Henoch Schonlein Purpura
-
Upload
yellowsunfire102 -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
4.431 -
download
5
description
Transcript of Henoch Schonlein Purpura

Henoch Schonlein Purpura
Ahmad Abid Abas 2

What is HSP?
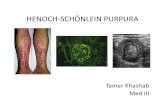
• Anaphylactoid purpura,Purpura rheumatica, Leukocytoclastic vasculitis.
• It is an inflammatory disorder characterized by a generalized vasculitis involving the small vessels of the skin, GI tract, kidneys, joints, and, rarely, the lungs and CNS.
• Mainly affects children 3-15 yr age.Rarely below 2 yr age.

Etiopathogenesis
• Unknown etiology. Multifactorial with genetic, environmental and antigenic components.
• More than 75% of patients report antecedent upper-respiratory, pharyngeal, or GI infections.
• An immunoglobulin A (IgA)–mediated autoimmune phenomenon. (clinical manifestation result fr this Ag-Ab complex)

How to Approach ?
• c/o – Usually the rash is the first to appear and the child is brought to medical attention by his/her parents.
• Hx – Prodromal symptoms such as headache,fever,anorexia.
• O/E – Rash --> Morphology (palpable) ?,(What type cutaneous lesions (petichea,ecchymosis)?,Site of distribution (thighs,buttocks) ?

How to Approach ?
• Other clinical features to be considered :1) Abdomen – crampy abdominal pain.2) Joints – migratory arthralgia,arthritis in ankles,knees (big joints) – expect periarticular swelling + significant pain.3) Renal – (HTN,edema,oliguria and hematuria +/- azotemia) similar CP of APSGN.

How to Approach ?Dx - Palpable purpura (mandatory) in the presence of at least one of the following four features:
• Abdominal pain• Arthritis (acute) or arthralgia• Renal involvement (any haematuria and/or
proteinuria)• Any biopsy showing predominant Iga deposition

What to be expected in Investigations?
• Electrolyte values Normal unless excess vomit.• BUN/creatinine(RFT) – May ↑ in presence renal
involvement.• CBC – (exclude thrombocytopenia) leukocytosis
possibly eosinophilia,Platelet counts N or ↑.Hb or Ht values may be N or ↓ 2ry to bleeding.
• Urinalysis – (hematuria, proteinuria, and occasional red cell casts.) (like APSGN)

How to Approach ? Criteria ITP Acute
LeukimiaAplastic Anemia
HSP
Hb/RBC count Normal ↓ ↓ Normal
WBC count Normal ↑↑↑ ↓ ↑ in some cases.
Platelet count ↓ ↓ ↓ Normal

How to narrow DDx ? • Tourniquet test [Hge tendency,capillary fragility]• Antistreptolysin-O (ASO) titer [recent Strept. infection]• Monospot test [rapid test for Mono. (EBV)]• Antinuclear antibody (ANA) test [exclude SLE]• Rheumatoid factor (RF) test [exclude RA]• Determination of C3/C4 levels (diff. fr APSGN)• Prothrombin time (PT) and activated partial
thromboplastin time (aPTT)• Blood cultures [potential infection,meningitis)• Abd U/S – [Evaluate Intussusception & exclude
appendicitis]

How to Manage ?• Rx is largely supportive.• Abdominal pain – Common and self-limited.• Joint pain – NSAID agents• Cutaneous manifest. – self-limited may relapse.• Ch. Cutaneous lesion –
colchicine,aspirin,systemic CST.• No optimal management for GIT and Renal
involvement.Should be follow up closely.

Conclusion (clinical point of view)
HSP is diagnosed clinically.GI involvement is early symptom and renal disease is late symptom.If occur in adults , it is more severe.Palpable purpura,abd pain and arthritis is clinical characteristic triad of HSP in pediatric.

References
• 1) The Indian Academy of Pediatrics,Bulletin of Rheumatology Chapter IAP September 2010.
• 2)http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/804681-clinical
• 3) http://www.orpha.net/data/patho/GB/uk-HSP1.pdf