Human Excretory System Name: ___________________ Date: __________________.
Human urinary excretory system
-
Upload
mahlatse-ledwaba -
Category
Education
-
view
2.271 -
download
3
Transcript of Human urinary excretory system

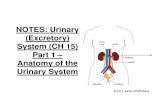
Human Excretory urinary System
The kidney- grade 11

Structure of the urinary excretory system

This system includes 4 main organs:
Excretory
system
Kidneys
ureters
Urethra
Bladder

Main function of the urinary System
The human excretory system functions to remove waste from the human body.
During urination animals get rid of nitrogenous waste products of metabolism, including ammonia, urea, and uric acid.

The internal & external structures of a kidney

The flow of urine inside the kidney
Glomerulus
Renal tubules
Renal pelvis
Renal calicesUreter

Purpose of a kidney
Filters blood, redirecting wastes as urine through the ureter and to the urinary bladder and out of the body via urethra.
Each kidney consists of millions of nephrons – the fundamental units of the kidney

Structure of a nephron

What is a nephron?
A functional unit of a kidney.
Blood enters the nephron
at the Bowman’s
capsule and is filtered by
the glomerulus, a
ball of capillaries.
Bowman’s capsule collects filtrate, plasma
forced out of the blood.
Filtrate passes
through the entire
nephron becoming
modified into urine.

Blood Flow through the Kidneys
Blood enters via
renal arteryArterioles Nephron Renal
corpuscle

The 3 processes of blood purification inside the kidneys.
Filtration – blood is filtered through the glomerulus,
allowing small substances to pass further; ions, urea and
amino acids. All these substances make up a fluid
called filtrate.

Reabsorption – Small solutes such as
water, nutrients, and salts are reabsorbed
and then urine remains.

Secretion – Substances including H+, potassium, and
ammonium ions enter the tubules as part of
urine.

Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
Renal tubuleExcretion
Filtration
Reabsorption to blood
Secretion from blood
Glomerulus
Bowman'scapsule

The remaining urine goes to the collecting duct and into the ureters, the
bladder and out of the body via the urethra.

Normal & abnormal flow of urine

References
The slides above have been re-purposed from the following presentation links from slideshare:
http://www.slideshare.net/itutor/excretory-system-23183659?qid=6d3c0d3b-e56c-4c57-83c0-98fbae82b3eb&v=qf1&b=&from_search=1
http://www.slideshare.net/jgthatsme/excretory-system?qid=9ee1584a-3dda-4d5a-b11b-e75b5400133f&v=qf1&b=&from_search=1
http://www.slideshare.net/132cool/excretory-system-8430788?qid=81f3882c-84d0-46f6-867b-782728c2fc79&v=default&b=&from_search=12

THE END!201125991
Ledwaba .M