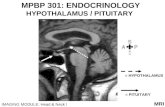
Hypothalamus
description
Transcript of Hypothalamus











Hypothalamus
GHRH(+)
GHIH
(-)
Pituitary
SleepStressExercise
Limbicstructures
Metabolicsignals
Glucocorticoids
GHsomatotropin
Direct effects mobilize fat insulin antagonist
Indirect effects Somatomedins:IGF-1 protein synthesis tissue growth
(-)
(-)



Thyroid Hormones
• Include
– Triiodothyronine or T3
– Tetraiodothyronine or T4 or thyroxine
• Transported in blood• Bind with intracellular receptor molecules and
initiate new protein synthesis• Increase rate of glucose, fat, protein metabolism
in many tissues thus increasing body temperature• Normal growth of many tissues dependent on



Thyroid Hormone Hyposecretion and Hypersecretion
• Hypothyroidism– Decreased metabolic rate– Weight gain, reduced
appetite– Dry and cold skin– Weak, flabby skeletal
muscles, sluggish – Myxedema– Apathetic, somnolent– Coarse hair, rough dry
skin– Decreased iodide uptake– Possible goiter
• Hyperthyroidism– Increased metabolic rate– Weight loss, increased
appetite– Warm flushed skin– Weak muscles that
exhibit tremors– Exophthalmos– Hyperactivity, insomnia– Soft smooth hair and skin– Increased iodide uptake– Almost always develops
goiter

Parathyroid Glands
• Embedded in thyroid
• Secrete PTH
– Increases blood calcium levels
– Stimulates osteoclasts
– Promotes calcium reabsorption by kidneys


Regulation of PTH Secretion


Decreasing bloodCalcium
Parathyroids
Parathyroid hormone
Kidneys Bone
Reabsorption of Calcium
Dissolution of CaPO4 crystals
Increased blood Calcium
Active Vitamin D
Increased Calcium absorption in
Small Intestine
.

Adrenal Glands
• Functions as part of sympathetic nervous system• Composed of medulla and cortex (3 layers)• Hormones
– Medulla secretes epinephrine and norepinephrine– Cortex secretes mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, androgens



Hormones of Adrenal Cortex• Mineralocorticoids
– Zona glomerulosa– Aldosterone produced in greatest amounts
• Increases rate of sodium reabsorption by kidneys increasing sodium blood levels (regulates water volume)
• Glucocorticoids– Zona fasciculata– Cortisol is major hormone
• Increases fat and protein breakdown, increases glucose synthesis, decreases inflammatory response
• Androgens– Zona reticularis– Converted to androgen and testosterone

Blood Pressure Chloride Ion
Kidney
Renin
Lungs
Angiotensin II
ZonaGlomerulosa
Aldosterone
Reabsorption of Na+Excretion of K+ & H+ Blood Volume
Vasoconstriction Blood Pressure
(+) (-)
(-)
K+ (+)
.


Nonspecific StressHigher Brain
Centers
Hypothalamus
ZonaFasciculata
Anterior Pituitary
CRH
ACTH
Cortisol
(-)
(-)
GluconeogenesisMobilization of fat stores bone formation immune system
(+)




Pancreas
• Located along small intestine and stomach
• Exocrine gland– Produces pancreatic
digestive juices• Endocrine gland
– Consists of pancreatic islets– Composed of
• Alpha cells secrete glucagon
• Beta cells secrete insulin• Delta cells secrete
somatostatin


Insulin and Glucagon
Insulin
• Target tissues: liver, adipose tissue, muscle, and satiety center of hypothalamus
• Increases uptake of glucose and amino acids by cells
Glucagon
• Target tissue is liver
• Causes breakdown of glycogen and fats for energy

Regulation of Insulin Secretion

Regulation of Blood Nutrient Levels After a Meal

Regulation of Blood Nutrient Levels During Exercise

Hormones of the Reproductive System
Male: Testes• Testosterone
– Regulates production of sperm cells and development and maintenance of male reproductive organs and secondary sex characteristics
• Inhibin– Inhibits FSH secretion
Female: Ovaries• Estrogen and Progesterone
– Uterine and mammary gland development and function, external genitalia structure, secondary sex characteristics, menstrual cycle
• Inhibin– Inhibits FSH secretion
• Relaxin– Increases flexibility of
symphysis pubis

Pineal Body
• In epithalamus
• Produces
– Melatonin• Enhances sleep
– Arginine vasotocin• Regulates function of
reproductive system in some animals

Effects of Aging on Endocrine System
• Gradual decrease in secretory activity of some glands– GH as people age– Melatonin– Thyroid hormones– Kidneys secrete less renin
• Familial tendency to develop type II diabetes

Diabetes Mellitus
• Results from inadequate secretion of insulin or inability of tissues to respond to insulin
• Types– Type I or IDDM (Insulin-dependent)
• Develops in young people
– Type II or NIDDM (Non-insulin dependent)• Develops in people older than 40-45
• More common



![Thalamus Hypothalamus [Repaired].pdf](https://static.fdocuments.us/doc/165x107/577cd6b41a28ab9e789d06fd/thalamus-hypothalamus-repairedpdf.jpg)













