltoid Turberosity
CAPITULUM
TROCHLEA
____________ (lateral side) Articulates with the radius
___________-(spool shaped) Articulates with the ulna.
_________________________- Articulates with the ulna when arm is bent.
CORONOID FOSSA
Ulna – enlarged proximal end; lateral view
_______________where the humerus fits
Trochlear notch_____________________“point” of elbow
Olecranon process
________________________-articulate with coronoid fossa of humerus
CORONOID PROCESS
_____________________Where the radius fits.
Radial Notch
_______________Articulates with the capitulum. (allows the hand to face “palms up”)
head
_______________ (commonly “fall”fracture by people over 50)
Styloid process
1. ______________________________ - the head of the radius slides past or ruptures the ligament that forms a collar around the head of the radius (most common upper limb dislocation in children).
Dislocation of the radial head
8 bones in the wrist F. Carpals - _______________________________
______________________- when the nerves of this tunnel are compressed and cause numbness, tingling & weakening in the hand.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
_______________2 rows of bones that forms a tunnel for nerves & tendons to pass through.
CARPALS
5 bones that make up the palm of the hand
METACARPALS
G. Metacarpals - ___________________________
______________________
- Each metacarpal has a base (proximal), body & a head (distal).-It is the _____________ of the metacarpal that makes _________________ when you clench your fist.
head
knuckles
Pollex – no middle phalange
I. Pollex - ____________________________Specialized phalange that makes up the thumb
IV. _________________________- both hip bonesA. Three functions of the pelvic girdle:
1. _________________ the vertebral column2. _____________________________ of the pelvis (bladder, reproductive
organs, rectum).
3. __________________________ to the axial skeleton.
Pelvic Girdle
supports
Protects the organs
Attaches lower limbs
B. Features of the Pelvic Girdle
______________- the two “hip” bones that are made up of the: ______________________________________ which fuse together by age 23.
Coxal
Illium, ischium & pubis
_________________- joint on the posterior side where the 2 coxal bones join the sacrum.
Sacroilliac joint
_________________everything above the pelvic brim. It is actually considered to be part of the ______________ & only contains the bladder when it is _________ and uterus during _____________.
False Pelvis
abdomen
full
pregnancy
Lateral View of Coxal Bone
_________________________ - where the sciatic nerve (longest nerve in body) passes through.
Greater sciatic notch
F. Features created by the joining of the bones of the coxal. (lateral view)
____________- socket for the head of the femur formed by the joining of all 3 coxal bones.
Acetabulum
__________________- largest foramen of the skeleton where nerves and vessels pass (formed by joining of ischium & pubis.
Obturator Foramen
G. Structural differences between a male and female pelvis
1. ____________________- of the female
is larger and the _________________ is
oriented so that a baby can fit through.
2. The angle made by the two ischium bones is a larger _______ shape in
females, and narrower _________ shape
in males.
Pelvic InletPelvic outlet
UV
V. __________________ (the leg)A. _________________(thigh bone) – the STRONGEST bone in the body
Lower LimbFemur
__________________- “ball” of the femur which articulates with the acetabulum.
Head ______________________- projection on side of femur where muscles attach(also landmark for injections in the thigh).
Greater Trochanter
__________________- towards the inside of the leg. Articulates with the tibia.
Medial Condyle
______________________- Towards the outside of the leg. Articulates with the tibia.
Lateral Condyle
B. ___________________ (“knee cap”) – normally tracks(moves) up & down in a __________ between the femoral condyles.
Patellagroove
1. ___________________________- “runner’s knee” occurs when the patella tracks _________________ and causes pain. (due to running on the same side of
the road that is naturally sloped).
Patellofemoral Stress Syndrome
laterally
________________________-Articulates with the lateral condyle of the femur.
Lateral condyle ______________________-Articulates with the medial condyle of the femur.
Medialcondyle
1. ______________- pain along the tibia
that results from inflammation of the tibia’s ___________________ (usually
caused by over-exertion of the calf muscles)
Shin splints
periosteum
___________________-Forms the prominence you feel on the lateral part of the ankle surface.
Lateral malleolus
E. The FOOT & its functions 1. ______________- 7 ankle bones of the foot
___________________-•It is the only tarsal that articulates with the tibia & fibula. •It initially bears the _________ of the entire body when walking.
Tarsals
Talus
weight
___________________-(heel bone) It is the largest & strongest tarsal. _________ the weight is transferred to it from the __________ when walking.
Calcaneous
Half
Talus
2. _______________________- 5 bones that are similar to the metacarpals that make up the “sole” of the foot. a. like the metacarpals, each have a __________ base, a body, and a ___________ head.
metatarsals
proximaldistal
5. The four ___________ of the arches foot:a. _________________ leverage when walkingb. _________________ shock (by “giving when weight is applied & “springing back” afterwards).c. ____________________ body weight over parts of the foot.d. ____________________ the weight of the
body.Acronym help: ______________ (think…..the “PADS” of your feet)
functionsP.rovidesA.bsorbs
D.istributes
S.upports
P. A. D. S.
6. Three arches of the foot
________________-Runs horizontally across the foot. Formed by the navicular, cuniforms, & bases of metatarsals.
Transverse arch
_________________________-Runs front to back of foot by the inside of the foot.
Medial Longitudinal Arch
______________________-Runs front to back of foot by the outside of the foot.
Lateral Longitudinal Arch
VI. Joints of the Skeletal SystemA. __________________- point of contact between ___________, between
________________________ or between ____________________.
Jointbones
Cartilage & bonesTeeth & bones
B. Divisions of Medical Studies of Joints1. ______________________- the study of joints.2. ______________________- study
of joint disease and related
conditions
Arthology
Rheumatology
C. Movement of Joints1. Range of motion:
a. in general, the _______________ the distance between the
articulating bone, more _________________
the range of motion for that joint.Ex -
shorter
restricted
• Skull bones- very close together no range of motion• femur & tibia are farther apart large range of motion
2. Three Factors that determine joint flexibility:a. ____________________ of the ligaments that bind the bones together.b. _____________________of articulating bones.c. _____________________tension of associated muscles and tendons.
ACRONYM HELP: What’s your favorite math class at DPHS? __________________
F.lexibility
S.hape
T.ension
F. S. T.
JOINTS
Fibrous-Bones are held together by__________connective tissue.
-Lack a ________________ cavity
-Three Types _____________ _____________ _____________
fibrous
synovial
suturesyndesmosisgomphosis
D. Classes of Joints
JOINTS
Synovial-____________ a synovial cavity
-Most ___________
-Six Types ______________ ______________ ______________ ______________ ______________ ______________
contains
movable
planarcondyloidhingesaddlepivot
Ball & socket
JOINTS
Cartilaginous-Bones are held together by ______________.
-Also _________ a synovial cavity.
-Two Types ______________ ______________
cartilage
lacks
synchondrissymphasis
SUTURE
-They are ________________-Found where__________ unite
immovableSkull bones
1. FIBROUS JOINTS
SYNDESMOSIS(sin-dez-MŌ-sis)
-They are ________________-Found in_____________________
Slightly movableTibia/fibula connection & sacrum/coxal connection
GOMPHOSIS(gom-FŌ-sis)
-They are ________________-Found only in_________________
immovableTooth sockets
PLANAR
-Found in _________________ _________________
_________________
Wrist & anklesBtwn clavicle & sternumBtwn clavicle & scapula
2. SYNOVIAL JOINTS
b. specific joint structures of the knee:
_________________________________________-Ligament that extends posteriorly & laterally from the tibia to the fibula.
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL)
___________________________-Found on the outside of the knee. Meniscus allow for a____________ fit between two different shaped bones.
Lateral Meniscus
tighter
c. Common injuries of the knee:1. _____________________- when the anterior cruciate ligament is stretched
or torn (70% of all serious knee injuries).
ACL injury
2. _______________________________ - when the lateral or medial meniscus is damaged. (If the damaged cartilage is not removed, it may lead to arthritis)
Torn Cartilage of the knee
SYNCHONDROSIS(sin-kon-DRŌ-sis)
-They are ________________-Found in _____________ of elongating bones & between the ____________ & ____________
immovableGrowth plates
Rib cage sternum
3. CARTILAGENOUS JOINTS
SYMPHASIS(sim-fi-sis)
-They are ________________-Found between the __________ bones and between ____________
Slightly movablepubis
vertebrae
E. Common Joint Diseases & Complications1. _______________________- an autoimmune disease in which the
immune system of the body attacks its own cartilage & joint linings. It is characterized by _______________ of the synovial cavity.
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
swelling
2. _________________________- degenerative joint disease characterized by deterioration of ________________ cartilage. (the “wear & tear” arthritis)
Osteoarthritis
articular
3. ________________- forcible wrenching or twisting of the ________________ of a joint.
Sprainligaments