Guide Wire and Guide Catheter Training
-
Upload
naveenchandrags -
Category
Documents
-
view
420 -
download
42
Transcript of Guide Wire and Guide Catheter Training

Guide wire & Guide catheter!

PTCA Guidewires

PTCA Guidewires
One of the most difficult Interventional products to convert due to its physicians “personal” relationship with their wire of choice.

PTCA Guidewire Functions
PTCA Guidewires are designed to:Access to a lesion“Atraumatically” cross a lesionProvide device delivery supportProvide unhampered device movementUnobstructed lesion visualization
(radiopacity)

Guide wire Characteristics
Tip Trackability Tip softness Ease of tip forming Tip Shape retention
Radiopacity Wire Steering in
anatomy PCI device support PCI Device
trackability
Design trade-offs occur when one of these characteristics are out of balance

Guidewire Overview
Guidewire Construction Coatings Extension Systems

Core Wire
Core Wire: Stainless Steel or Stainless Steel/Nitinol wire (Fusion/BMW family)
The series of barrels and tapers (or transitions), with varying lengths and diameters determine many of the key performance characteristics of the wire

Guidewire Construction Design
Support wire for device delivery (stents)
POBA (balloons)
Crossing Wire-CTO’s
Two Barrel
Single Barrel
Tapered Barrel

Trade-offs
If you have more wire supportStraightens vesselsMore vessel contact during device advancement
increases resistance during advancement
May be the only option for stiff device delivery
If you have less wire support•Conforms to the natural curves in the anatomy•Requires more trackable devices (balloons)•Safer ?

Outer Covering: Spring(s)Helical Coil is wound from Stainless Steel. To provide desired radiopacity the distal tip is either Stainless Steel with gold Markers or more commonly made of Platinum.The Coil fills out the body of the wire “0.014”.
Spring (s)

Forming Ribbon Tip DesignFlat stainless steel wire extending from the distal core wire designed to provide:
-Tip softness
-Tip shape retention/tip shaping
-Tip trackability/prolapsability
SpringsCore wireForming ribbon

Coatings
Reduce friction during wire placement and device delivery
TypesPTFE (Teflon)Silicone (Pro/Pel)Hydrophilic (Hi-Per Coat)

Extension/Exchange Area
Medtronic AVE: Linx – EZ & DocACS: Doc, AnchorCordis: CinchSciMed: Magnet

Challenges of Coronary GW
CTO - Chronic Total Occlusions Vessel Tortuosity Device Delivery

CTO Technique
Operators may start with soft wire Increase tip stiffness incrementally by
trading up wire type Advance balloon closer to wire tip Increase distal vessel visualization by
contralateral Angiography

WiringTechniques
Track Straight Turn/Steer

Guidewire Induced Vessel Straightening

Medtronic AVE PTCA Guidewires
GT2 Fusion GT1 Product Line
Floppy Direct Light Support Support
Hi Per Flex Standard

Factors for Selling Success Know your Doctor’s Preferences
Lucent vs. Opaque“Steerer” vs. “Driver”Support vs. FloppyOne Wire vs. Start Wire/Stent WireRx vs. OTWDevices used in lab (I.e. stents, Rotablator,
DVI, IVUS, etc.)

Medtronic AVE Guidewires
Floppy
Direct
Light Support
Support
GT1 Product Line

Start-to-Finish Performance
Confident access and crossSuperior vessel trackingMaximum push and torque efficiency
Endurance and supportNitinol always “in shape” throughout the caseDevice support from POBA to stentingOptimal in-device wire movement

Union of Technology-Tip to Tail Atraumatic forming ribbon tip design Spring length
25 cm distal spring/3 cm radiopaque length 45 cm Nitinol core wire segment Single-joint, stainless steel, hypotube shaft
supporting Nitinol 180 cm DOC* Compatible/300 cm Pro/Pel silicone-type coating *DOC ®is a registered trademark of Guidant Corporation.

Design Features & Benefits
Nitinol-to-stainless-steel constructionKink-resistant NitinolNitinol memory durability throughout the caseStainless steel hypotube strength and torqueSuperior push efficiencyOutstanding torque transmission

Design Features & Benefits
Precision core wire and tip geometryTip softnessVessel trackingDevice support

A Powerful Union Single-joint design
Joint location in the straight segment of the guide
Provides seamless, transition for device delivery
Enhances torque transmission to the distal Nitinol segment
Superior torque transmission Optimal wire movement

Innovative Hypotube Design
Nitinol and stainless steel are joined 45 cm from the distal tip,ensuring that the joint location is in the straight segment of the guiding catheter

Fusion vs. BMW
Fusion Similarities Nitinol/Stainless steel
construction Forming ribbon tip 3 cm radiopaque length 25 cm spring DOC® Extension-
compatible
•Fusion Differences-Hypotube enhances torque transmission-Single joint attachment process-Superior distal vessel tracking-Distal tip column support-Pro/Pel silicone coating

Distal Tip Comparisons
The Fusion guidewire distal tip design offers ideal,workhorse tip support while minimizing tip stiffness.

Outstanding Torque Response
Fusion’s stainless steel hypotube shaft offers outstanding torque transmission for improved steering capability

Torque Response:It ’s all in the Physics!
Torque forces applied to ahollow tube are transmittedmore efficiently due to asmaller cross-sectional area

Standard (Steerable) 0.014” and 0.016” diametersCore to tipPTFE or Silicone Coatings ‘J’ tip and 180cm onlyTotal occlusion (CTO) wire, very stiff tip
Other Medtronic AVE PTCA Guidewires

Competitive Overview
Market TrendsCompetitive Products

PTCA Guidewire Market
OTW to RX balloons = 300 cm (exchange) to 180 cm (standard) length trend
Stent trackability Wire support needed Purchasing contracts = more compliance
and fewer choices for physician

PTCA Guidewire Competitors
ACS/Guidant SciMed/Boston Scientific Cordis/J&J Medtronic AVE

Top Selling Wire Brands ACS Balance Wires (BMW and BHW) ACS Support Wires (S’port, All-Star, Support) ACS Hi-Torque Floppy II SciMed Choice Extra SupportCordis Stabilizer XSCordis ATWMedtronic AVE

Factors for Selling Success
Knowledge of ProductHow your wires differ/similarTranslation of design feature into performance
benefit Knowledge of Competitors’ Product
How is yours different, thus better!

Summary Know your products Know your competitors’ products Know your account targets’
Wire preferencesCurrent product used and likes and dislikesContract status and compliance

Functions of a Guide Catheter
• The main functions of a Guide Catheter:
• Conduit for contrast, wire & device transport
• Support for device advancement

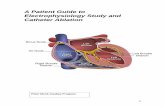
Relevant Anatomy
RCA
LCA or Left Main
LAD
LCXCusp of the heart’s Aortic valve
Descending Aorta
Ascending Aorta

Coronary Anatomy
The point at which the ostium of the RCA or LCA is attached to the aortic root can vary.
Right Coronary Ostia
Left Coronary Ostia
Sinuses of Valsalva
Ascending Aorta
• Left Cusp
•Right Cusp•Posterior Cusp
Aortic Valve
Cut away view of Aorta & flattened

RCA
LCA or Left Main
LAD
LCX
Cusp of the heart’s Aortic valve
Ascending Aorta
Coronary Anatomy

Access Site Options
Femoral Approach Radial/ Brachial Approach
1- Heart2- Aorta3- Femoral Artery4- Radial Artery

Access Site Issues
Scar Tissue Tortuosity Surgical Graft Diseased Iliacs (PVD)

The Conduit to the Target Vessel

Important Features of a Guide Catheter
Atraumatic tip Preformed curves & configurations Torque control Kink resistance Radiopacity Support Device Compatibility

Guide Catheter Construction All Guide catheters have the same basic construction:
Primary Curve
Tip
Radiopaque Marker
ShaftStrain Relief
Hub/Luer
Secondary Curve

Guide Catheter Construction
I.D.O.D.Key Measurements:
6 French 7 French5 French 8 French
(1-French = 0.33 mm)
Catheters are named by their OD in French:

Guide Catheter Shaft Construction
Inner LinerStainless Steel braid
Outer jacket
Internal Lumen
Smooth or Lubricious
Material
Device Compatibility
1:1 Torque
Kink resistance
Strength
Support/ Flexibility
Kink resistance

Numerous curve configurations

Importance of Co-Axial Alignment
Coaxial or parallel alignment of the catheter will affect how well the guide catheter operates as a conduit
Non-Coaxial
Coaxial

Curve Selection Factors Anatomical Approach Access Site Issues French Size Influence Back-up Support Aortic Width Coronary Anatomy Native Coronary vs. CABG/IMA Location and Severity of Target Lesion Amount of Calcification in Target
Vessel

Types of Guide Catheter CurvesBroadly split into three categories:StandardStandard guides provide coaxial alignment for the majority of patients with relatively straight forward aortas and vessel orientation. These guides often ride above the sinuses or barely reach into the sinus. (JL, JR, LCB, RCB)
Support– Support guide catheters derive their support
primarily from the Sinus of Valsalva. (AL, AR, Hockey Stick)
Extra Support – Gather their support from the opposite wall
of the aorta (EBU)

Sizing based on Aortic Width
Narrow
Normal
< 3.5 cm
Dilated
> 4.0 cm3.5 - 4.0cm

Aortic Width Determines the Choice of Curve Length
3.04.0
5.0
Judkins Left
P
S
P = Primary Curve S = Secondary Curve
Curve Length = distance (cm) between P & S
Choice of Curve Length

Aortic Width Determines Curve Length
Judkins Right
S
3.04.0
5.0
P = Primary CurveS = Secondary Curve
P
Curve Length = distance (cm) between P & S

The Perfect FitProper fit is a 45o angle at the primary curve with coaxial alignment and the secondary curve buttressing against the contralateral wall

Curve Length Considerations
• Shorter curve:
• May be useful for vessels with superior orientation
Longer curve: May be useful for vessels
with inferior orientation
Tip Orientation

French Size Influence Historically, 8F guides were necessary to deliver devices
because of their larger internal lumens.
Current 6-7F catheters have internal lumens just as large as previous generation 8F catheters.
Small guides require ‘back-up” curves more frequently for added support.
Large guides require side-holes more frequently to improve perfusion.

French Size Influence
Better passive support
Better visualization
Better torque
transmission
Small arterial puncture
Brachial/radial access
Permit active support
Less contrast
PROS
Larger arterial puncture
Pressure dampening
More contrast
Smaller internal lumen
Less visualization
CONS
7-8F Guides6F Guides
6F = 2mm/0.79” OD 7F = 2.3mm/0.92” OD
8F = 2.7mm/0.105” OD

Perfusion of Target Vessel
Smaller Diameter catheters, such as a 5F or 6F allow for perfusion of the target vessel.
Larger diameter catheters such as 7F and 8F, or deep seated catheters may cut off perfusion of the target vessel. Side-holes in the guide help to alleviate this issue. Location for side holes

Deep-seating

Pressure Damping
Note: Side holes allow perfusion, but don’t prevent guiding catheter injury to the ostium
Normal Ventricularization Damped

Types of Catheter Support The ability of the guiding catheter to remain in position
and provide a stable platform for the advancement of interventional equipment.
There are three main types of catheter support: Active Support Passive Support Balanced Support
Distal Segment

Active Support Active Support users typically:
Use the artery itself to ensure guide curve conformability and back-up (deep seating)
Relies on active manipulation of guiding catheter to: Obtain stable position Seat coaxially Pre-select LAD or LCX

Passive Support Passive support users typically:
Rely on properties of the shaft and tip to maintain position in the ostium
Depend on Support provided by either anatomy or catheter composition/curve shape
Rarely deep-seat the catheter Prefer minimal manipulation of the guide catheter Prefer guides with a stiffer distal segment

Balanced Support Balanced support users typically:
Rely on properties of the shaft and tip to maintain position in the ostium but prefer a flexible distal segment that can be manipulated/seated for extra back up if needed

Choosing Types of Support
Requires precise curve selection and sizing Requires large Ostia
Requires
disease-free ostia
Active Support
No Yes Yes
Balanced Support
No Indeterminate Indeterminate
Passive Support
Yes Indeterminate Indeterminate
Soft Distal Segment
Firm Distal Segment
Active Balanced Passive

Four Families of Medtronic Guide Catheters
Active Support: Sherpa NX, Zuma 2 Balanced Support: Sherpa NX, Launcher Passive Support: Zuma

Launcher: Largest ID 6F (0.071”) Full Wall Technology
Sherpa NX: Consistent Lubricity Full Wall Technology Extra-Soft tip Choice of distal segment support in 6F
Over 240 curves on every platform Custom curves – made to order
Medtronic Guide Catheters
Note: Zuma and Z2 are still available, however Launcher and Sherpa are actively promoted as the latest guide catheter technology from Medtronic.

Full Wall Technology
Nylon liner and outer jacket fuse together through the flat wire braid
during extrusion process
• PTFE liner• Round/flat braid layer• Outer Jacket

Medtronic Guides at a Glance…
Sherpa NX Active Sherpa NX Balanced
Launcher Z2
French Size / ID
5: 0.058”
6: 0.070”
6: 0.070”
7: 0.080”
8: 0.088”
5: 0.058”
6: 0.071”
7: 0.081”
8: 0.090”
5: 0.058”
6: 0.070”
7: 0.081”
8: 0.091”
Primary Curve
Active: Soft Balanced: Flexible Flexible Flexible
Secondary Curve
Supportive Supportive Supportive Flexible
Liner HDPE HDPE Coated / Silicone Coated
Marker Band Yes, 3 mm proximal from tip
Yes, 3 mm proximal from tip
Yes, 3 mm proximal from tip
Yes, 3 mm proximal from tip
Distal Segment
Secondary Curve
Tip