Human Physiology (SKELETON SYSTEM) · They are the axial skeletal bones and appendicular skeletal...
Transcript of Human Physiology (SKELETON SYSTEM) · They are the axial skeletal bones and appendicular skeletal...
SKELETON COMPONENTS
The skeleton is composed of fibrous and mineralized connective tissues that
give it firmness and flexibility. It consists of bone, cartilage, tendons, joints, and
ligaments.
Bone - a type of mineralized connective tissue that contains collagen and
calcium phosphate, a mineral crystal. Calcium phosphate gives bone its
firmness. Bone tissue may be compact or spongy. Bones provide support and
protection for body organs.
Cartilage - a form of fibrous connective tissue that is composed of closely
packed collagenous fibers in a rubbery gelatinous substance called chondrin.
Cartilage provides flexible support for certain structures in adult humans
including the nose, trachea, and ears.
Tendon - a fibrous band of connective tissue
that is bonded to bone and connects bone to
bone.
Ligament - a fibrous band of connective tissue
that joins bones and other connective tissues
together at joints.
DLB 11
Fibrous Joints: Fibrous joints are held together by strong connective tissue with only a slight capacity to stretch. This tough connection allows very little movement between the joined bones, thus providing great stability. Fibrous joints are found in the skull, which is made up of several bone plates held tightly together to protect the fragile brain. A dense band of tissue connects the radius and ulna bones in the lower arm forming a fibrous joint that keeps these bones stable as the forearm rotates. The lower leg bones, called the tibia and fibula, are also joined by a fibrous joint that limits movement between these bones. Fibrous joints also hold the teeth firmly within their sockets in the jaw bones
DLB 12
Cartilaginous JointsCartilaginous joints allow for slight movement and occur where bone ends are covered by a somewhat flexible, compressible connective tissue called cartilage. Some cartilaginous joints are temporary, such as those present during the growth of the long bones of the arms and legs in children. Other cartilaginous joints allow limited flexibility and provide shock absorption. These joints are found where the ribs attach to the breastbone and between some of the pelvic bones. They also occur between the bones of the spine, where they provide strength, flexibility and cushioning.
DLB 13
Synovial joints allow the greatest degree of
movement due to their structure. These joints consist of a capsule of connective tissue that encloses a space or cavity between the bones. The cavity contains fluid that lubricates the joint and reduces friction. Most joints of the body are synovial joints, which are found in the elbow, shoulder, knee, wrist, hand, ankle and foot. There are several different types of synovial joints that are classified by their shape and the range of movement they allow
SKELETON DIVISIONS
Bones are a major component of the skeletal
system. Bones that comprise the human skeleton
are divided into two groups. They are the axial
skeletal bones and appendicular skeletal bones. An
adult human skeleton contains 206 bones, 80 of
which are from the axial skeleton and 126 from the
appendicular skeleton.
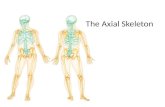
Axial Skeleton
The axial skeleton includes bones that run along the medial
sagittal plane of the body. Imagine a vertical plane that runs
through your body from front to back and divides the body
into equal right and left regions. This is the medial sagittal
plane. The axial skeleton forms a central axis that includes
bones of the skull, hyoid, vertebral column, and thoracic
cage. The axial skeleton protects numerous vital organs and
soft tissues of the body. The skull provides protection for the
brain, the vertebral column protects the spinal cord, and the
thoracic cage protects the heart and lungs.
Axial Skeleton Components
Skull - includes bones of the cranium, face, and
ears (auditory ossicles).
Appendicular SkeletonThe appendicular skeleton is comprised of body limbs
and structures that attach limbs to the axial skeleton.
Bones of the upper and lower limbs, pectoral girdles, and
pelvic girdle are components of this skeleton. Although
the primary function of the appendicular skeleton is for
bodily movement, it also provides protection for organs
of the digestive system, excretory system, and
reproductive system.
DLB 25
Appendicular Skeleton Components
Pectoral Girdle - includes shoulder bones (clavicle and
scapula).
Upper Limbs - includes bones of the arms and hands.
Pelvic Girdle - includes hip bones.
Lower Limbs - includes bones of the legs and feet.
Skeletal Bones
Bones are a type of mineralized
connective tissue containing collagen
and calcium phosphate. As a
component of the skeletal system, a
major function of bone is to assist in
movement. Bones work in concert with
tendons, joints, ligaments and skeletal
muscles to produce various
movements. Nutrients are provided to
bone through blood vessels that are
contained within canals in bone.
BONE FUNCTION
Bones provide several important functions
in the body. Some major functions
include:
Structure - Bones compose the skeleton,
which provides structure and support for
the body.
Protection - Bones provide protection for
numerous vital organs and soft tissues of
the body. For example, the vertebral
column protects the spinal cord, and the
thoracic (rib) cage protects the heart and
lungs.
DLB 33
मानव कॊ काऱ तॊत्र (Human skeleton system):
मनुष्य के कॊ काऱ में कुऱ 206 अस्थियाॉ होती हैं। मनुष्य के कॊ काऱ को दो भागों में ववभास्ित ककया िा सकता है-
(A) अऺीय कॊ काऱ (Axial skeleton): इसके अन्तगगत खोऩडी (Skull), कशरेुक दण्ड (vertebral column) तिा छाती की अस्थियाॉ आती हैं।
(B) अनुबॊधी कॊ काऱ (Appendicular skeleton): इसके अन्तगगत मेखऱाएॉ (Girdles) तिा हाि-ऩैरों की अस्थियाॉ आती हैं।
DLB 34
हड्डी - एक प्रकार का खनिजयुक्त सॊयोजी ऊतक जजसमें कोऱेजि और कैजशियम फॉस्फेट, एक खनिज क्रिस्टऱ होता है। कैजशियम फॉस्फेट हड्डी को अपिी दृढ़ता देता है। अजस्ि ऊतक कॉम्पकै्ट या स्पॊजी हो सकता है। हड्डडयाॊ िरीर के अॊगों के लऱए सहायता और सुरऺा प्रदाि करती हैं।
उपाजस्ि - तॊतुमय सॊयोजी ऊतक का एक रूप जो चोंड्रीि िामक रबरयुक्त जजऱेटटिस पदािथ में बारीकी से पैक कोऱेजिस फाइबर से बिा होता है। काटटथऱेज िाक, श्वासिऱी और काि सटहत वयस्क मिुष्यों में कुछ सॊरचिाओॊ के लऱए ऱचीऱा समिथि प्रदाि करता है।
DLB 35
टेंडि - सॊयोजी ऊतक का एक रेिदेार बैंड जो हड्डी से जुडा होता है और हड्डी से हड्डी को जोडता है।
लऱगामेंट - सॊयोजी ऊतक का एक रेिदेार बैंड जो जोडों में हड्डडयों और अन्य सॊयोजी ऊतकों से जुडता है।
जोड- एक साइट जहाॊ दो या अधिक हड्डडयों या अन्य कॊ काऱ घटक एक साि जुड जाते हैं। ये तीि प्रकार के होते है