HIS Histo 2007
-
Upload
karindranadya -
Category
Documents
-
view
218 -
download
0
Transcript of HIS Histo 2007
-
8/8/2019 HIS Histo 2007
1/48
1
HISTOLOGY DEPARTMENTMEDICAL FACULTY
UNIVERSITAS PADJADJARAN
LAB MANUALHematoimmunology System(Lymphoid System, CapillaryAnd Upper Respiratory Tract)
-
8/8/2019 HIS Histo 2007
2/48
2
I. LYMPHOID SYSTEM
I. LYMPHOID SYSTEM
The lymphoid (lymphatic) system consists
of organs whose tissues and cells impart
acquired immunity to organism.
-Immunity is the term use to describe this
protective response.
-Lymphoid organs : Thymus, spleen, lymph
nodes and tonsils
-
8/8/2019 HIS Histo 2007
3/48
3
C omponents lymphoid tissue :
1. Reticular connective tissue stroma2. Mesenchymal reticular cells
3. Epithelial reticular cells
4. Lymphocytes : T and B lymphocytes,Plasma cells
5. Macrophages
6. Antigen presenting cells
-
8/8/2019 HIS Histo 2007
4/48
-
8/8/2019 HIS Histo 2007
5/48
5
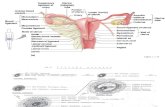
Distribution of lymphoid tissue in thebody
Distribution of lymphoid tissue in thebody
Tonsils
Lymph nodes
LymphaticvesselsThymus
Spleen
Payerspatches of the ileum
Lymph nodes
Bone marrow
-
8/8/2019 HIS Histo 2007
6/48
6
Bone marrow
Stem cellproduces cells
that .
Bone marrowThymus
Remain in theMigrate to the
Interleukins
T lymphocytes
Migrating to non-thymic lymphoidtissue. producing
B lymphocytes
Immunoblasts
Killer
Generating
Helper Suppressor Tlymphocytes
Generating
T and B memorycells Plasma cells
Immunoblasts
Blood,lymph
When activatedby antigens,
produce
Producing
-
8/8/2019 HIS Histo 2007
7/48
7
The thymus is a central lymphoid organsituated in the mediastinum at about the levelof great vessels of the heart.
Structure :Lobe
Lobules (2) :
1. Cortex : small lymphocyte, epithelial reticular celland blood-thymus barrier.
2. Medulla : - Hassalls corpuscles
- Extend into the core of each of the
lobules
THYMUSTHYMUS
-
8/8/2019 HIS Histo 2007
8/48
8
4 . Medulla
5. Lobule
1. C apsule
3. C ortex
2. Interlobular trabeculae
6. Secondary (incomplete)trabeculae7. Medulla continuous
8. Lobule sectioned tangentially
9. Thymic corpuscle (Hassalscorpuscles)
10. C ortex
11. Interlobular trabeculae
12. Blood vessels in trabeculae
1. Venula
2. C apillary
3. Trabecula
4 . C ortex (thymic
lymphocytes)
8. Degenerating center of thymiccorpuscle)
6. Aggregations of reticularcells
7. Thymic corpuscle (Hassalscorpuscle)
5. Medulla (thymic lymphocytesand stroma)
9. Reticular cells in10. Isolated reticular cells
THYMUSTHYMUS
-
8/8/2019 HIS Histo 2007
9/48
9
Desmosome
Desmosome
Desmosome
Epithelialreticular cell
Lymphocytes
-
8/8/2019 HIS Histo 2007
10/48
10
Histogenesis and involution :
Third pharyngeal pouches (endodermal)
F unctions :
1. T-lymphocyte production
2. Hormone production : thymopoietin, thymosin
3. Blood-thymus barrier
-
8/8/2019 HIS Histo 2007
11/48
11
Lymph nodes are encapsulated sphericalor kidney-shaped organ composed of lymphoid tissue.
S cattered in group along lymphatic vessels inthe neck, axilla, groin, thorax and abdomen,they act as in-line filter of the lymph,removing antigen and cellular debris andadding Ig.
LYMPH NODESLYMPH NODES
-
8/8/2019 HIS Histo 2007
12/48
12
Structure (5) :
1. C ortex :
The dark-staining owing to presence of tightly packedlymphocytes.
S econdary lymphoid nodules (containing primarily Blymphocytes) with germinal centers.
2. Medulla :Lighter staining than cortex.
Composed of cords of lymphoid tissue (medullary cord)
separated by medullary sinuses.
-
8/8/2019 HIS Histo 2007
13/48
13
3. Paracortical zone :
This is the T-dependent region, lying between the
cortical lymphoid nodules and the medulla.Characteristized by the presence of many high-endothelial post capillary venules.
4 . Lymphatic Vessels :- Afferent lymphatic vessels
- Efferent lymphatic vessels
Afferent vessels subcapsular sinus peritrabecular
S inuses medullary sinuses efferent vessels
exiting through the hilum
-
8/8/2019 HIS Histo 2007
14/48
14
F unction :- Filtration of lymph
- Lymphocyte production (lymphopoiesis)- Immunoglobulin production
-
8/8/2019 HIS Histo 2007
15/48
15
1. Pericapsular fat andconnective tissue
2. C apsule
3. Lymphatic tissue
4 . C apsule andafferent lymphatics
5.C
ortex
6. Medulla
7. Trabeculae
8. Blood vesselsin trabeculae
9. Marginal(subcapsular)
sinus
10. Arterioles
11. Efferentlymphatic vessels
12. Hilus
13. Medullarysinuses
14 . Medullary cords
15. C ortical nodules
(Lymphatic nodules)16. Marginal(subcapsular) sinus
17. Germinal centers
18. Veins
LYMPH NODE (PANORAMIC VIEW)LYMPH NODE (PANORAMIC VIEW)
-
8/8/2019 HIS Histo 2007
16/48
16
The largest of the lymphoid organ, the spleen
lies in the upper left quadrant of the
abdominal cavity. It serves as theimmunologic filter of the blood.
SPLEENSPLEEN
-
8/8/2019 HIS Histo 2007
17/48
17
Structure (2) :1. Splenic pulp :
a. White pulp- Periarterial lymphatic sheaths (PAL S ) :
T dependent region- Peripheral white pulp (PWP) :
B lymphocytes and secondary lymphoid noduleb. Red pulp :- Red pulp cords (Billroths)- S plenic sinusoid- Endothelial cells (elongated on the sinusoids
long axis)c. The marginal zone :
- Border between the white and red pulp- Marginal sinuses
-
8/8/2019 HIS Histo 2007
18/48
18
2. Splenic circulation :a. Arterial supply :
Abdominal aorta S plenic arteryTrabecular artery Central arteriesPenicilliar arteriole Capillaries and sheeted
arterioles sinuses of
red pulpb. Open and closed theories of splenic circulation
c. Venous drainage
S inusoid red pulp veins Trabecular vein
S plenic vein inferior mesenteric vein
Hepatic portal vein liver
-
8/8/2019 HIS Histo 2007
19/48
19
F unctions :
1. Production of blood cells
2. Destruction of erythrocytes
3. Defense of the organism : filter for the blood4. S torage of blood
-
8/8/2019 HIS Histo 2007
20/48
20
7. Germinal center
8. Tangentialsection of asplenic nodule
9. C entral arteries(t.s) in splenicnodules
10. Venoussinuses in thered pulp
11. Trabecular veins
12. Trabeculae (t.s)13. Sheathed artery
14 . Pulp arteries(arterioles)
1. Peritoneumand capsule
2. Splenic nodules(white pulp)
3. Trabeculae
4 . Trabecular artery
5. Splenic cords inthe red pulp
6. C entral artery(l.s)
SPLEENSPLEEN
-
8/8/2019 HIS Histo 2007
21/48
21
Peripheral whitepulp (B cells)
Trabecular artery
Marginal zonesinuses
Periarterial lymphaticsheath (T cells)
C losecirculation
Trabecula
Peniciliar arteriole
Trabecular veins
Pulp vein
Opencirculation
Sheath
Marginal zone
sinuses
S
S
S
S
C entral artery
Sinusoid
-
8/8/2019 HIS Histo 2007
22/48
22
Sinusoid (closedcirculation)
Splenic cord
Sinusoid (open
circulation)
-
8/8/2019 HIS Histo 2007
23/48
23
This incompletely encapsulated lymphoidaggregates contain many lymphoid
nodules, they underlie the mucousmembranes (epithelial lining) of mouth andpharynx.
TONSILSTONSILS
-
8/8/2019 HIS Histo 2007
24/48
24
1. Stratified squamousepithelium
2. Lymphatic nodules
3. Tonsillar crypts
4 . Epithelium of crypt(tg.s)
5. Internodular septum (trabecula)
6. Skeletal musclefibers
7. Germinal center
8. Merging nodules
9. Internodular septum (trabecula)
10. F undi of crypts
11. Blood vessel inthe capsule
12. Skeletal musclefibers
PALATINE TONSILPALATINE TONSIL
-
8/8/2019 HIS Histo 2007
25/48
25
Skeletalmuscle
C rypt
Epithelium
Salivary gland
-
8/8/2019 HIS Histo 2007
26/48
26
Location
Number per individual
Number of crypts per tonsil
Epithelial covering
Capsule
P alatine TonsilsLateral walls of theoral pharynx, belowthe level of the soft
palate
2
10 20
Nonkeratinizedstratified squamous
Thick partial capsuleof dense connectivetissue
P haryngeal TonsilBack of thenasopharynx in themidline, above the levelof the soft palate
1
Surface pleated, but nocrypts
Ciliated pseudostratifiedcolumnar epithelium
Thin partial connectivetissue capsule
Lingual TonsilsAt the back of thetongue (floor of the
pharynx)
Small and numerous
One crypt per tonsil
Lightly keratinizedstratified squamousepithelium
No definitivecapsule
Table : Comparison of the TonsilTable : Comparison of the Tonsil
-
8/8/2019 HIS Histo 2007
27/48
27
K ey Features
Cortex and Medulla
Lymphoid nodules
Cords and sinuses
Unique structure
Thymus
Yes
No
No
Hassallscorpuscles
Lymph Nodes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Corticalnodules,
subcapsular sinus
Spleen
No
Yes
Yes
Centralarteries
Tonsils
No
Yes
No
Epithelialcovering
Table : Distinguishing structural features of the
lymphoid organs
Table : Distinguishing structural features of the
lymphoid organs
-
8/8/2019 HIS Histo 2007
28/48
28
Lymph node
Spleen
Outer cortex(mainly B cells)
Inner cortex(mainly T cells)Medullary cord(mainly B cells)
White pulp
Peripheral white pulp(mainly B cells)
Trabecula
Red pulp
Peripheral lymphaticsheath (mainly B cells)
Artery
Distribution of B and T cells in lymph nodes andspleen S, sinusoid
Distribution of B and T cells in lymph nodes andspleen S, sinusoid
-
8/8/2019 HIS Histo 2007
29/48
29
II. BLOOD VESSELS
-
8/8/2019 HIS Histo 2007
30/48
30
BLOOD VESSELSBLOOD VESSELS
Classified according to type and size
A. BLOOD C APILLARIES
J 7 9 Qm
S ingle layer endothelial cells with bulging nuclei
Basal lamina
Pericytes / mesenchymall cell
At the junction of a capillary, there is a ring of smooth muscle (precapillary sphincter)
-
8/8/2019 HIS Histo 2007
31/48
31
TYPES O F C APILLARIES
a. Continuous capillaries
S mooth nonporous
Junctional complexes
Muscles, the brain and peripheral nerves
b. Fenestrated capillaries
Fenestrae : +
Two types : - unobstructed pores
- Pores + thin diaphragma
Kidneys, intestines, endocrine glands
-
8/8/2019 HIS Histo 2007
32/48
32
c. S inusoidal capillaries (discontinuous)
Wide lumens
Follow a tortuous path
Gaps between endothelial cells
Fenestration ++
Phagocytic cells
Discontinuous basal lamina
Liver, spleen, bone marrow
-
8/8/2019 HIS Histo 2007
33/48
33
2a
1
b
3 Fenestrated
Continuous
Discontinuous
-
8/8/2019 HIS Histo 2007
34/48
34
III. RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
-
8/8/2019 HIS Histo 2007
35/48
35
There is 3 major part :1. Ventilating mechanism :
Includes :DiaphragmRib cageIntercostal muscle
Abdominal musclesElastic connective tissue in the lungs
A . Components and Basic Functions
of Respiratory System
-
8/8/2019 HIS Histo 2007
36/48
36
2 . Conducting portion :
It includes :
Nasal cavity
Nasopharynx
Larynx
Trachea
BronchiBronchioles
Terminal bronchioles
-
8/8/2019 HIS Histo 2007
37/48
37
3. Respiratory portionIt includes :
Respiratory bronchioles
Alveolar ducts
Atria
Alveolar sac
-
8/8/2019 HIS Histo 2007
38/48
38
The main divisions ofthe respiratory tract.The natural proportions
of these structureshave been altered forclarity; the respiratorybronchiole, for example
is in reality a shorttransitional structure
-
8/8/2019 HIS Histo 2007
39/48
39
a. General features :Ciliated pseudo stratified columnar
Goblet cellsb. Epithelial cell types :
Ciliated columnar cells
Mucous goblet Brush cellsBasal cellsSmall granule cells
B.Wall Structure
1. Respiratory epithelium
-
8/8/2019 HIS Histo 2007
40/48
40
Trachea
In the bronchi : smooth muscle cells encircle the walls
The muscle layer gradually decrease until it disappears
at the level of the alveolar ducts
2 . Lamina propria
3. Smooth muscle
Loose connective tissueMucous glands ( upper tract )
-
8/8/2019 HIS Histo 2007
41/48
41
D istinguishing features of respiratory tract components
-
8/8/2019 HIS Histo 2007
42/48
42
The nasal cavity consists of 2 structures :
1. The external vestibule
2. The internal nasal fossae
N asal Cavity
-
8/8/2019 HIS Histo 2007
43/48
43
The paranasal sinuses are blindcavities in :
Frontal
Maxillary
Ethmoid
Sphenoid bones
Paranasal Sinuses
-
8/8/2019 HIS Histo 2007
44/48
44
The upper part of the pharynx
N asopharynx
LarynxEpiglottis
Laryngeal Cartilages
Vocal apparatus
-
8/8/2019 HIS Histo 2007
45/48
45
Respiratory epithelium
Lamina propria : mixed seromucous glands
Presence of 16 - 20 C-shape cartilage rings
Smooth muscle bundles : trachealis muscle
T rachea
-
8/8/2019 HIS Histo 2007
46/48
46
T RACHEA
-
8/8/2019 HIS Histo 2007
47/48
47
T RACHEA(SECTION AL VI EW)
1. Perichondrium
2. Cartilage :matrix
3. Flattenedchondrocytes
4. Cartilage :territorialmatrix
5. Epithelium :pseudostratifiedciliated columnar
6. Basementmembrane
7. Elastic fibers(elasticmembrane)
8. Duct of a trachealgland (t.s)
9. Mucous alveoluswith a serousdemilune
10. Goblet cell
-
8/8/2019 HIS Histo 2007
48/48
48