Histology and Functions of Blood...
Transcript of Histology and Functions of Blood...

Histology and Functions of Blood Vessels
WS O
Department of Anatomy, HKU

Objectives:
• Describe the basic histological structures and functions of endocardium, myocardium, epicardium and the conducting system of the heart.
• Define the basic structure and function of blood vessels.
• Distinguish the major differences between various types of vessels: elastic and muscular arteries, arterioles, venules, veins.
• Describe the various types of capillaries and define their functions.

21-3
Functions of the Circulatory System
1. Carry blood
2. Transport of hormones,
components of the immune system, molecules required for coagulation, enzymes, etc.
3. Exchange nutrients, waste products, and gases
4. Regulate blood pressure
5. Directs blood flow

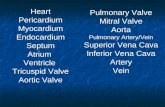
Organization of Heart & Blood Vessels
• Heart wall can be viewed as a three-layered structure Inner layer = endocardium Middle Layer = myocardium Outer layer = epicardium (part
of the pericardium)
• Blood and lymphatic vessel walls (except for capillaries) can also be viewed as three-layered structures Inner layer = tunica intima Middle layer = tunica media Outer layer = tunica adventitia
Endocardium
Epicardium
Myocardium
Tunica adventitia
Tunica media
Tunica intima

Heart Wall has Three Layers

Cardiac Muscle
Intercalated Disc

Conducting system of the heart• Consists of modified cardiac muscle and conducting fibers that are specialized for initiating impulses & conducting them rapidly through the heart
• Made up of three components:- sinoatrial (SA) node serve as thepacemaker
- atrioventricular (AV) node receive the wave of excitation from the cardiac muscle of the atria and pass the excitation on to the bundle of His
- Purkinje fibers are organized into a branched bundle (Bundle of His)which extends from the atrio-ventricular (AV) node, through the interventricular septum down to the apex of the ventricles
Purkinje fibers
Cardiac muscle

Tunica intima
Tunica media
Tunica adventitia
1. Smooth muscle cells, collagen fibers
2. Elastic fenestrated lamellae
3. External elastic lamina
Blood Vessel Wall has three layers1. Endothelial cell lining
2. Subendothelial layer
3. Internal elastic membrane
1. Mostly collagen fibers
2. Elastic fibers (not lamellae)
3. Fibroblasts and macrophages
4. Vasa vasorum

20-9
Vessel Wall Tunica intima
– lines the blood vessel and is exposed to blood
– endothelium – simple squamousepithelium overlying a basement membrane and a sparse layer of loose connective tissue• acts as a selectively permeable
barrier• secrete chemicals that stimulate
dilation or constriction of the vessel• normally repels blood cells and
platelets that may adhere to it and form a clot
• when tissue around vessel is inflamed, the endothelial cells produce cell-adhesion molecules that induce leukocytes to adhere to the surface
– causes leukocytes to congregate in tissues where their defensive actions are needed
Tunica intima

20-10
Vessel Wall
Tunica media
– middle layer
– consists of smooth muscle, collagen, and elastic tissue
– strengthens vessel and prevents blood pressure from rupturing them
– vasomotion – changes in diameter of the blood vessel brought about by smooth muscle
Tunica media

20-11
Vessel Wall
• tunica externa (tunica adventitia)
– outermost layer – consists of loose connective
tissue that often merges with that of neighboring blood vessels, nerves, or other organs
– anchors the vessel and provides passage for small nerves, lymphatic vessels
– vasa vasorum – small vessels that supply blood to at least the outer half of the larger vessels• blood from the lumen is
thought to nourish the inner half of the vessel by diffusion
Tunica adventitia

Thin-walled vessel Thick-walled vessel
Tunica intima Tunica intima
Tunica media Tunica media
Tunica externa
Tunica externa
Differences of Vessel Wall
Large artery
Medium artery
Medium vein

Ascending aorta
Pulmonary trunk (artery)
Arteries
Elastic artery
Tunica intima
Tunica media
Tunica externa
Tunica intimaInternal elastic laminaTunica mediaExternal elastic laminaTunica externa
Arteriole
Muscular artery
Tunica intimaTunica media
Tunica externa
Basement membrane
Endothelium
Capillary
Tunica intima
Valve
Tunica media
Tunica externa
Tunica intimaValve
Tunica media
Tunica externa
Tunica intima
Tunica mediaTunica externa
Venule
Small to medium-sized vein
Large vein
Superiorvena cava
Inferiorvena cava
Descendingaorta
Veins
Comparison of Blood vessels

Blood Pressure Changes With Distance
Ao
rta
Arterio
les
Cap
illaries
Ven
ules
120
100
80
60
40
20
0
Syst
em
ic b
loo
d p
ress
ure
(m
m H
g) Systolic pressure
Diastolicpressure
Large arteries
Small arteries
Ven
a cava
Large veins
Small vein
s
Distance from left ventricle
• Due to increase in overall cross-sectional area of vessels in branching

Artery
Artery
Tunica intima Tunica media Tunica externa

21-16
Structural Features of Blood Vessels
• Arteries– Elastic– Muscular– Arterioles
• Capillaries: site of exchange with tissues
• Veins: thinner walls than arteries, contain less elastic tissue and fewer smooth muscle cells– Venules– Small veins– Medium or large veins

21-17
Elastic Artery• Elastic or conducting arteries
– Largest diameters, pressure high and fluctuates between systolic and diastolic. More elastic tissue than muscle.
– Relatively thin tunica intima & tunica adventitia, thick tunica media (40-60 distinct concentrically arranged elastic laminae)
– Include aorta, pulmonary arteries, common carotid arteries, common iliac arteries
Elastic arteries. Elastic laminae in the Tunica media gives these vessels elastic properties. They expand as the heart contracts (to modulate BP and store energy) and recoil during ventricular relaxation (to maintain more even pressure in large arteries)

Elastic Artery

Muscular Artery• Muscular or medium or distributing arteries
– Smooth muscle allows vessels to regulate blood supply by constricting or dilating
– Thick tunica media due to 25-40 layers of smooth muscle. Thin intima– Also called distributing arteries because smooth muscle allows vessels
to partially regulate blood supply to different regions of the body.– Mostly named arteries, such as brachial & femoral arteries but also
include some smaller unnamed arteries
• Smaller muscular arteries– Adapted for vasodilation and vasoconstriction.
External elastic membrane
Internal elastic membrane
Prominent in muscular artery
Muscular arteries. The thick muscular layer in the tunica media resists damage due to relatively high BP in these vessels. They regulate blood flow to different regions of the body.


Elastic artery(tunica media – elastic fibers)
Muscular artery(tunica media – smooth muscles)

21-22
Arterioles
• Transport blood from small arteries to capillaries
• Smallest arteries where the three tunics can be differentiated
• Tunica media-one or more layers of smooth muscle cells
• Like small arteries, capable of vasoconstriction and dilation- metarterioles are short vessels that
link arterioles to capillaries- contain small muscle cells formprecapillary sphincters~ control blood flow to capillary bed~ alter BP by altering peripheral
resistance to blood flow –“peripheral resistance vessels”

Tunica media
Tunica adventitia
Endothelial cell
Arteriole
Arteriole H&E

21-24
Capillaries• Thin walled single endothelial cells (simple squamous epithelium),
basement membrane and a delicate layer of loose C.T. • Specialized for exchange of substances -Many pinocytic vesicles
• Pericytes:– have their own basement membrane– may develop into smooth muscle cells (capillary → arteriole)
• Presence of tight-junction between endothelial cells – Blood-brain Barrier
• Tight junction is complete in brain capillaries • Very few or absence of pinocytic vesicles
Pericyte

Three Types of Capillaries
Sinusoids or Sinusoidal capillary

Pericyte
Erythrocyte
Basallamina
Intercellularcleft
Pinocytoticvesicle
Endothelialcell
Tightjunction
Continuous capillaries
• Have relatively think cytoplasmand the capillary wall continuous
• Presence of tight junctions between adjacent cells
• Less permeable to large molecules than other capillary types
• Cytoplasm contains pinocytoticvesicles
• Found in muscle, nervous tissue

Continuous capillary

20-28
Fenestrated CapillaryCopyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
Erythrocyte
Endothelialcells
Filtration pores(fenestrations)
Basallamina
Intercellularcleft
Nonfenestratedarea
• Have thin cytoplasm and capillary wall is perforated at intervals by pores (fenestrations)
• Materials can cross the cellthrough the fenestrations
• Found in kidney &endocrine glands

Fenestrated Capillary

20-30
Sinusoid in LiverCopyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
Macrophage
Sinusoid
Microvilli
Endothelialcells
Erythrocytesin sinusoid
Liver cell(hepatocyte)
• Larger in diameter than theother types
• have wide spaces betweenedges of adjacent cells
• Materials can move freelyin and out
• Found in liver, spleen, &bone marrow

21-31
Aging of the Arteries
• Arteriosclerosis:general term for degeneration changes in arteries making them less elastic
• Atherosclerosis:deposition of plaque on walls

Vein
Vein
Tunica intima Tunica media Tunica externa

21-33
Venules and Small Veins
• Venules drain capillary network. Endothelial cells and basement membrane with a few smooth muscle cells. As diameter of venulesincreases, amount of smooth muscle increases.
• Small veins. Tunica intima is thin; tunica media is thin with circular smooth muscle. Smooth muscle cells form a continuous layer. Tunica adventitia is well developed and is made of longitudinally arranged collagenouselastic fibers

Medium vein

21-35
Medium and Large Veins
• Medium veins. Go-between between small veins and large veins.
• Large veins. Tunica intima is thin: endothelial cells, relatively thin layer of C.T and a few scattered elastic fibers. Tunica media is thin and poorly developed. Adventitia is thick and a predominant layer with spirally arranged collagen fibers, elasticlamellae, longitudinal smooth muscle

Large Vein

Veins

Comparison of Major Features of Artery & Veins
Arteries – carrying blood at high pressure• Smooth muscle and/or elastic
fibers/lamellae predominate over collagen fibers in tunica media
• Elastic fibers/lamellae are highlydeveloped in the tunica media
• Smooth muscles and other componentsare arranged circularly in tunica media –allows change in diameter to regulate blood pressure and blood flow
• No valves Veins - carrying blood at very low pressure• Collagen fibers are relatively abundant among
the smooth muscles in the tunica media• Collagen fibers and othe components arranged
longitudinally - prevent excess stretching of vessel wall
• Valves present; to prevent backflow

Lymphatic Vessels
• Larger than blood capillaries• Very irregular shaped• Basal lamina is almost absence• Endothelial cells do not form tight
junctions (allow entry of flluid)• Larger lymph vessels contain valves
A villus of the jejunum containin a lymph capillary. A lacteal is a lymphatic capillary that absorbs dietary fats in the villi of small intestien.

References
1. Hole’s Human Anatomy & Physiology, 13th Edition, David Shier, McGraw-Hill
2. Seeley’s Principles of Anatomy & Physiology, 2nd Edition, Philip Tate, McGraw-Hill
3. Anatomy & Physiology with Integrated Study Guide, 5th
Edition, Stanley E Gunstream, McGraw-Hill4. Histology, A Text and Atlas, 6th Edition, Michael H Ross &
Wojciech Pawlina, Wolters Kluwer/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins