Homeostasis Intro.Doc
-
Upload
barshingert -
Category
Technology
-
view
464 -
download
3
Transcript of Homeostasis Intro.Doc

Homeostasis
Stable internal condition

Three requirements of living thingsExchanging gases (CO2 out; O2
in)Taking in water, minerals, and
foodEliminating wastes
These tasks require molecules to move through the cell membrane.

Exchanging gases (CO2 out; O2 in)Taking in water, minerals,
and foodEliminating wastes
These tasks require molecules to move through the cell membrane.

Molecule movement through membranePassive transport
No energy used by the cell occurs naturally
Active transportRequires energy by the cell to
move molecules

Three functions of cell membraneSeparate contents of cell
from its surroundingsControls movement of
materials into and out of cellInteracts with the
environment surrounding the cell

Cell Membrane
http://www.wisc-online.com/objects/index_tj.asp?objID=AP1101

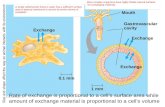
Diffusion
Movement of molecules from a region in which they are highly concentrated to a region in which they are less concentrated.
It will continue until the system reaches equilibrium, which means the molecules are randomly distributed throughout the system.
http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter2/animation__how_diffusion_works.html

Equilibrium
Static- occurs when there is no action taking place
Dynamic-occurs when two opposing actions occur at the same rate but in opposite directions

Factors of diffusion
Amount of kinetic energy (temperature)
Size of the moleculeSmaller molecules will move
faster than larger onesCharges on the molecuesNature of material molecules
are moving through

Molecules permeable to cell membraneSmall molecues like:
CO2O2H2O
More oxygen would move into the cell then out if there is more oxygen outside the cell