Heart - Revision Doc [06Nov'10]
-
Upload
dev-ebenezer-johnson -
Category
Documents
-
view
218 -
download
0
Transcript of Heart - Revision Doc [06Nov'10]
-
8/7/2019 Heart - Revision Doc [06Nov'10]
1/9
Heart The Heart is a muscular organ that lies in the thoracic cavity
behind the septum.
Operates continually and tirelessly throughout a life of anorganism.
Create PDF files without this message by purchasing novaPDF printer (http://www novapdf com)
http://www.novapdf.com/http://www.novapdf.com/http://www.novapdf.com/http://www.novapdf.com/ -
8/7/2019 Heart - Revision Doc [06Nov'10]
2/9
Create PDF files without this message by purchasing novaPDF printer (http://www novapdf com)
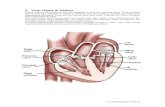
Structure of the Heart
Create PDF files without this message by purchasing novaPDF printer (http://www novapdf com)
http://www.novapdf.com/http://www.novapdf.com/http://www.novapdf.com/http://www.novapdf.com/http://www.novapdf.com/http://www.novapdf.com/ -
8/7/2019 Heart - Revision Doc [06Nov'10]
3/9
Structure of the Heart The Atrium has thin walls and its elastic and thus it stretches
as it collects blood. It pumps blood to the ventricles.
Ventricles has a much thicker muscular walls. It pumps
blood either to lungs or to the rest of the body.
Both Atria contracts together and both ventricles contract
together.
The left atrioventricular (bicuspid) values, is present in the
left side of the heart has two flaps of fibrous tissue.
The right atrioventricular (tricuspid) valves, present in theright side of the heart has three flaps.
Create PDF files without this message by purchasing novaPDF printer (http://www novapdf com)
http://www.novapdf.com/http://www.novapdf.com/http://www.novapdf.com/http://www.novapdf.com/ -
8/7/2019 Heart - Revision Doc [06Nov'10]
4/9
Structure of the Heart The aorta is connected to the left ventricle and carries
oxygenated blood to all parts of the body except the lungs
The venacava is connected to the right atrium and brings
deoxygenated blood back from the tissues of the body.
The Pulmonary artery carries blood from the right ventricles
to the lungs
The pulmonary vein carries blood from the left ventricles to
the rest of the body.
Create PDF files without this message by purchasing novaPDF printer (http://www novapdf com)
http://www.novapdf.com/http://www.novapdf.com/http://www.novapdf.com/http://www.novapdf.com/ -
8/7/2019 Heart - Revision Doc [06Nov'10]
5/9
Supplying the Heart MuscleThe heart muscle is supplied by its own blood vessels, called the
coronary arteries, which branch off the aorta shortly after it leaves
the heart. Blockage of these arteries, e.g. by a blood clot, leads to
myocardial infarction, also known as heart attack, this is because
an area of the heart muscle is kept away from something needed,
i.e. oxygen and so dies.
Create PDF files without this message by purchasing novaPDF printer (http://www novapdf com)
http://www.novapdf.com/http://www.novapdf.com/http://www.novapdf.com/http://www.novapdf.com/ -
8/7/2019 Heart - Revision Doc [06Nov'10]
6/9
The Cardiac Cycle Relaxation of the heart (diastole) - blood enters the atria
from the pulmonary artery and the vena cava. As the atria
fills the pressure in the atrioventricular valves are forced
open allowing the blood to pass into the ventricles. The
muscular walls of both atria and ventricles are relaxed at this
stage.
Contraction of the atria (atrial systole) The muscle of the
atrial walls contract, forcing the remaining blood that they
contain (around 20% of the total blood in the heart) into the
ventricles
Create PDF files without this message by purchasing novaPDF printer (http://www.novapdf.com)
http://www.novapdf.com/http://www.novapdf.com/http://www.novapdf.com/http://www.novapdf.com/ -
8/7/2019 Heart - Revision Doc [06Nov'10]
7/9
The Cardiac Cycle Contraction of the ventricles (ventricular systole) After a
short delay to allow the ventricles to fill with blood, their
walls contract simultaneously.
This increases blood pressure within them forcing shutting
the atrioventricular valves and preventing the back flow of
blood into the atria.
With the atrioventricular valves closed, the pressure rises
further, forcing opening the semi lunar valves and pushing
blood into the pulmonary artery and aorta.
Create PDF files without this message by purchasing novaPDF printer (http://www.novapdf.com)
http://www.novapdf.com/http://www.novapdf.com/http://www.novapdf.com/http://www.novapdf.com/ -
8/7/2019 Heart - Revision Doc [06Nov'10]
8/9
Cardiac output Is the volume of blood pumped by one ventricle of the heart
in one minute. It is usually measured in dmmin and
depends upon two factors:
The heart rate (the rate at which the heart beats)
The stroke volume (volume of blood pumped out at each
beat)
Cardiac Output = heart rate x stroke volume
Create PDF files without this message by purchasing novaPDF printer (http://www.novapdf.com)
http://www.novapdf.com/http://www.novapdf.com/http://www.novapdf.com/http://www.novapdf.com/ -
8/7/2019 Heart - Revision Doc [06Nov'10]
9/9
Control of Heart Beat Mynogenic is also known as the cardiac muscle, i.e. its
contraction is initiated from within the muscle itself, rather
than by nervous impulses from outside (neurogenic), as in the
case of other muscles.
Within the walls of the right atrium of the heart is a distinct
group of cells known as the sinoatrial node (SAN). It is from
here that the initial stimulus for contraction originates. Has a
basic rhythm of stimulation that determines the beat of the
heart aka pacemaker.
Create PDF files without this message by purchasing novaPDF printer (http://www novapdf com)
http://www.novapdf.com/http://www.novapdf.com/http://www.novapdf.com/http://www.novapdf.com/
![download Heart - Revision Doc [06Nov'10]](https://fdocuments.us/public/t1/desktop/images/details/download-thumbnail.png)