Health Disorders - Carbohydrates
-
Upload
glydenne-glaire-poncardas-gayam -
Category
Documents
-
view
11 -
download
3
description
Transcript of Health Disorders - Carbohydrates

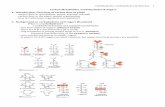
HEALTH DISORDERS


Diabetes Mellitus • a disorder of energy
metabolism due to failure of insulin to regulate blood glucose
• results in hyperglycemia• acute symptoms include
thirst, increased urine production, hunger
• long term consequences include increased risk of heart disease, kidney disease, blindness, neural damage and death
• two forms: Type I and Type II

Diabetes Mellitus
• Type 1 diabetes– Accounts for 10% of all cases– occurs when b cells of the pancreas are destroyed
• insulin cannot be synthesized
– Patients do not produce enough insulin– Causes hyperglycemia – high blood sugar (glucose)– Requires insulin injections– May be an autoimmune disease

Diabetes Mellitus
• Type 2 diabetes– Most diabetics have Type 2 diabetes– Body cells are insensitive or unresponsive to
insulin– Excess insulin is often produced• leads to hyperinsulinemia
– blood glucose levels rise– Causes hyperglycemia because cells cannot
remove glucose from the blood

Diabetes Mellitus

Hypoglycemia

Hypoglycemia
– Low blood sugar (glucose)– symptoms similar to an anxiety attack: rapid weak heart
beat, sweating, anxiety, hunger, trembling, weakness– RARE in healthy people– Reactive hypoglycemia results when too much
insulin is produced after a meal• Causes shakiness, sweating, anxiety
– Fasting hypoglycemia results when too much insulin is produced even when the patient has not eaten


Lactose Intolerance

Lactose Intolerance
– Insufficient lactase production = inability to digest lactose (milk sugar)
– lactose intolerance milk allergy– lactose molecules from milk remain in the intestine
undigested– undigested lactose digested by bacteria producing
irritating acid and gas– Symptoms = intestinal gas, bloating, nausea, cramping,
diarrhea– Alternate sources of calcium• Tomato juice, seaweed, cabbage, squashes, beets

Lactose Intolerance
• individuals who consume little or no milk products may be at risk of developing nutrient deficiencies
• dairy options: yogurt, aged cheddar, small quantities of milk (~ ½ cup), acidophilus milk, cottage cheese
• best to consume with other foods and spread intake throughout day
• gradual increases in milk intake may cause intestinal bacteria to adapt

Alternatives to Milk1. Calcium• canned fish with bones, bone soup stock, broccoli,
cauliflower, bok choy, calcium fortified beverages, blackstrap molasses
2. Vitamin D• 15 minutes exposure to SUNLIGHT several times per week• fortified margarine, fortified cereals, fatty fish (herring,
tuna, salmon, sardines), fortified soy or rice milk3. Riboflavin• beef, chicken, liver, clams, mushrooms, broccoli, breads,
fortified cereals